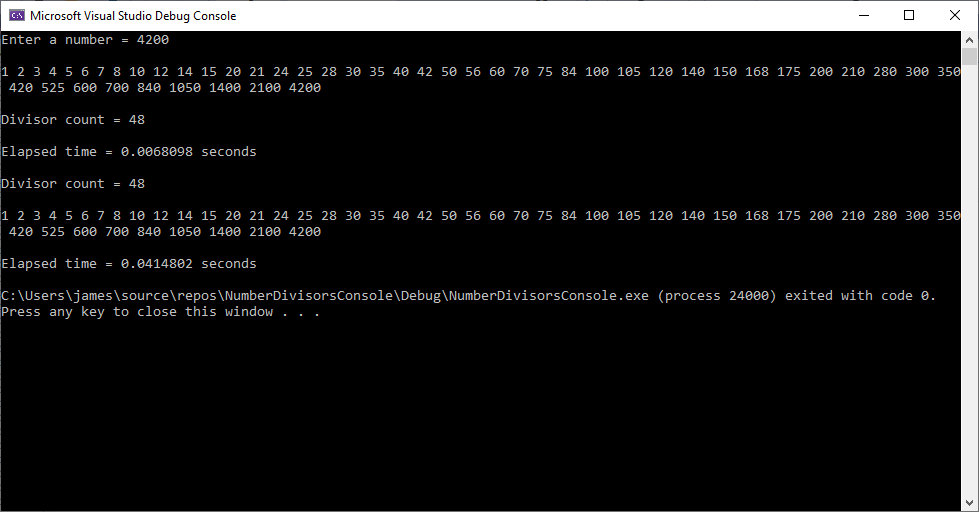
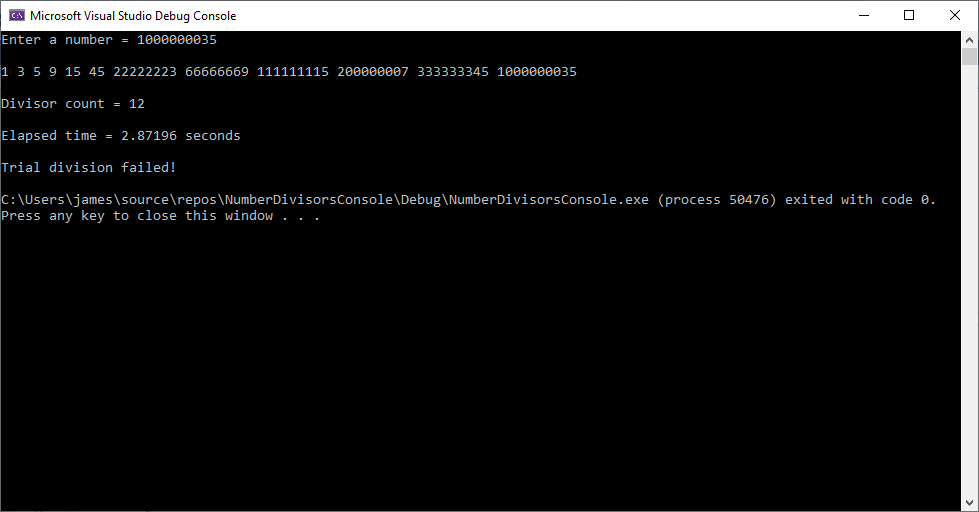
A simple number theoretic problem is to count and enumerate the number of divisors of a natural number which is the set { 1, 2, 3, … }. An Order(n) method is to find all numbers between 1 and n such that the number divides n. If you have the prime factorization of n then the number of divisors is the product of the prime factorization (exponents + 1). For example the divisors of 100 are:
1 2 4 5 10 20 25 50 100
The prime factorization of 100 = 2^2 * 5 ^ 2. So the number of divisors is (2 + 1) * (2 + 1) = 9.
Below is a C++ implementation of an algorithm to enumerate and count the number of divisors of a natural number and count the divisors by using the factorization found by trial division.
#include <algorithm>
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int B0 = 10000000;
bool sieve[B0 + 1];
vector<int> prime, divisors, expon, primes, primesSquares;
void Sieve()
{
// Sieve of Eratosthenes
// find all prime numbers
// less than or equal B0
int c = 3, i, inc;
sieve[2] = true;
for (i = 3; i <= B0; i++)
if (i % 2 == 1)
sieve[i] = true;
do
{
i = c * c;
inc = c + c;
while (i <= B0)
{
sieve[i] = false;
i += inc;
}
c += 2;
while (!sieve[c])
c++;
} while (c * c <= B0);
for (i = 2; i <= B0; i++)
{
if (sieve[i])
{
primes.push_back(i);
primesSquares.push_back(i * i);
}
}
}
bool TrialDivision(int number)
{
int bound = B0; // (int)sqrt(number);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)primes.size(); i++)
{
int p = primes[i];
if (p <= bound)
{
if (number % p == 0)
{
int e = 0;
while (number % p == 0)
{
e++;
number /= p;
}
prime.push_back(p);
expon.push_back(e);
}
if (number == 1)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void GetDivisors(int n, int count)
{
divisors.push_back(1);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)prime.size(); i++)
{
int p = prime[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= (int)expon[i]; j++)
{
int q = (int)pow(p, j);
divisors.push_back(q);
}
}
bool done = false;
int limit;
do
{
limit = (int)divisors.size();
for (int i = 1; i < limit - 1; i++)
{
int di = divisors[i];
for (int j = i + 1; !done && j < limit; j++)
{
int dj = divisors[j], product = di * dj;
vector<int>::iterator it =
find(divisors.begin(), divisors.end(), product);
if (it == divisors.end())
{
if (divisors.size() < count &&
product <= n && n % product == 0)
divisors.push_back(product);
else if (divisors.size() == count)
done = true;
}
}
}
} while (!done);
std::sort(divisors.begin(), divisors.end());
}
int main()
{
int count = 0, number;
std::cout << "Enter a number = ";
cin >> number;
std::cout << endl;
auto start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++)
{
if (number % i == 0)
{
cout << i << ' ';
count++;
}
}
auto finish = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::cout << endl << endl;
std::cout << "Divisor count = " << count << endl << endl;
chrono::duration<double> elapsed = finish - start;
std::cout << "Elapsed time = " << elapsed.count()
<< " seconds" << endl << endl;
start = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
Sieve();
if (!TrialDivision(number))
{
cout << "Trial division failed!" << endl;
return 0;
}
count = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)expon.size(); i++)
count *= expon[i] + 1;
finish = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::cout << "Divisor count = " << count << endl << endl;
GetDivisors(number, count);
for (int i = 0; i < (int)divisors.size(); i++)
std::cout << divisors[i] << " ";
std::cout << endl << endl;
elapsed = finish - start;
std::cout << "Elapsed time = " << elapsed.count()
<< " seconds" << endl;
}