Rexx was a popular computer programming language on IBM main frame computers. I found an interesting website: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rexx#NUMERIC\
I use a very slowly converging infinite series and Fourier series to compute Pi.

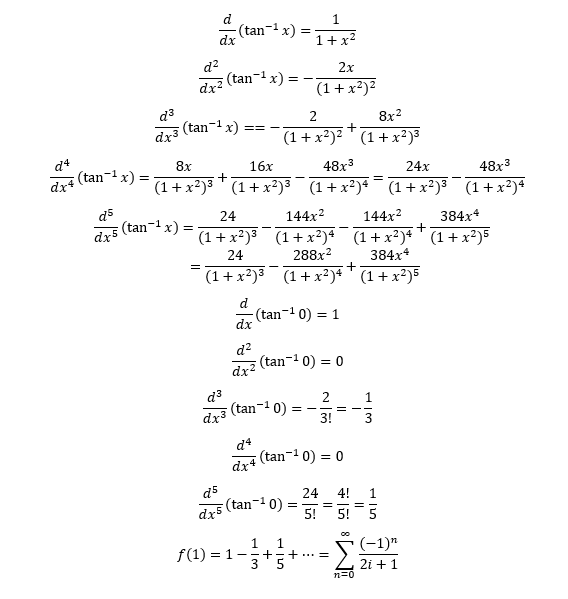



// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rexx#NUMERIC\
// Translated from Rexx code
// by James Pate Williams, Jr.
// Added a lot of functionality
// Copyrighted February 7 - 10, 2023
#include "FourierSeries.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
typedef chrono::high_resolution_clock Clock;
void Option3(int digits, int N)
{
long double i = 0;
long double sgn = 1;
long double sum = 0;
long double pi0 = Pi;
long double pi1 = 0.0;
while (i <= N)
{
sum += sgn / (2.0 * i + 1);
sgn *= -1;
i = i + 1.0;
}
pi1 = 4.0 * sum;
cout << setw(static_cast<std::streamsize>((int)digits) + 2);
cout << setprecision(digits) << pi1 << '\t';
cout << setprecision(digits) << (fabsl(pi0 - pi1)) << endl;
}
void Option4(int digits, int N)
{
long double* a = new long double[N + 1];
long double* b = new long double[N + 1];
memset(a, 0, (N + 1) * sizeof(long double));
memset(b, 0, (N + 1) * sizeof(long double));
FourierSeries::CreateCosSeries(N, a);
FourierSeries::CreateSinSeries(N, b);
long double pi = 4.0 * FourierSeries::Series(N, 1.0, a, b);
cout << setw(static_cast<std::streamsize>((int)digits) + 2);
cout << setprecision(digits) << pi << '\t';
cout << setprecision(digits) << (fabsl(pi - Pi)) << endl;
delete[] a;
delete[] b;
}
int main()
{
int choice, digits, N = 0, N1 = 0;
while (1)
{
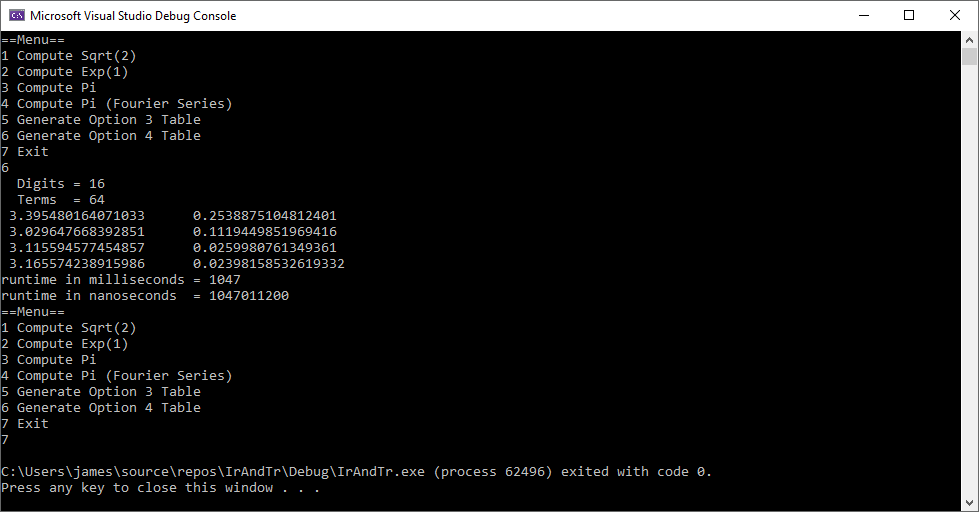
cout << "==Menu==" << endl;
cout << "1 Compute Sqrt(2)" << endl;
cout << "2 Compute Exp(1)" << endl;
cout << "3 Compute Pi" << endl;
cout << "4 Compute Pi (Fourier Series)" << endl;
cout << "5 Generate Option 3 Table" << endl;
cout << "6 Generate Option 4 Table" << endl;
cout << "7 Exit" << endl;
cin >> choice;
if (choice == 7)
break;
cout << " Digits = ";
cin >> digits;
if (choice >= 3)
{
cout << " Terms = ";
cin >> N;
N1 = N + 1;
}
auto start_time = Clock::now();
if (choice == 1)
{
long double n = 2;
long double r = 1;
while (1)
{
long double rr = (n / r + r) / 2;
if (rr == r)
break;
r = rr;
}
cout << setprecision(digits) << r << endl;
}
else if (choice == 2)
{
long double e = 2.5;
long double f = 0.5;
long double n = 3;
do
{
f /= n;
long double ee = e + f;
if (ee == e)
break;
e = ee;
n += 1;
} while (1);
cout << setprecision(digits) << e << endl;
}
else if (choice == 3)
Option3(digits, N);
else if (choice == 4)
Option4(digits, N);
else if (choice == 5)
{
for (int n = 8; n <= N; n *= 2)
Option3(digits, n);
}
else if (choice == 6)
{
for (int n = 8; n <= N; n *= 2)
Option4(digits, n);
}
auto end_time = Clock::now();
cout << "runtime in milliseconds = ";
cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>
(end_time - start_time).count();
cout << endl;
cout << "runtime in nanoseconds = ";
cout << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>
(end_time - start_time).count();
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
#pragma once
const long double c = 2.0e9;
const long double Pi = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
class FourierSeries
{
private:
static long double f(long double x);
static long double cosTermFunction(int n, long double x);
static long double sinTermFunction(int n, long double x);
public:
static void CreateCosSeries(int N, long double a[]);
static void CreateSinSeries(int N, long double b[]);
static long double Series(int N, long double x,
long double a[], long double b[]);
};
#include <math.h>
#include "FourierSeries.h"
#include "Integral.h"
long double FourierSeries::f(long double x)
{
return atanl(x);
}
long double FourierSeries::cosTermFunction(int n, long double x)
{
return cosl(n * x * Pi / c) * f(x);
}
long double FourierSeries::sinTermFunction(int n, long double x)
{
return sinl(n * x * Pi / c) * f(x);
}
void FourierSeries::CreateCosSeries(int N, long double a[])
{
long double e[7] = { 0 };
e[1] = e[2] = 1.0e-12;
for (int n = 0; n <= N; n++)
a[n] = Integral::integral(
n, -c, c, cosTermFunction, e, 1, 1) / c;
}
void FourierSeries::CreateSinSeries(int N, long double b[])
{
long double e[7] = { 0 };
e[1] = e[2] = 1.0e-12;
for (int n = 1; n <= N; n++)
b[n] = Integral::integral(
n, -c, c, sinTermFunction, e, 1, 1) / c;
}
long double FourierSeries::Series(int N, long double x,
long double a[], long double b[])
{
long double sum = 0.0;
for (int n = 1; n <= N; n++)
sum += a[n] * cosl(2.0 * n * x) + b[n] * sinl(2.0 * n * x);
return a[0] / 2.0 + sum / 2.0;
}
#pragma once
// Translated from C source code found in the tome
// "A Numerical Library in C for Scientists and
// Engineers" by H.T. Lau, PhD
class Integral
{
private:
static long double integralqad(
int n,
int transf, long double (*fx)(int, long double), long double e[],
long double* x0, long double* x1, long double* x2, long double* f0, long double* f1,
long double* f2, long double re, long double ae, long double b1);
static void integralint(
int n,
int transf, long double (*fx)(int, long double), long double e[],
long double* x0, long double* x1, long double* x2, long double* f0, long double* f1,
long double* f2, long double* sum, long double re, long double ae, long double b1,
long double hmin);
public:
static long double integral(int n, long double a, long double b,
long double (*fx)(int, long double), long double e[],
int ua, int ub);
};
#include <math.h>
#include "Integral.h"
long double Integral::integral(
int n,
long double a, long double b,
long double (*fx)(int, long double), long double e[],
int ua, int ub)
{
long double x0, x1, x2, f0, f1, f2, re, ae, b1 = 0, x;
re = e[1];
if (ub)
ae = e[2] * 180.0 / fabsl(b - a);
else
ae = e[2] * 90.0 / fabsl(b - a);
if (ua) {
e[3] = e[4] = 0.0;
x = x0 = a;
f0 = (*fx)(n, x);
}
else {
x = x0 = a = e[5];
f0 = e[6];
}
e[5] = x = x2 = b;
e[6] = f2 = (*fx)(n, x);
e[4] += integralqad(n, 0, fx, e, &x0, &x1, &x2, &f0, &f1, &f2, re, ae, b1);
if (!ub) {
if (a < b) {
b1 = b - 1.0;
x0 = 1.0;
}
else {
b1 = b + 1.0;
x0 = -1.0;
}
f0 = e[6];
e[5] = x2 = 0.0;
e[6] = f2 = 0.0;
ae = e[2] * 90.0;
e[4] -= integralqad(n, 1, fx, e, &x0, &x1, &x2, &f0, &f1, &f2, re, ae, b1);
}
return e[4];
}
long double Integral::integralqad(
int n,
int transf, long double (*fx)(int, long double), long double e[],
long double* x0, long double* x1, long double* x2, long double* f0, long double* f1,
long double* f2, long double re, long double ae, long double b1)
{
/* this function is internally used by INTEGRAL */
long double sum, hmin, x, z;
hmin = fabs((*x0) - (*x2)) * re;
x = (*x1) = ((*x0) + (*x2)) * 0.5;
if (transf) {
z = 1.0 / x;
x = z + b1;
(*f1) = (*fx)(n, x) * z * z;
}
else
(*f1) = (*fx)(n, x);
sum = 0.0;
integralint(n, transf, fx, e, x0, x1, x2, f0, f1, f2, &sum, re, ae, b1, hmin);
return sum / 180.0;
}
void Integral::integralint(
int n,
int transf, long double (*fx)(int, long double), long double e[],
long double* x0, long double* x1, long double* x2, long double* f0, long double* f1,
long double* f2, long double* sum, long double re, long double ae, long double b1,
long double hmin)
{
/* this function is internally used by INTEGRALQAD of INTEGRAL */
int anew;
long double x3, x4, f3, f4, h, x, z, v, t;
x4 = (*x2);
(*x2) = (*x1);
f4 = (*f2);
(*f2) = (*f1);
anew = 1;
while (anew) {
anew = 0;
x = (*x1) = ((*x0) + (*x2)) * 0.5;
if (transf) {
z = 1.0 / x;
x = z + b1;
(*f1) = (*fx)(n, x) * z * z;
}
else
(*f1) = (*fx)(n, x);
x = x3 = ((*x2) + x4) * 0.5;
if (transf) {
z = 1.0 / x;
x = z + b1;
f3 = (*fx)(n, x) * z * z;
}
else
f3 = (*fx)(n, x);
h = x4 - (*x0);
v = (4.0 * ((*f1) + f3) + 2.0 * (*f2) + (*f0) + f4) * 15.0;
t = 6.0 * (*f2) - 4.0 * ((*f1) + f3) + (*f0) + f4;
if (fabsl(t) < fabsl(v) * re + ae)
(*sum) += (v - t) * h;
else if (fabsl(h) < hmin)
e[3] += 1.0;
else {
integralint(n, transf, fx, e, x0, x1, x2, f0, f1, f2, sum,
re, ae, b1, hmin);
*x2 = x3;
*f2 = f3;
anew = 1;
}
if (!anew) {
*x0 = x4;
*f0 = f4;
}
}
}