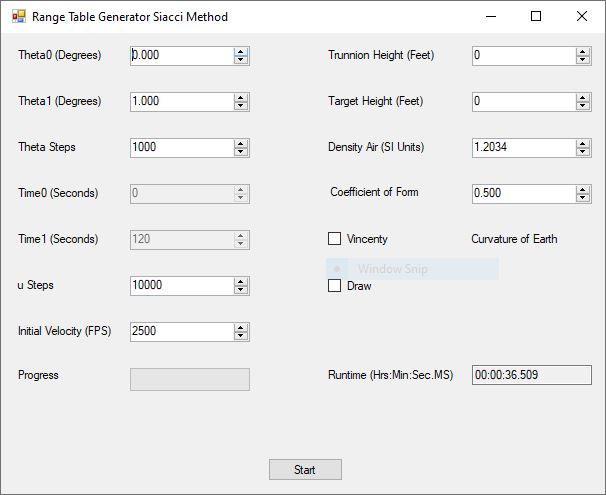
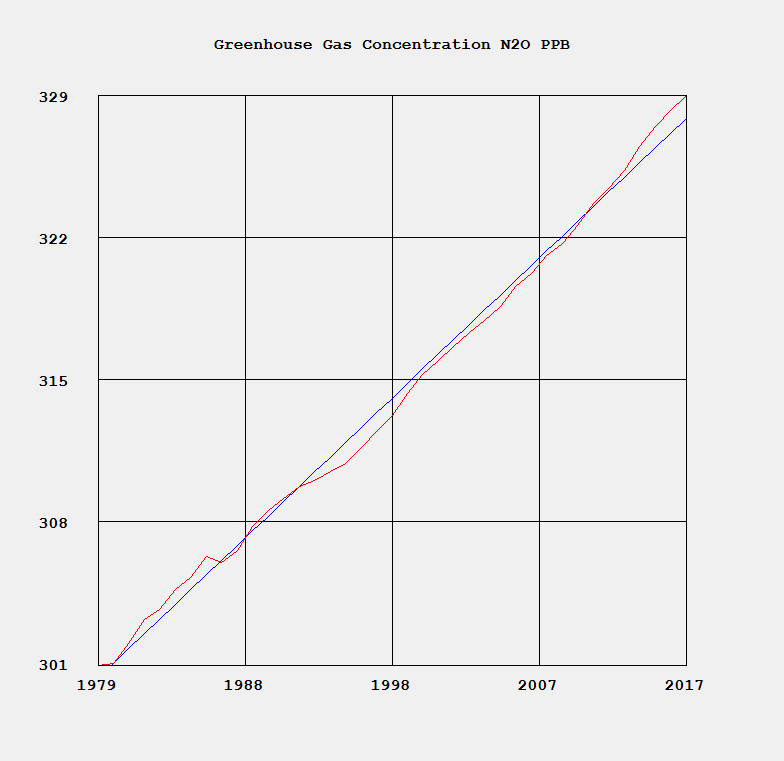
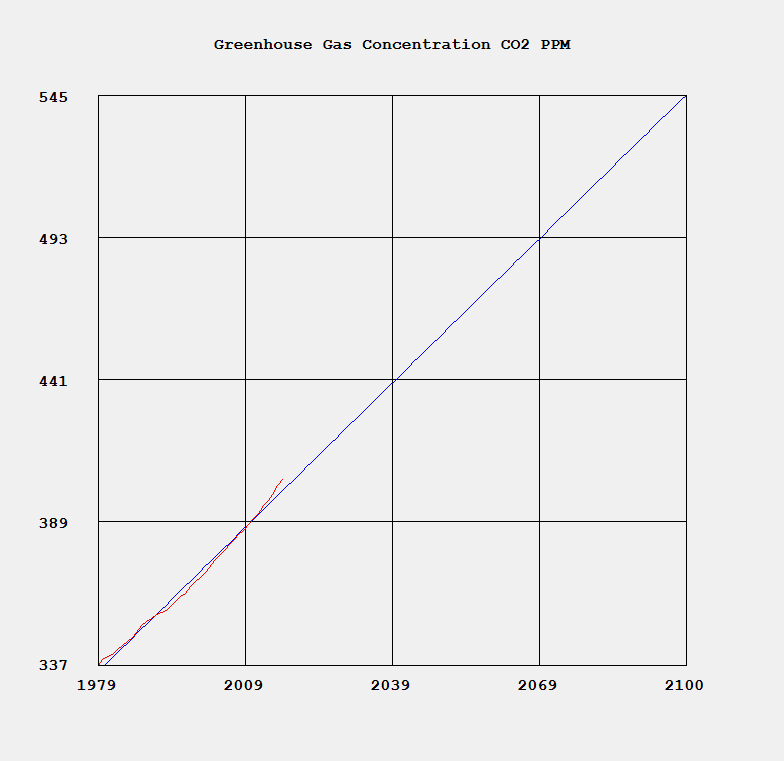
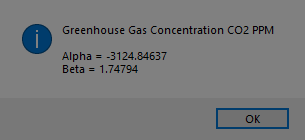
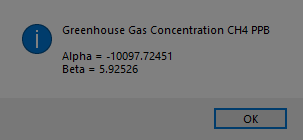
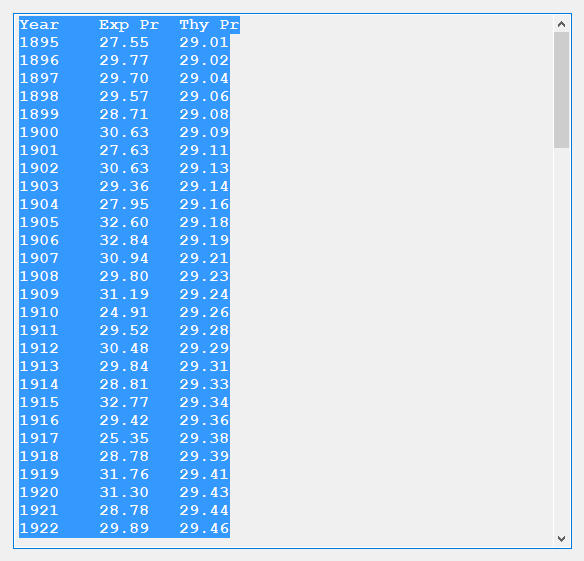
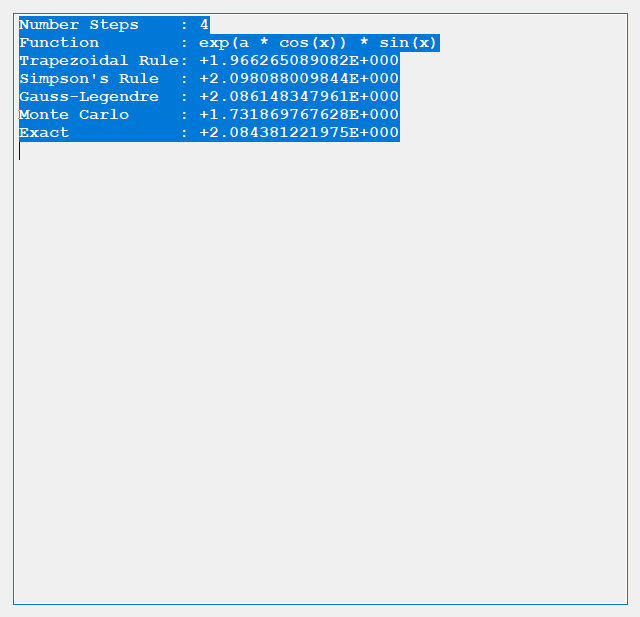
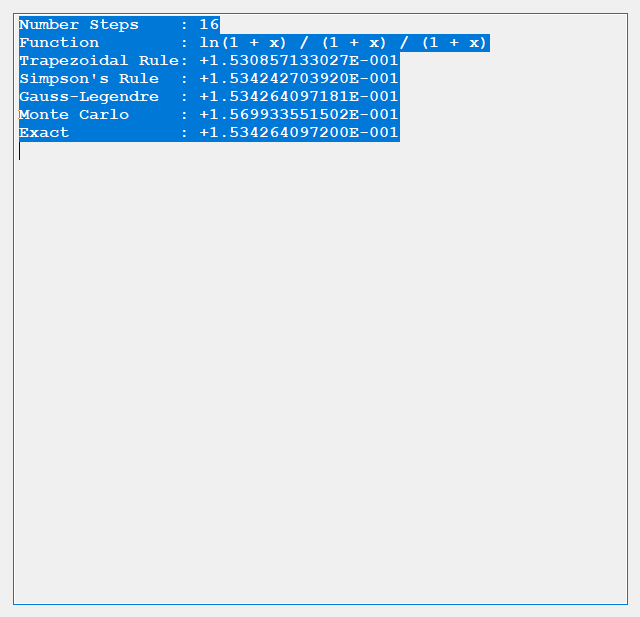
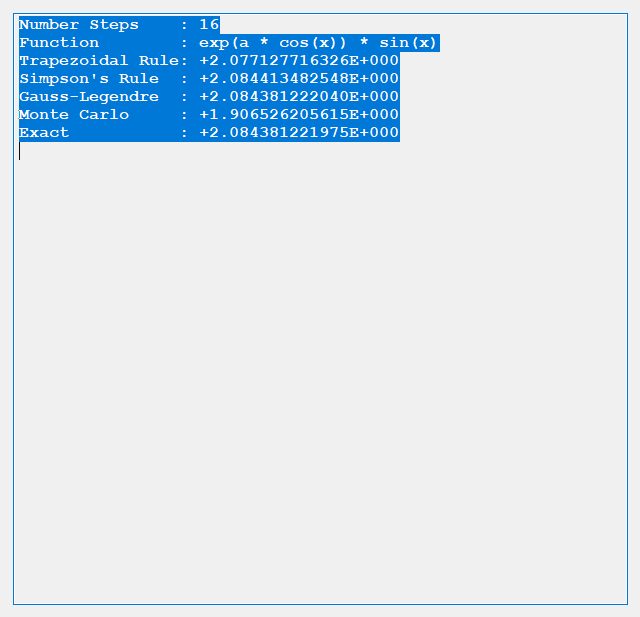
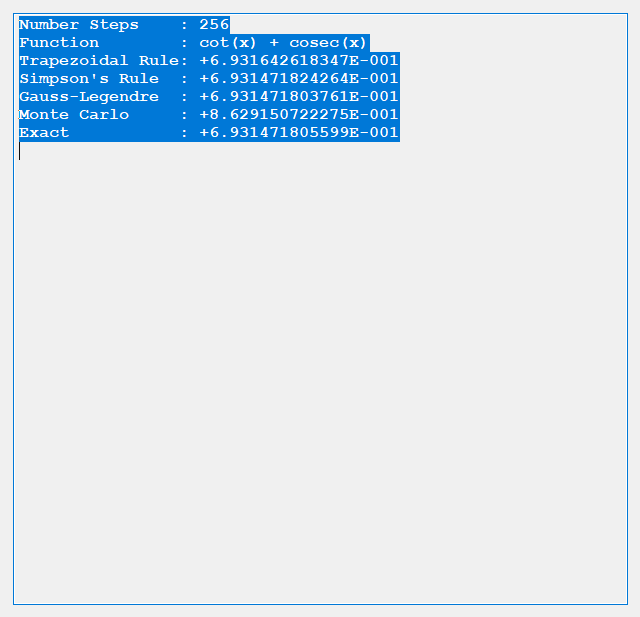
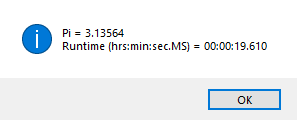
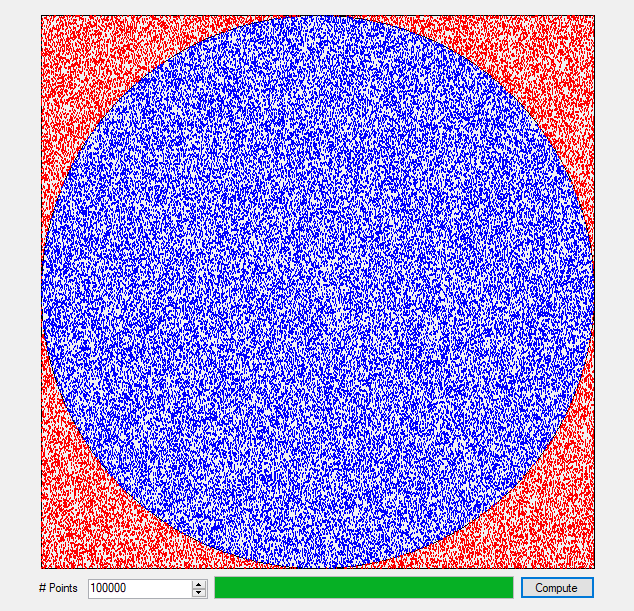
Merry Christmas to all you devout Christians. I am not one of you. I am about to embark on a mission to carefully annotate with open source C# computer code my copy of “Exterior Ballistics, 1935” by Professor Ernest Edward Herrmann of then the United States Naval Academy at Annapolis, Maryland. This book set the standard for naval gunnery in World War II. Of course, our navy and especially our battle-wagons had the largest rifled artillery of any United States service. The 105 mm = 105 mm / 25.4 mm / inch = 4.13 inches, 120 mm / 25.4 mm / inch = 4.72 inches, and 155 mm / 25.4 mm / inch = 6.10 inch of our excellent United States Army and United States Marine Corps (semper fidelis) are puny in comparison to the mighty 8, 10, 12, 14, and finally 16 inch mostly rifled artillery of our incredible navy’s cruisers, dreadnoughts, and battleships of the World War I and World War II era ships. Even a destroyer of the USN Fletcher class had 5-inch (127 mm) / 38 caliber rifled artillery which had a 5 inch * 38 = 190-inch barrel length. Our mightiest naval artillery was, of course, my favorite the mighty 16 inch (406.4 mm) / 50 caliber rifles that had a barrel length of 16 * 50 inches = 800 inches = 66.6 feet!
Thanks,
James Pate Williams, Jr.
Bachelor of Arts Chemistry LaGrange College 1979
Bachelor of Science Computer Science LaGrange College 1994
Master of Software Engineering Auburn University 2000
Doctor of Philosophy Computer Science Auburn University 2005
Gratis Open Source Computer Software Developer Since Summer 1978
1980 – 1983 Graduate Work in Chemistry and Mathematics at Georgia Tech
A Current Website I developed for my friends Wesley “Wes” and Missy Cochran:
http://thecochrancollection.com/Home