/*
Author: Pate Williams (c) 1997
"Algorithm 2.3.2 (Image of a Matrix). Given an
m by n matrix M = (m[i][i]) with 1 <= i <= m and
1 <= j <= n having coefficients in the field K,
this algorithm outputs a basis of the image of
M, i. e. vector space spanned by the columns of
M." -Henri Cohen- See "A Course in Computational
Algebraic Number Theory" by Henri Cohen pages
58-59. We specialize the code to the field Zp.
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
long** create_matrix(long m, long n)
{
long i, ** matrix = (long**)calloc(m, sizeof(long*));
if (!matrix) {
fprintf(stderr, "fatal error\ninsufficient memory\n");
fprintf(stderr, "from create_matrix\n");
exit(1);
}
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
matrix[i] = (long*)calloc(n, sizeof(long));
if (!matrix[i]) {
fprintf(stderr, "fatal error\ninsufficient memory\n");
fprintf(stderr, "from create_matrix\n");
exit(1);
}
}
return matrix;
}
void delete_matrix(long m, long** matrix)
{
long i;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) free(matrix[i]);
free(matrix);
}
void Euclid_extended(long a, long b, long* u,
long* v, long* d)
{
long q, t1, t3, v1, v3;
*u = 1, * d = a;
if (b == 0) {
*v = 0;
return;
}
v1 = 0, v3 = b;
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("----------------------------------\n");
printf(" q t3 *u *d t1 v1 v3\n");
printf("----------------------------------\n");
#endif
while (v3 != 0) {
q = *d / v3;
t3 = *d - q * v3;
t1 = *u - q * v1;
*u = v1, * d = v3;
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("%4ld %4ld %4ld ", q, t3, *u);
printf("%4ld %4ld %4ld %4ld\n", *d, t1, v1, v3);
#endif
v1 = t1, v3 = t3;
}
*v = (*d - a * *u) / b;
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("----------------------------------\n");
#endif
}
long inv(long number, long modulus)
{
long d, u, v;
Euclid_extended(number, modulus, &u, &v, &d);
if (d == 1) return u;
return 0;
}
void image(long m, long n, long p,
long** M, long** X, long* r)
{
int found;
long D, i, j, k, s;
long* c = (long*)calloc(m, sizeof(long));
long* d = (long*)calloc(n, sizeof(long));
long** N = create_matrix(m, n);
if (!c || !d) {
fprintf(stderr, "fatal error\ninsufficient memory\n");
fprintf(stderr, "from kernel\n");
exit(1);
}
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
c[i] = -1;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) N[i][j] = M[i][j];
}
*r = 0;
for (k = 0; k < n; k++) {
found = 0, j = 0;
while (!found && j < m) {
found = M[j][k] != 0 && c[j] == -1;
if (!found) j++;
}
if (found) {
D = p - inv(M[j][k], p);
M[j][k] = p - 1;
for (s = k + 1; s < n; s++)
M[j][s] = (D * M[j][s]) % p;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (i != j) {
D = M[i][k];
M[i][k] = 0;
for (s = k + 1; s < n; s++) {
M[i][s] = (M[i][s] + D * M[j][s]) % p;
if (M[i][s] < 0) M[i][s] += p;
}
}
}
c[j] = k;
d[k] = j;
}
else {
*r = *r + 1;
d[k] = -1;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (c[j] != -1) {
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < m) X[i][j] = N[i][c[j]];
else X[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
delete_matrix(m, N);
free(c);
free(d);
}
void print_matrix(long m, long n, long** a)
{
long i, j;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
printf("%2ld ", a[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int main(void)
{
long i, j, m = 8, n = 8, p = 13, r;
long a[8][8] = { {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{2, 0, 7, 11, 10, 12, 5, 11},
{3, 6, 3, 3, 0, 4, 7, 2},
{4, 3, 6, 4, 1, 6, 2, 3},
{2, 11, 8, 8, 2, 1, 3, 11},
{6, 11, 8, 6, 2, 6, 10, 9},
{5, 11, 7, 10, 0, 11, 6, 12},
{3, 3, 12, 5, 0, 11, 9, 11} };
long** M = create_matrix(m, n);
long** X = create_matrix(n, n);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
M[i][j] = a[j][i];
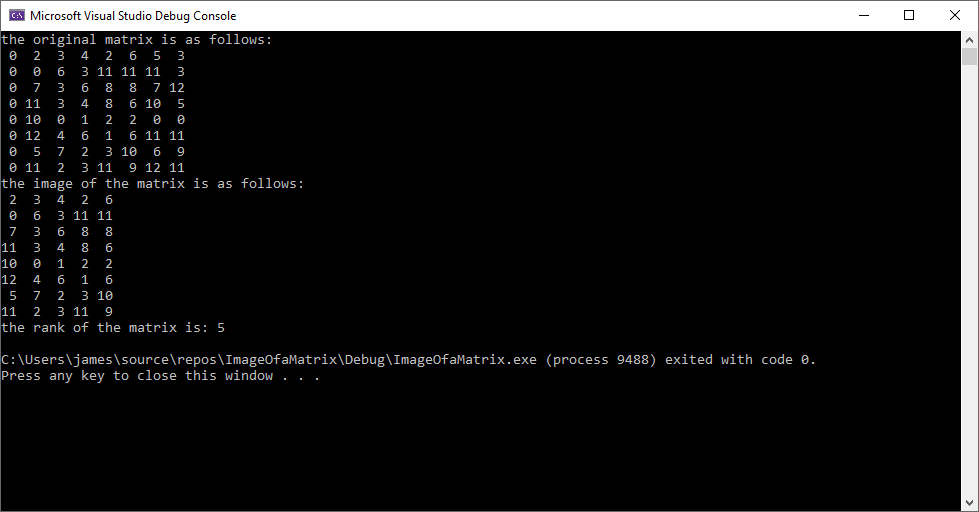
printf("the original matrix is as follows:\n");
print_matrix(m, n, M);
image(m, n, p, M, X, &r);
printf("the image of the matrix is as follows:\n");
print_matrix(n, n - r, X);
printf("the rank of the matrix is: %ld\n", n - r);
delete_matrix(m, M);
delete_matrix(n, X);
return 0;
}