This computation took a lot longer time to reach a much better solution than my previously published result.
Category: C++ Computer Applications
A Calculus of Variations Solution to the Quantum Mechanical Schrödinger Wave Equation for the Lithium Like Atom (Atomic Number Z = 3) by James Pate Williams, Jr.
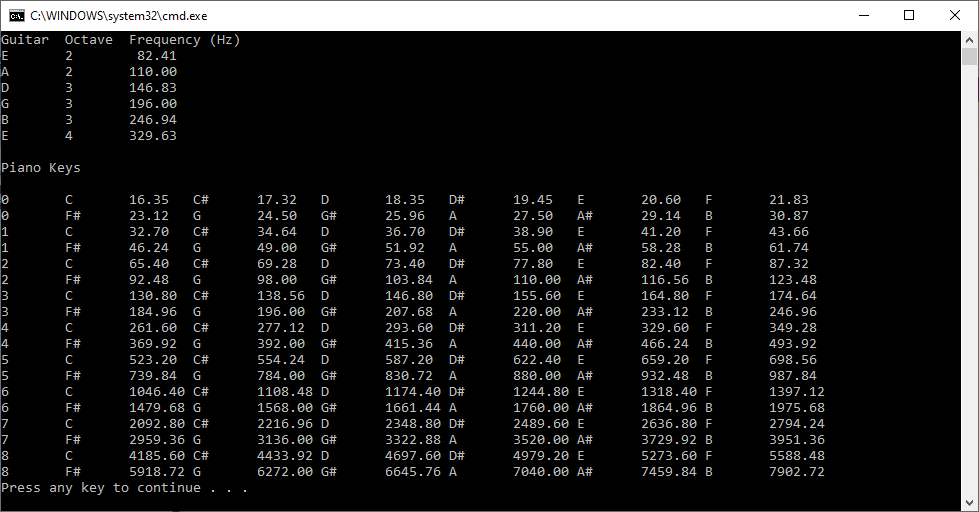
Guitar String and Piano Key Frequencies by James Pate Williams, Jr.
// FrequencyKey.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
// James Pate Willims, Jr. (c) All Applicable Rights Reserved
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<string> pnote;
double a = pow(2.0, 1.0 / 12.0);
double f0 = 440.0, gStrF[6];
double e2, a2, d3, g3, b3, e4;
double pfreq[9 * 12];
int offset = 0;
double fn(int n)
{
return f0 * pow(a, n);
}
void printFrequency(char note, int octave, double frequency)
{
cout << note << "\t" << octave << "\t";
cout << setw(6) << fixed << setprecision(2);
cout << frequency << endl;
}
int main()
{
for (int octave = 0; octave <= 8; octave++)
{
pnote.push_back("C");
pnote.push_back("C#");
pnote.push_back("D");
pnote.push_back("D#");
pnote.push_back("E");
pnote.push_back("F");
pnote.push_back("F#");
pnote.push_back("G");
pnote.push_back("G#");
pnote.push_back("A");
pnote.push_back("A#");
pnote.push_back("B");
}
pfreq[0] = 16.35;
pfreq[1] = 17.32;
pfreq[2] = 18.35;
pfreq[3] = 19.45;
pfreq[4] = 20.6;
pfreq[5] = 21.83;
pfreq[6] = 23.12;
pfreq[7] = 24.5;
pfreq[8] = 25.96;
pfreq[9] = 27.5;
pfreq[10] = 29.14;
pfreq[11] = 30.87;
for (int octave = 1; octave <= 8; octave++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
pfreq[octave * 12 + i] = 2.0 * pfreq[(octave - 1) * 12 + i];
}
}
gStrF[0] = e2 = fn(offset - 29);
gStrF[1] = a2 = fn(offset - 24);
gStrF[2] = d3 = fn(offset - 19);
gStrF[3] = g3 = fn(offset - 14);
gStrF[4] = b3 = fn(offset - 10);
gStrF[5] = e4 = fn(offset - 5);
cout << "Guitar\tOctave\tFrequency (Hz)" << endl;
printFrequency('E', 2, e2);
printFrequency('A', 2, a2);
printFrequency('D', 3, d3);
printFrequency('G', 3, g3);
printFrequency('B', 3, b3);
printFrequency('E', 4, e4);
cout << endl;
cout << "Piano Keys" << endl << endl;
for (int octave = 0; octave <= 8; octave++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
cout << octave << '\t';
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
{
cout << pnote[(12 * octave + 6 * i + j) % 12] << '\t';
cout << pfreq[(12 * octave + 6 * i + j)] << '\t';
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
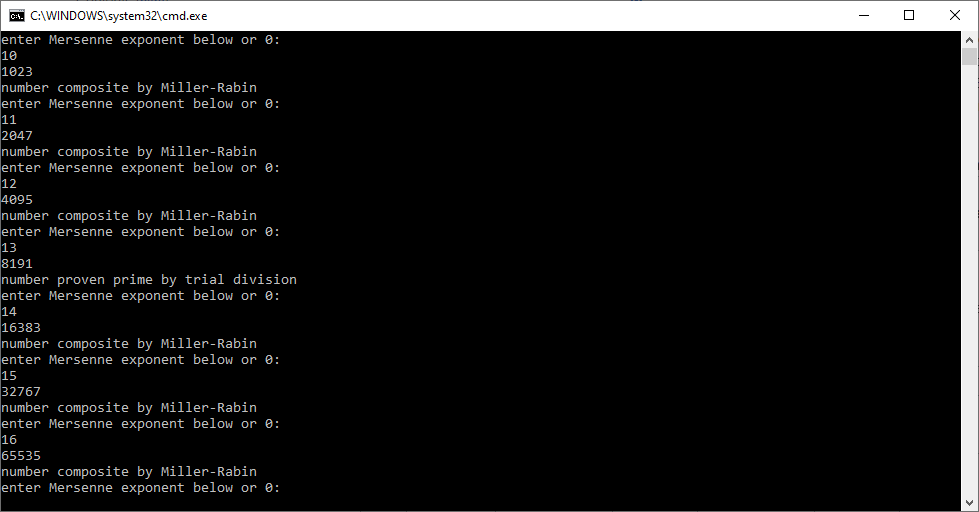
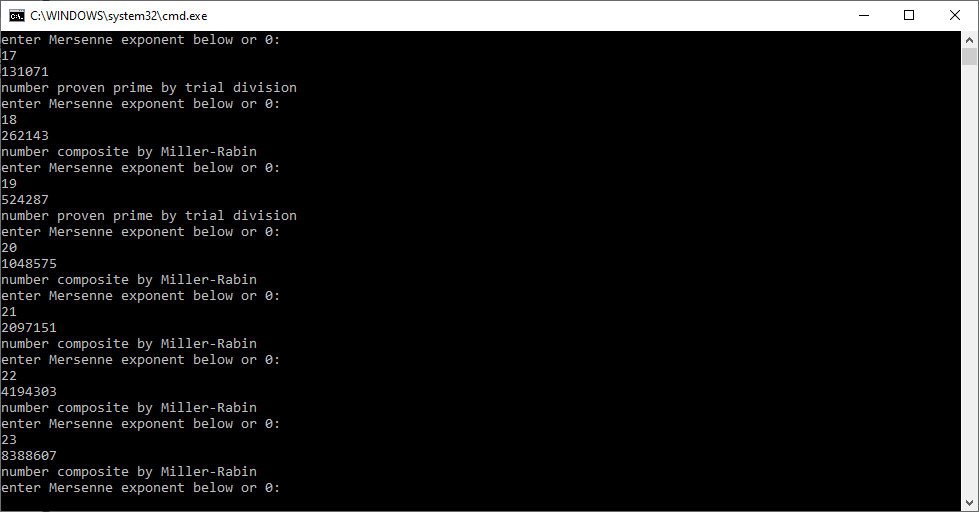
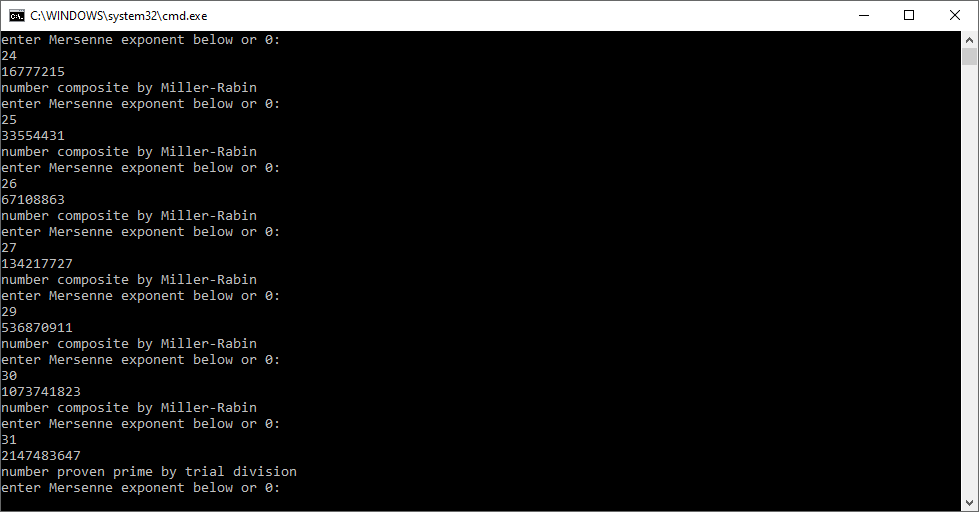
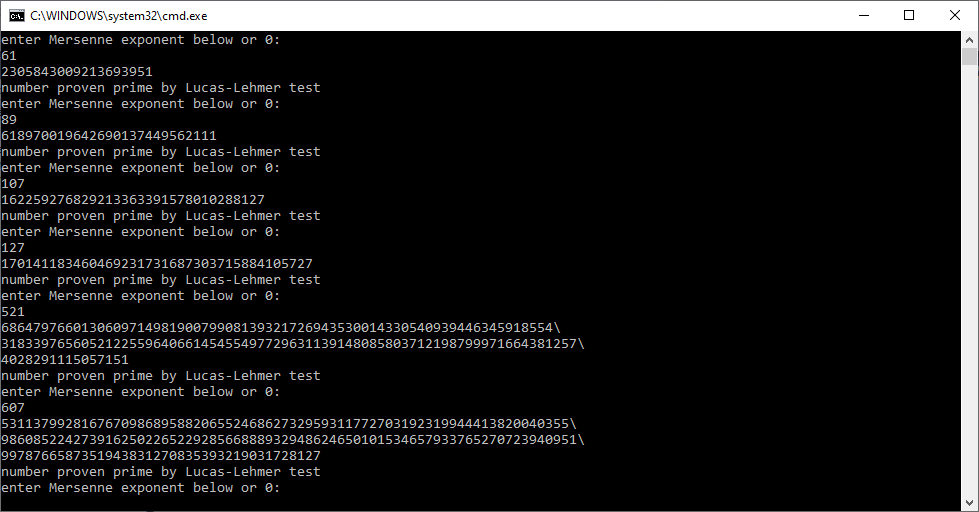
Lucas-Lehmer Primality Test in C Utilizing Arjen K. Lenstra’s FreeLIP (Free Large Integer Package) by James Pate Williams, Jr.

Comparison of Linear Systems Applications in C# and C++ by James Pate Williams, Jr.
Back in 2017 I created a C# application that implemented the direct methods: Cholesky decomposition, Gaussian elimination with partial pivoting, LU decomposition, and simple Gaussian elimination. The classical iterative methods Gauss-Seidel, Jacobi, Successive Overrelaxation, and gradient descent were also implemented along with the modern iterative methods: conjugate gradient descent and Modified Richardson’s method. Recently I translated the C# code to C++. I used the following test matrices: Cauchy, Lehmer, Pascal, and other. Below are some results. As is apparent the C++ runtimes are faster than the C# execution times.
Euler’s Method and Runge-Kutta 4 Algorithm for Numerically Solving an Ordinary Differential Equation by James Pate Williams, Jr.
I added the Runge-Kutta 4 algorithm found in Numerical Analysis: An Algorithmic Approach Third Edition by S. D. Conte and Carl de Boor. I also added a multistep method, the Adams-Bashforth Method.




Two-Tank Mixing Problem C++ Implementation Using Runge-Kutta 4 for a System of Two Ordinary Differential Equations Implementation by James Pate Williams, Jr.
// Two-tank Mixing Problem
// x'(t) = f(t, x, y)
// y'(t) = g(t, x, y)
// x(0) = 5, y(0) = 1
// See “Ordinary Differential Equations
// from Calculus to Dynamical Systems”
// by Virginia W. Noonburg for the exact
// solution, view pages 165 – 167. Also
// see “Elementary Numerical Analysis:
// An Algorithmic Approach Third
// Edition” by S. D. Conte and Carl de
// Boor pages 398 – 491 for the Runge-
// Kutta-4 equations.

#include "RK4System.h"
void RK4System::Solve(
real t0, real t1,
real x0, real z0,
real(*f)(real, real, real),
real(*g)(real, real, real),
int nSteps, vector<real>& tv,
vector<real>& xv, vector<real>& yv)
{
real k1, k2, k3, k4, l1, l2, l3, l4;
real h, tn, xn, yn, xn1, yn1;
h = (t1 - t0) / nSteps;
tn = t0;
xn = x0;
yn = z0;
tv.push_back(tn);
xv.push_back(xn);
yv.push_back(yn);
for (unsigned int n = 1; n <= nSteps; n++)
{
tn = t0 + n * h;
k1 = h * f(tn, xn, yn);
l1 = h * g(tn, xn, yn);
k2 = h * f(tn + 0.5 * h, xn + 0.5 * k1, yn + 0.5 * l1);
l2 = h * g(tn + 0.5 * h, xn + 0.5 * k1, yn + 0.5 * l1);
k3 = h * f(tn + 0.5 * h, xn + 0.5 * k2, yn + 0.5 * l2);
l3 = h * g(tn + 0.5 * h, xn + 0.5 * k2, yn + 0.5 * l2);
k4 = h * f(tn + h, xn + k3, yn + l3);
l4 = h * g(tn + h, xn + k3, yn + l3);
xn1 = xn + (k1 + 2 * k2 + 2 * k3 + k4) / 6.0;
yn1 = yn + (l1 + 2 * l2 + 2 * l3 + l4) / 6.0;
xn = xn1;
yn = yn1;
tv.push_back(tn);
xv.push_back(xn);
yv.push_back(yn);
}
}
#pragma once
// Solves the following system of first order
// ordinary differential equations. Formulas
// are from "Elementary Numerical Analysis:
// An Algorithmic Approach" by S. D. Conte &
// Carl de Boor (c) 1980 8.12 page 398.
// x' = f(t, x, y)
// y' = g(t, x, y)
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long double real;
class RK4System
{
public:
static void Solve(
real t0, real t1,
real x0, real y0,
real(*f)(real, real, real),
real(*g)(real, real, real),
int nSteps, vector<real>& tv,
vector<real>& xv, vector<real>& yv);
};
Brute Force Elliptic Curve Point Counting Algorithm Implementation by James Pate Williams, Jr.
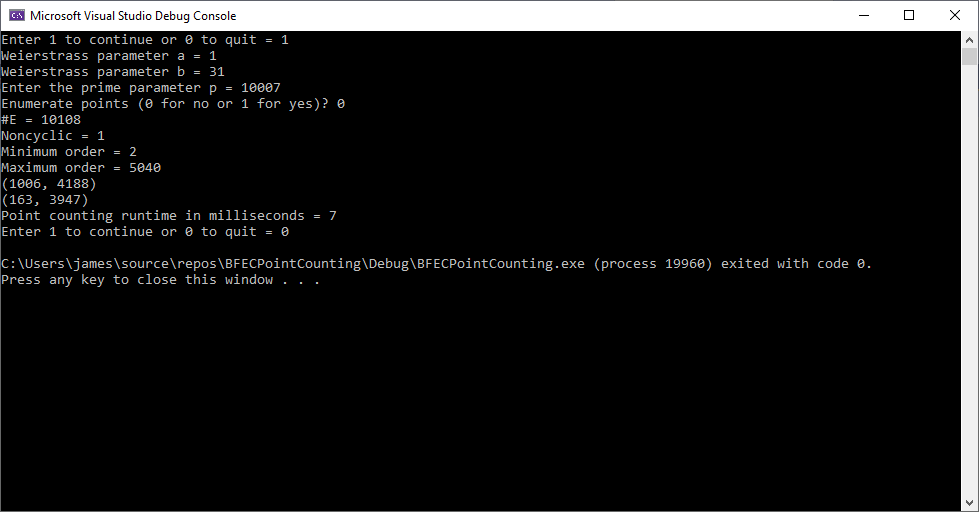

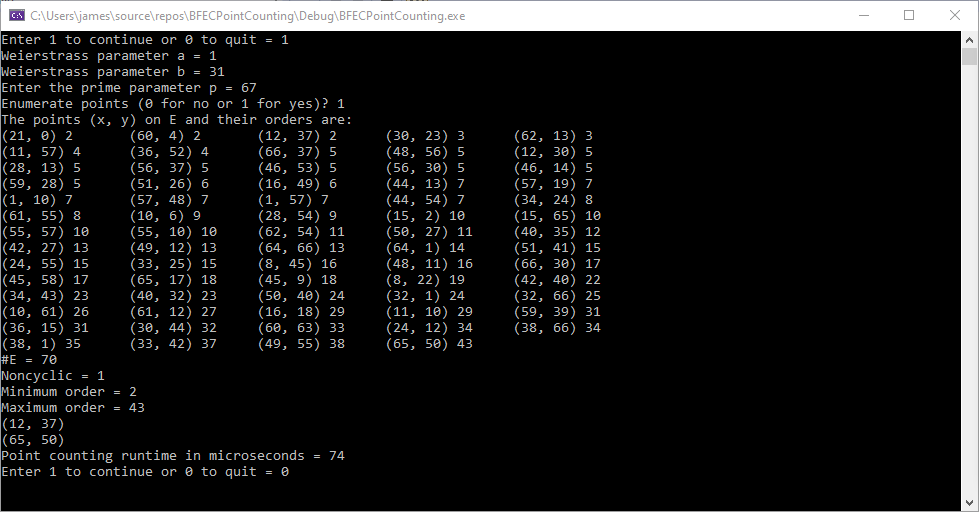



#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <chrono>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef struct ecPoint
{
ll x, y;
} ECPOINT, *PECPOINT;
typedef struct ecPointOrder
{
ll order;
ECPOINT pt;
} ECPOINTORDER, * PECPOINTORDER;
int JACOBI(ll a, ll n)
{
int e = 0, s;
ll a1, b = a, m, n1;
if (a == 0) return 0;
if (a == 1) return 1;
while ((b & 1) == 0)
{
b >>= 1;
e++;
}
a1 = b;
m = n % 8;
if (!(e & 1)) s = 1;
else if (m == 1 || m == 7) s = +1;
else if (m == 3 || m == 5) s = -1;
if (n % 4 == 3 && a1 % 4 == 3) s = -s;
if (a1 != 1) n1 = n % a1; else n1 = 1;
return s * JACOBI(n1, a1);
}
ll ExpMod(ll x, ll b, ll n)
/* returns x ^ b mod n */
{
ll a = 1LL, s = x;
if (b == 0)
return 1LL;
while (b != 0) {
if (b & 1l) a = (a * s) % n;
b >>= 1;
if (b != 0) s = (s * s) % n;
}
if (a < 0)
a += n;
return a;
}
ll ExtendedEuclidean(ll b, ll n)
{
ll b0 = b, n0 = n, t = 1, t0 = 0, temp, q, r;
q = n0 / b0;
r = n0 - q * b0;
while (r > 0) {
temp = t0 - q * t;
if (temp >= 0) temp = temp % n;
else temp = n - (-temp % n);
t0 = t;
t = temp;
n0 = b0;
b0 = r;
q = n0 / b0;
r = n0 - q * b0;
}
if (b0 != 1) return 0;
else return t % n;
}
ll Weierstrass(ll a, ll b, ll x, ll p)
{
return ((((x * x) % p) * x) % p + (a * x) % p + b) % p;
}
ll EPoints(
bool print,
ll a, ll b, ll p,
vector<ECPOINT>& e)
/* returns the number of points on the elliptic
curve y ^ 2 = x ^ 3 + ax + b mod p */
{
ll count = 0, m = (p + 1) / 4, x, y;
ECPOINT pt{};
if (p % 4 == 3) {
for (x = 0; x < p; x++) {
y = Weierstrass(a, b, x, p);
if (JACOBI(y, p) != -1) {
y = ExpMod(y, m, p);
if (print)
{
cout << "(" << setw(2) << x << ", ";
cout << y << ") " << endl;
}
pt.x = x;
pt.y = y;
e.push_back(pt);
count++;
y = -y % p;
if (y < 0) y += p;
if (y != 0)
{
if (print)
{
cout << "(" << setw(2) << x << ", ";
cout << y << ") " << endl;
}
pt.x = x;
pt.y = y;
e.push_back(pt);
count++;
}
if (print && count % 5 == 0)
cout << endl;
}
}
if (print && count % 5 != 0)
cout << endl;
}
return count;
}
void Add(ll a, ll p, ECPOINT P,
ECPOINT Q, ECPOINT& R)
/* elliptic curve point partial addition */
{
ll i, lambda;
if (P.x == Q.x && P.y == 0 && Q.y == 0) {
R.x = 0;
R.y = 1;
return;
}
if (P.x == Q.x && P.y == p - Q.y) {
R.x = 0;
R.y = 1;
return;
}
if (P.x == 0 && P.y == 1) {
R = Q;
return;
}
if (Q.x == 0 && Q.y == 1) {
R = P;
return;
}
if (P.x != Q.x) {
i = Q.x - P.x;
if (i < 0) i += p;
i = ExtendedEuclidean(i, p);
lambda = ((Q.y - P.y) * i) % p;
}
else {
i = ExtendedEuclidean((2 * P.y) % p, p);
lambda = ((3 * P.x * P.x + a) * i) % p;
}
if (lambda < 0) lambda += p;
R.x = (lambda * lambda - P.x - Q.x) % p;
R.y = (lambda * (P.x - R.x) - P.y) % p;
if (R.x < 0) R.x += p;
if (R.y < 0) R.y += p;
}
void Multiply(
ll a, ll k, ll p,
ECPOINT P,
ECPOINT& R)
{
ECPOINT S;
R.x = 0;
R.y = 1;
S = P;
while (k != 0) {
if (k & 1) Add(a, p, R, S, R);
k >>= 1;
if (k != 0) Add(a, p, S, S, S);
}
}
ll Order(ll a, ll p, ECPOINT P)
{
ll order = 1;
ECPOINT Q = P, R{};
do {
order++;
Add(a, p, P, Q, R);
Q = R;
} while (R.x != 0 && R.y != 1);
return order;
}
const int PrimeSize = 10000000;
bool sieve[PrimeSize];
void PopulateSieve() {
// sieve of Eratosthenes
int c, inc, i, n = PrimeSize - 1;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sieve[i] = false;
sieve[1] = false;
sieve[2] = true;
for (i = 3; i <= n; i++)
sieve[i] = (i & 1) == 1 ? true : false;
c = 3;
do {
i = c * c;
inc = c + c;
while (i <= n) {
sieve[i] = false;
i += inc;
}
c += 2;
while (!sieve[c])
c++;
} while (c * c <= n);
}
ll Partition(
vector<ECPOINTORDER>& a, ll n, ll lo, ll hi)
{
ll pivotIndex = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
ECPOINTORDER po = a[(unsigned int)pivotIndex];
ECPOINTORDER x = po;
ECPOINTORDER t = x;
a[(unsigned int)pivotIndex] = a[(unsigned int)hi];
a[(unsigned int)hi] = t;
ll storeIndex = lo;
for (unsigned int i = (unsigned int)lo; i < (unsigned int)hi; i++)
{
if (a[i].order < x.order)
{
t = a[i];
a[i] = a[(unsigned int)storeIndex];
a[(unsigned int)(storeIndex++)] = t;
}
}
t = a[(unsigned int)storeIndex];
a[(unsigned int)storeIndex] = a[(unsigned int)hi];
a[(unsigned int)hi] = t;
return storeIndex;
}
static void DoQuickSort(
vector<ECPOINTORDER>& a, ll n, ll p, ll r)
{
if (p < r)
{
ll q = Partition(a, n, p, r);
DoQuickSort(a, n, p, q - 1);
DoQuickSort(a, n, q + 1, r);
}
}
void QuickSort(vector<ECPOINTORDER>& a, ll n)
{
DoQuickSort(a, n, 0, n - 1);
}
int main()
{
PopulateSieve();
while (true)
{
bool noncyclic = false;
int option;
ll a, b, p;
cout << "Enter 1 to continue or 0 to quit = ";
cin >> option;
if (option == 0)
break;
cout << "Weierstrass parameter a = ";
cin >> a;
cout << "Weierstrass parameter b = ";
cin >> b;
cout << "Enter the prime parameter p = ";
cin >> p;
if (!sieve[p])
{
cout << "p is not a prime number. " << endl;
continue;
}
if (p % 4 != 3)
{
cout << "p mod 4 must be 3 for this algorithm." << endl;
continue;
}
bool print = false, enumerate = false;
vector<ECPOINT> e;
vector<ECPOINTORDER> eOrder;
cout << "Enumerate points (0 for no or 1 for yes)? ";
cin >> option;
enumerate = option == 1;
auto time0 = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
ll count = EPoints(print, a, b, p, e);
auto time1 = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto elapsed = time1 - time0;
ll h = count + 1;
ll maxOrder = 0;
ll minOrder = h;
ll order = -1;
ECPOINT P{}, Q{};
if (enumerate)
cout << "The points (x, y) on E and their orders are:" << endl;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
ECPOINTORDER ptOrder{};
order = Order(a, p, e[i]);
ptOrder.order = order;
ptOrder.pt = e[i];
eOrder.push_back(ptOrder);
if (order < h)
noncyclic = true;
if (order < minOrder) {
P = e[i];
minOrder = order;
}
if (order > maxOrder) {
Q = e[i];
maxOrder = order;
}
}
if (enumerate)
{
QuickSort(eOrder, count);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < eOrder.size(); i++)
{
cout << "(" << eOrder[i].pt.x << ", ";
cout << eOrder[i].pt.y << ") ";
cout << eOrder[i].order << "\t";
if ((i + 1) % 5 == 0)
cout << endl;
}
if (count % 5 != 0)
cout << endl;
}
cout << "#E = " << h << endl;
cout << "Noncyclic = " << noncyclic << endl;
cout << "Minimum order = " << minOrder << endl;
cout << "Maximum order = " << maxOrder << endl;
cout << "(" << P.x << ", " << P.y << ")" << endl;
cout << "(" << Q.x << ", " << Q.y << ")" << endl;
long long runtime = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::milliseconds>(elapsed).count();
if (runtime != 0)
cout << "Point counting runtime in milliseconds = " << runtime << endl;
else
{
runtime = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(elapsed).count();
cout << "Point counting runtime in microseconds = " << runtime << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Stinson Exercise 5.6 Galois Field

/*
Author: Pate Williams (c) 1997
Exercise
"5.6 The field GF(2 ^ 5) can be constructed as
Z_2[x]/(x ^ 5 + x ^ 2 + 1). Perform the following
computations in this field.
(a) Compute (x ^ 4 + x ^ 2) * (x ^ 3 + x + 1).
(b) Using the Extended Euclidean algorithm
compute (x ^ 3 + x ^ 2) ^ - 1.
(c) Using the square and multiply algorithm,
compute x ^ 25." -Douglas R. Stinson-
See "Cryptography: Theory and Practice" by
Douglas R. Stinson page 201.
*/
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 32l
void poly_mul(long m, long n, long *a, long *b, long *c, long *p)
{
long ai, bj, i, j, k, sum;
*p = m + n;
for (k = 0; k <= *p; k++) {
sum = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
j = k - i;
if (i > m) ai = 0; else ai = a[i];
if (j > n) bj = 0; else bj = b[j];
sum += ai * bj;
}
c[k] = sum;
}
}
void poly_div(long m, long n, long *u, long *v,
long *q, long *r, long *p, long *s)
{
long j, jk, k, nk, vn = v[n];
for (j = 0; j <= m; j++) r[j] = u[j];
if (m < n) {
*p = 0, *s = m;
q[0] = 0;
}
else {
*p = m - n, *s = n - 1;
for (k = *p; k >= 0; k--) {
nk = n + k;
q[k] = r[nk] * pow(vn, k);
for (j = nk - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
jk = j - k;
if (jk >= 0)
r[j] = vn * r[j] - r[nk] * v[j - k];
else
r[j] = vn * r[j];
}
}
while (*p > 0 && q[*p] == 0) *p = *p - 1;
while (*s > 0 && r[*s] == 0) *s = *s - 1;
}
}
void poly_exp_mod(long degreeA, long degreem, long n,
long modulus, long *A, long *m, long *s,
long *ds)
{
int zero;
long dp, dq, dx = degreeA, i;
long p[SIZE], q[SIZE], x[SIZE];
*ds = 0, s[0] = 1;
for (i = 0; i <= dx; i++) x[i] = A[i];
while (n > 0) {
if ((n & 1) == 1) {
/* s = (s * x) % m; */
poly_mul(*ds, dx, s, x, p, &dp);
poly_div(dp, degreem, p, m, q, s, &dq, ds);
for (i = 0; i <= *ds; i++) s[i] %= modulus;
zero = s[*ds] == 0, i = *ds;
while (i > 0 && zero) {
if (zero) *ds = *ds - 1;
zero = s[--i] == 0;
}
}
n >>= 1;
/* x = (x * x) % m; */
poly_mul(dx, dx, x, x, p, &dp);
poly_div(dp, degreem, p, m, q, x, &dq, &dx);
for (i = 0; i <= dx; i++) x[i] %= modulus;
zero = x[dx] == 0, i = dx;
while (i > 0 && zero) {
if (zero) dx--;
zero = x[--i] == 0;
}
}
}
void poly_copy(long db, long *a, long *b, long *da)
/* a = b */
{
long i;
*da = db;
for (i = 0; i <= db; i++) a[i] = b[i];
}
int poly_Extended_Euclidean(long db, long dn,
long *b, long *n,
long *t, long *dt)
{
int nonzero;
long db0, dn0, dq, dr, dt0 = 0, dtemp, du, i;
long b0[SIZE], n0[SIZE], q[SIZE];
long r[SIZE], t0[SIZE], temp[SIZE], u[SIZE];
*dt = 0;
poly_copy(dn, n0, n, &dn0);
poly_copy(db, b0, b, &db0);
t0[0] = 0;
t[0] = 1;
poly_div(dn0, db0, n0, b0, q, r, &dq, &dr);
nonzero = r[0] != 0;
for (i = 1; !nonzero && i <= dr; i++)
nonzero = r[i] != 0;
while (nonzero) {
poly_mul(dq, *dt, q, t, u, &du);
if (dt0 < du)
for (i = dt0 + 1; i <= du; i++) t0[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= du; i++)
temp[i] = t0[i] - u[i];
dtemp = du;
poly_copy(*dt, t0, t, &dt0);
poly_copy(dtemp, t, temp, dt);
poly_copy(db0, n0, b0, &dn0);
poly_copy(dr, b0, r, &db0);
poly_div(dn0, db0, n0, b0, q, r, &dq, &dr);
nonzero = r[0] != 0;
for (i = 1; !nonzero && i <= dr; i++)
nonzero = r[i] != 0;
}
if (db0 != 0 && b0[0] != 1) return 0;
return 1;
}
void poly_mod(long da, long p, long *a, long *new_da)
{
int zero;
long i;
for (i = 0; i <= da; i++) {
a[i] %= p;
if (a[i] < 0) a[i] += p;
}
zero = a[da] == 0;
for (i = da - 1; zero && i >= 0; i--) {
da--;
zero = a[i] == 0;
}
*new_da = da;
}
void poly_write(char *label, long da, long *a)
{
long i;
printf("%s", label);
for (i = da; i >= 0; i--)
printf("%ld ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main(void)
{
long da = 4, db = 3, dc = 3, dd = 5;
long de, dq, dr, ds, p = 2;
long a[5] = { 0, 0, 1, 0, 1 };
long b[4] = { 1, 1, 0, 1 };
long c[4] = { 0, 0, 1, 1 };
long d[6] = { 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1 };
long e[SIZE], q[SIZE], r[SIZE], s[SIZE];
poly_write("A = ", da, a);
poly_write("B = ", db, b);
poly_write("C = ", dc, c);
poly_write("D = ", dd, d);
poly_mul(da, db, a, b, e, &de);
poly_mod(de, p, e, &de);
poly_div(de, dd, e, d, q, r, &dq, &dr);
poly_mod(dq, p, q, &dq);
poly_mod(dr, p, r, &dr);
poly_write("A * B mod 2 = ", de, e);
poly_write("A * B / D mod 2 = ", dq, q);
poly_write("A * B mod D, 2 = ", dr, r);
if (!poly_Extended_Euclidean(dc, dd, c, d, e, &de))
printf("*error*\in poly_Extended_Euclidean\n");
poly_mod(de, p, e, &de);
poly_write("C ^ - 1 mod D = ", de, e);
poly_mul(dc, de, c, e, s, &ds);
poly_mod(ds, p, s, &ds);
poly_div(ds, dd, s, d, q, r, &dq, &dr);
poly_mod(dr, p, r, &dr);
poly_write("C * C ^ - 1 mod D, 2 = ", dr, r);
dq = 1;
q[0] = 0;
q[1] = 1;
poly_exp_mod(dq, dd, 7, p, q, d, s, &ds);
poly_mod(ds, p, s, &ds);
poly_write("x ^ 7 mod D, 2 = ", ds, s);
poly_exp_mod(dq, dd, 9, p, q, d, s, &ds);
poly_mod(ds, p, s, &ds);
poly_write("x ^ 9 mod D, 2 = ", ds, s);
poly_exp_mod(dq, dd, 10, p, q, d, s, &ds);
poly_mod(ds, p, s, &ds);
poly_write("x ^ 10 mod D, 2 = ", ds, s);
poly_exp_mod(dq, dd, 25, p, q, d, s, &ds);
poly_mod(ds, p, s, &ds);
poly_write("x ^ 25 mod D, 2 = ", ds, s);
return 0;
}
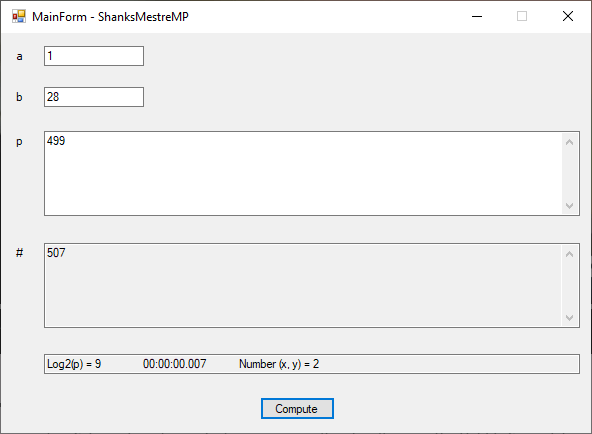
More Elliptic Curve Point Counting Results Using the Shanks-Mestre Algorithm by James Pate Williams, Jr.




As can be seen the C++ application appears to be much faster than the C# application. Also, in my humble opinion, C++ with header files and C++ source code files is much more elegant than C# with only class source code. I leave it to someone else to add C# interfaces to my class source code files.