Factorizations of the Seventh Fermat Number
and Other Composite Integers Using the
Pollard-Shor-Williams C# App and the LIP
Lenstra Elliptic Curve Method
It took 20.1 hours for J. M. Pollard to
factor the Seventh Fermat Number in
December 1988. He was using an 8-bit
Philips P2012 personal computer with
64k RAM and two 640k floppy drives.
His seven programs were written in the
Pascal computer language. The current
author was using a 64-bit Core i5 Dell
Latitude 3410 notebook computer with
8 GB RAM and a 235 GB solid state
hard drive. The computer language was
Windows 32 vanilla C in the Release x64
Configuration. The operating system was
Windows 11 Pro with the Visual Studio
2022 Community Version Integrated
Development Environment and C#.
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 1
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:20:31.359
Function Evaluations = 661379586
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 2
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:12:31.146
Function Evaluations = 283327140
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 3
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:21:53.637
Function Evaluations = 371472150
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 4
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:15:25.712
Function Evaluations = 197866620
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 5
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:03:06.030
Function Evaluations = 19501012
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 6
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:12:25.076
Function Evaluations = 198404541
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 7
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:20:59.172
Function Evaluations = 168943987
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457 39
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 8
59649589127497217 p 17
5704689200685129054721 p 22
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:04:58.588
Function Evaluations = 13754504
Using Lenstra's Elliptic Curve Method
enter the number to be factored below:
2^128+1
340282366920938463463374607431768211457
number has 39 digits
== Menu ==
1 Cohen's Brent-Pollard Method
2 Cohen's Trial Division
3 Lenstra's Elliptic Curve Method
4 Pollard p-1 Method First Stage
5 Pollard p-1 Both Stages
6 Pollard-Shor-Williams Method
7 Exit Application
Enter an option '1' to '7':
3
factorization is complete
Runtime in seconds:
1.00000 sec.
original number has 39-decimal digits
'c' means composite and 'p' means prime
59649589127497217 17-decimal digits p
5704689200685129054721 22-decimal digits p
enter the number to be factored below:
Miscellaneous numbers using the C# app:
2^32+1
4294967297 10
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 1
641 p 3
6700417 p 7
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:00.034
Function Evaluations = 57
2^41-1
2199023255551 13
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 1
13367 p 5
164511353 p 9
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:00.003
Function Evaluations = 1128
2^67-1
147573952589676412927 21
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 1
193707721 p 9
761838257287 p 12
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:00.065
Function Evaluations = 30519
2^144-3
22300745198530623141535718272648361505980413 44
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 1
492729991333 p 12
45259565260477899162010980272761 p 32
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:04.804
Function Evaluations = 2458746
2^32+1
4294967297 10
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 5
641 p 3
6700417 p 7
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:00.001
Function Evaluations = 81
2^41-1
2199023255551 13
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 5
13367 p 5
164511353 p 9
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:00.002
Function Evaluations = 174
2^67-1
147573952589676412927 21
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 5
193707721 p 9
761838257287 p 12
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:00.050
Function Evaluations = 35949
2^144-3
22300745198530623141535718272648361505980413 44
Pseudo-Random Number Generator Seed = 1
Number of Tasks = 5
492729991333 p 12
45259565260477899162010980272761 p 32
Total Elapsed Runtime Hrs:Min:Sec.MS = 00:00:01.613
Function Evaluations = 632928
Now Lenstra's ECM:
enter the number to be factored below:
2^32+1
4294967297
number has 10 digits
== Menu ==
1 Cohen's Brent-Pollard Method
2 Cohen's Trial Division
3 Lenstra's Elliptic Curve Method
4 Pollard p-1 Method First Stage
5 Pollard p-1 Both Stages
6 Pollard-Shor-Williams Method
7 Exit Application
Enter an option '1' to '7':
3
factorization is complete
Runtime in seconds:
0.00000 sec.
original number has 10-decimal digits
'c' means composite and 'p' means prime
641 3-decimal digits p
6700417 7-decimal digits p
enter the number to be factored below:
2^41-1
2199023255551
number has 13 digits
== Menu ==
1 Cohen's Brent-Pollard Method
2 Cohen's Trial Division
3 Lenstra's Elliptic Curve Method
4 Pollard p-1 Method First Stage
5 Pollard p-1 Both Stages
6 Pollard-Shor-Williams Method
7 Exit Application
Enter an option '1' to '7':
3
factorization is complete
Runtime in seconds:
0.00000 sec.
original number has 13-decimal digits
'c' means composite and 'p' means prime
13367 5-decimal digits p
164511353 9-decimal digits p
enter the number to be factored below:
2^67-1
147573952589676412927
number has 21 digits
== Menu ==
1 Cohen's Brent-Pollard Method
2 Cohen's Trial Division
3 Lenstra's Elliptic Curve Method
4 Pollard p-1 Method First Stage
5 Pollard p-1 Both Stages
6 Pollard-Shor-Williams Method
7 Exit Application
Enter an option '1' to '7':
3
factorization is complete
Runtime in seconds:
0.00000 sec.
original number has 21-decimal digits
'c' means composite and 'p' means prime
193707721 9-decimal digits p
761838257287 12-decimal digits p
enter the number to be factored below:
2^144-3
22300745198530623141535718272648361505980413
number has 44 digits
== Menu ==
1 Cohen's Brent-Pollard Method
2 Cohen's Trial Division
3 Lenstra's Elliptic Curve Method
4 Pollard p-1 Method First Stage
5 Pollard p-1 Both Stages
6 Pollard-Shor-Williams Method
7 Exit Application
Enter an option '1' to '7':
3
factorization is complete
Runtime in seconds:
0.00000 sec.
original number has 44-decimal digits
'c' means composite and 'p' means prime
492729991333 12-decimal digits p
45259565260477899162010980272761 32-decimal digits p
enter the number to be factored below:
For the last number 2^144-3 it took J. M. Pollard's
factoring with cubic integers 47 hours in 1988.
Category: Classical Shor’s Algorithm
Pollard-Shor-Williams Factor Method by James Pate Williams, Jr.
This factoring algorithm is based on Pollard’s rho, Shor’s classical, and my modification of the two preceding methods.
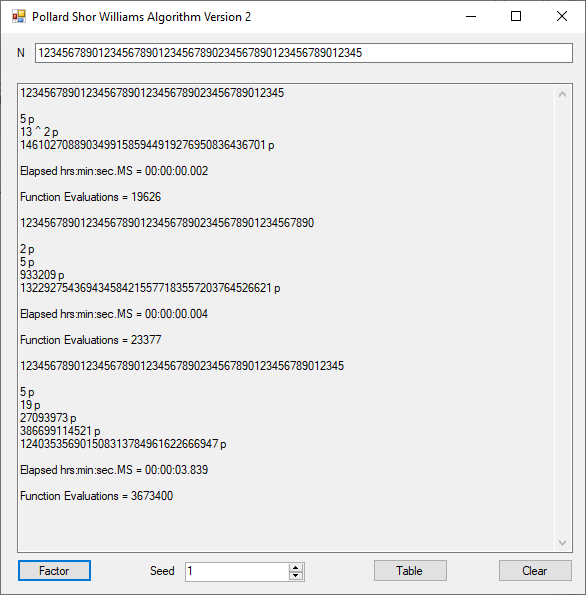
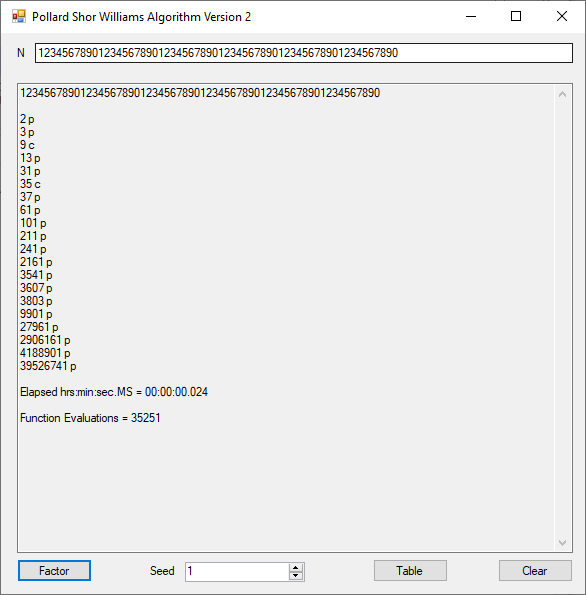
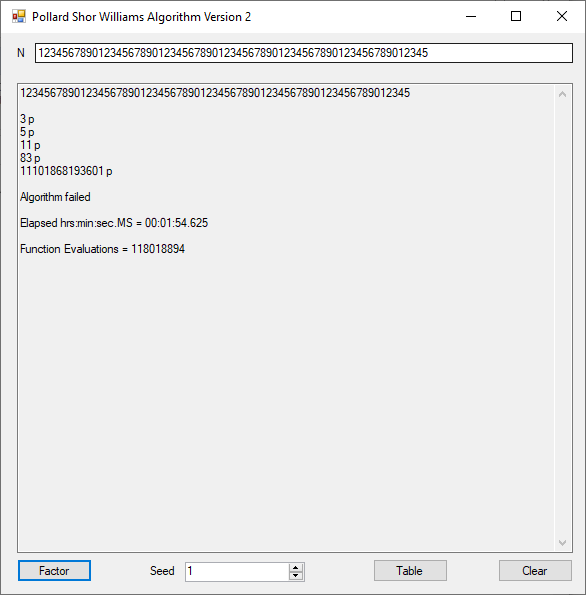
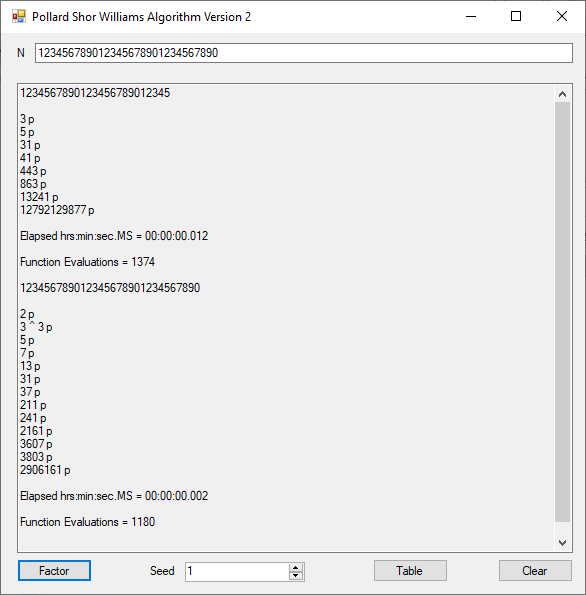

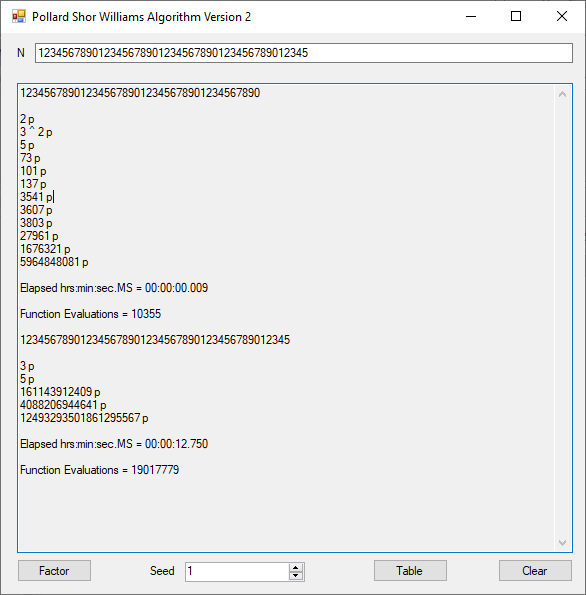
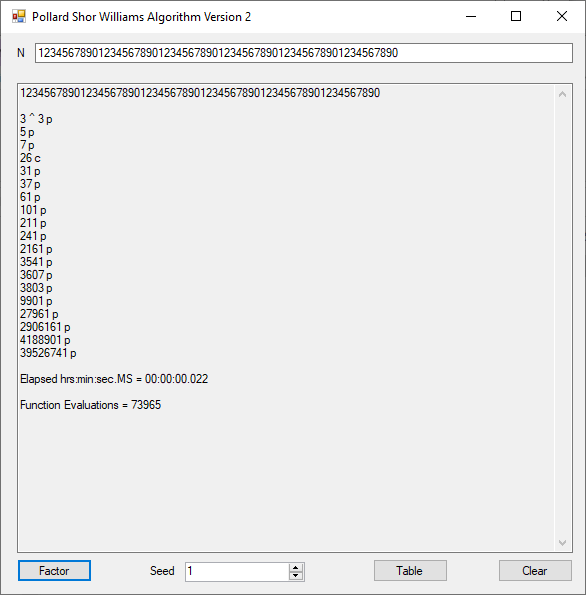
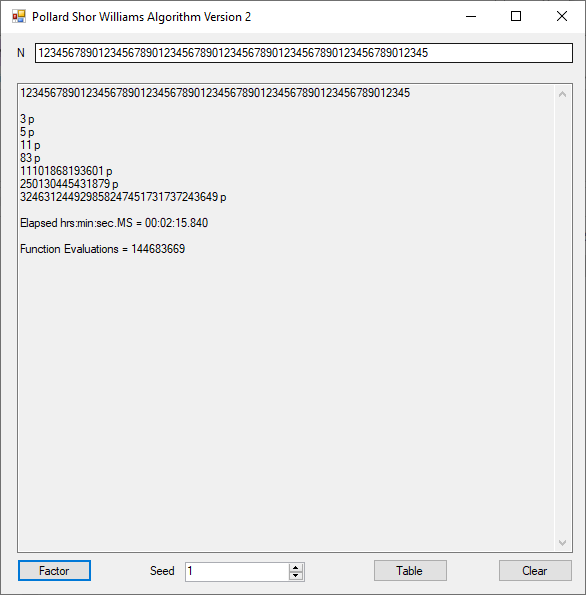
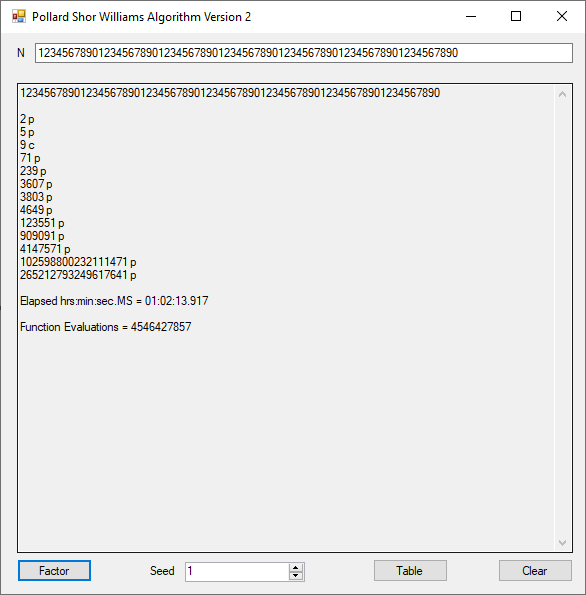
Classical Shor’s Algorithm Versus J. M. Pollard’s Factoring with Cubic Integers
We tried to factor the following numbers with each algorithm: 11^3+2, 2^33+2, 5^15+2, 2^66+2, 2^72+2, 2^81+2, 2^101+2, 2^129+2, and 2^183+2. Shor’s algorithm fully factored all of the numbers. Factoring with cubic integers fully factored all numbers except 2^66+2, 2^71+2, 2^129+2, and 2^183+2.
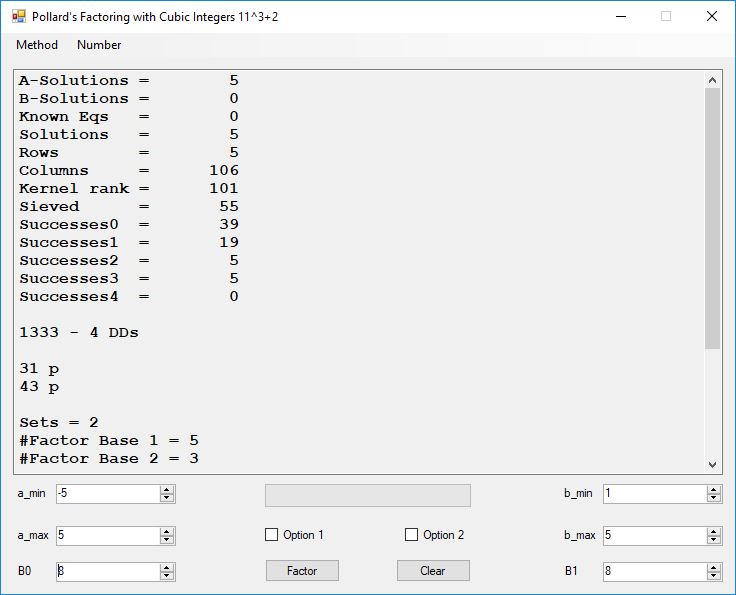
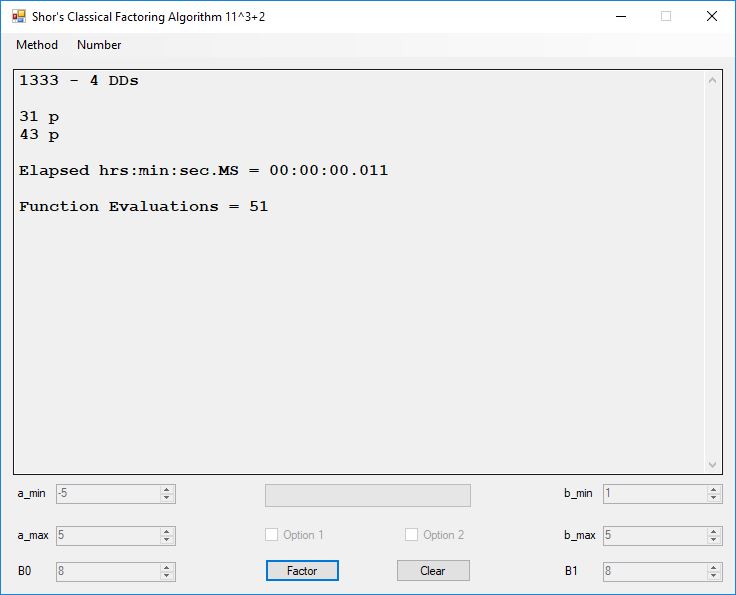
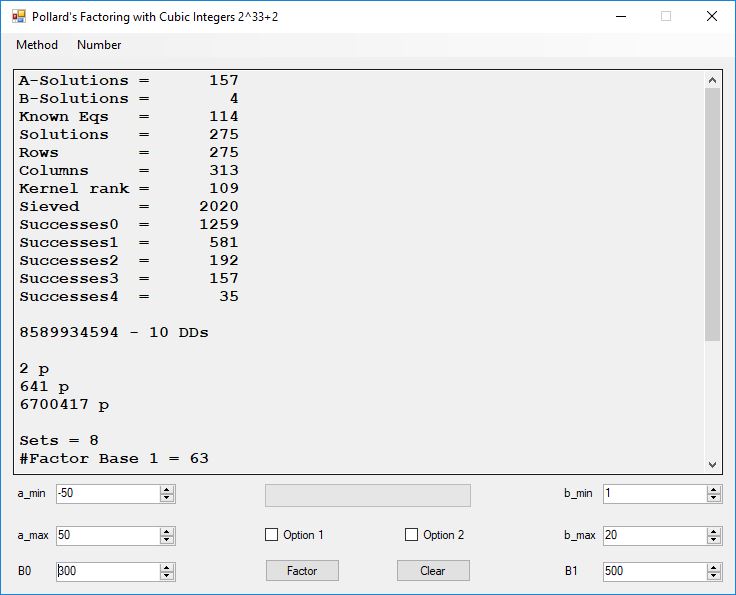
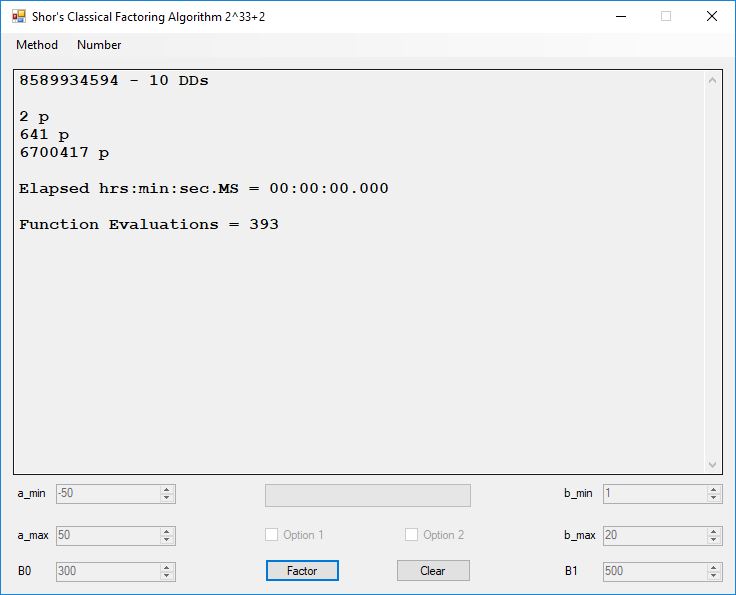
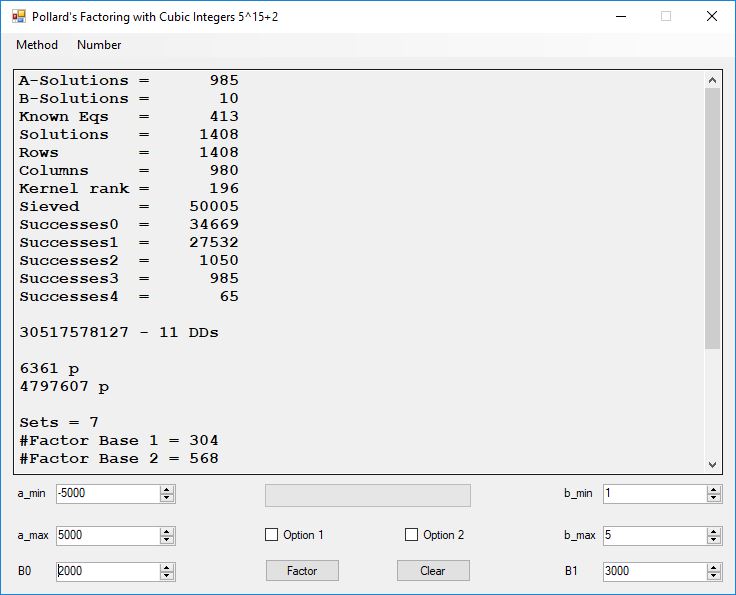
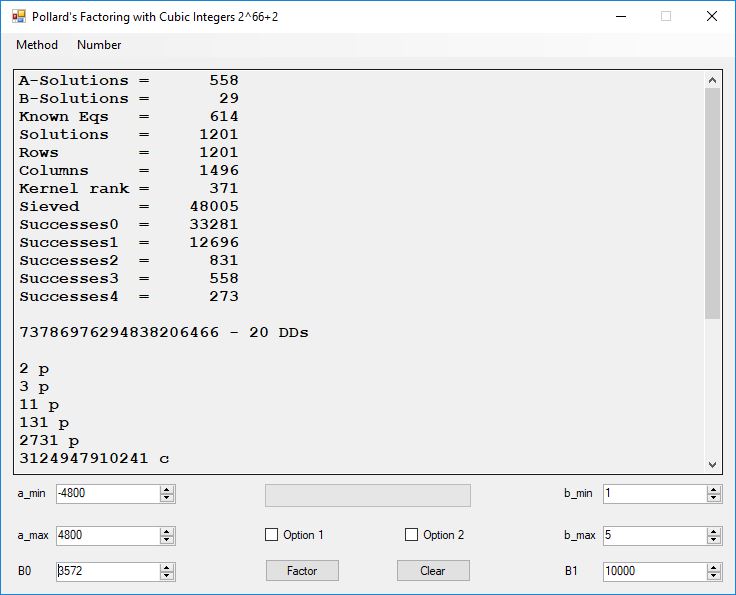
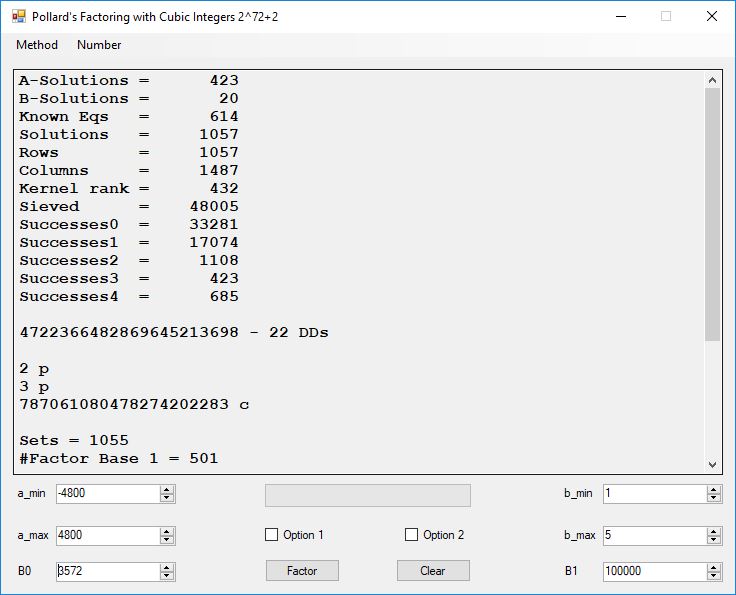
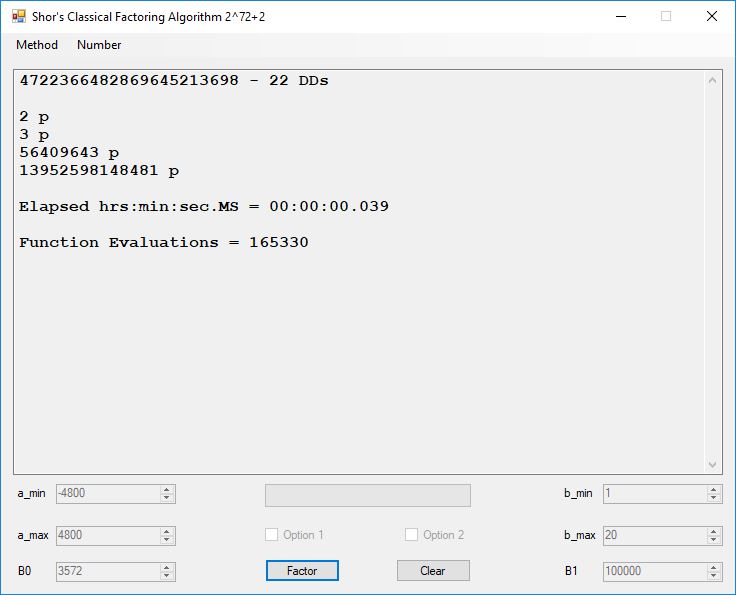
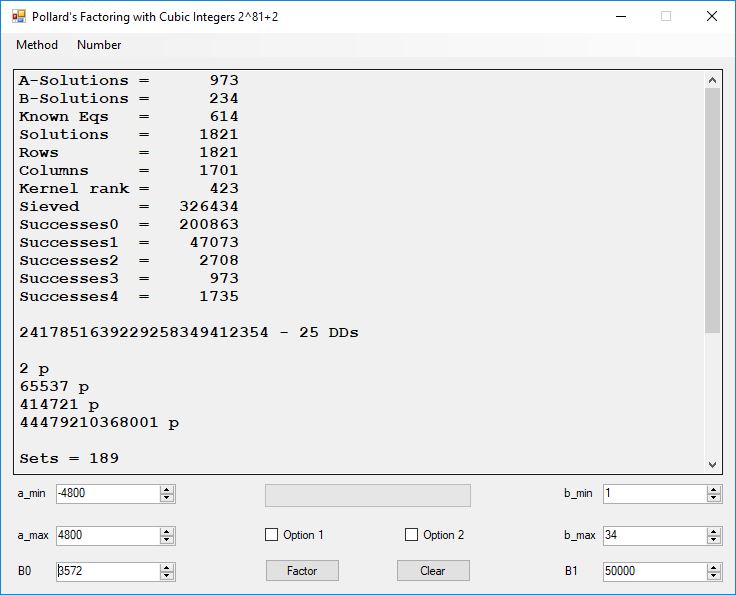
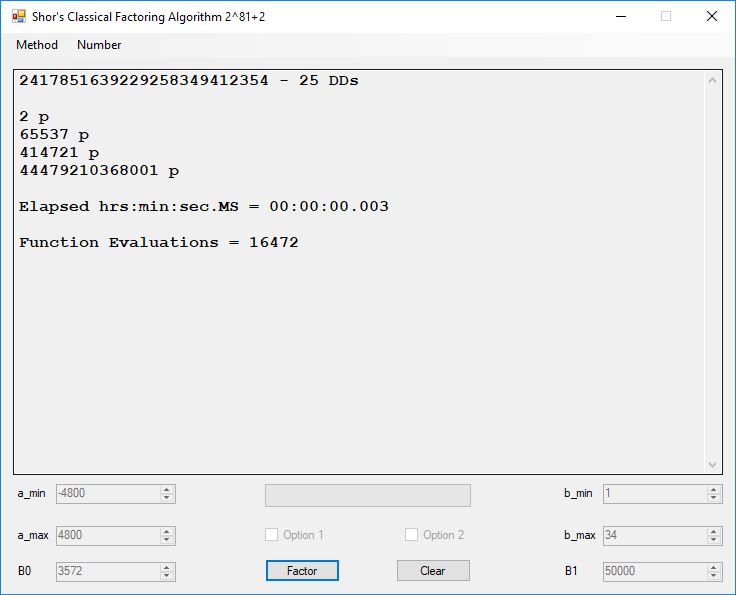
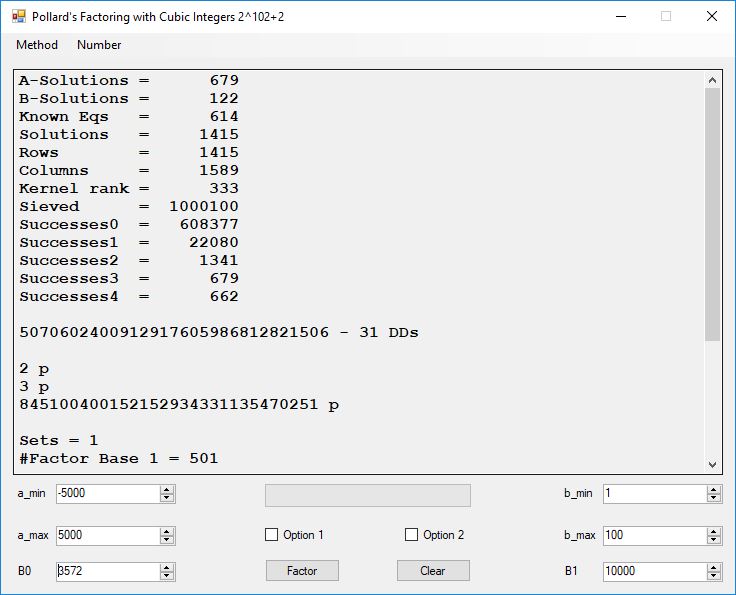
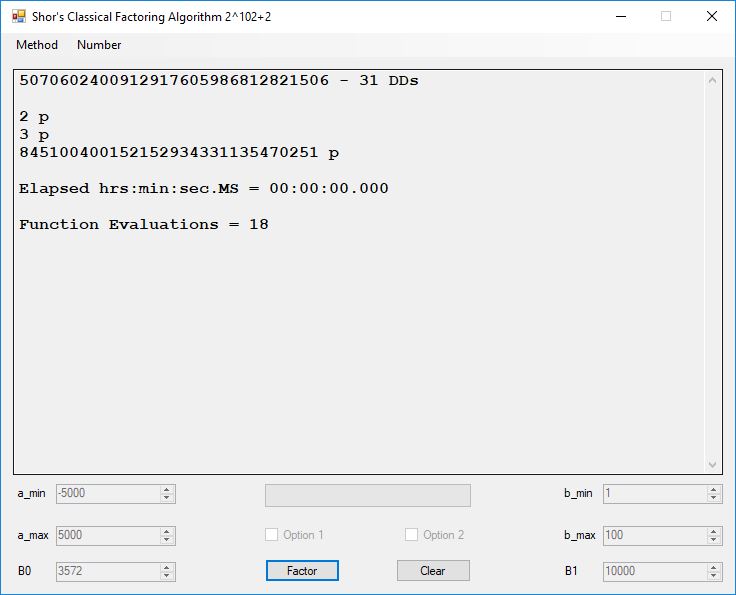
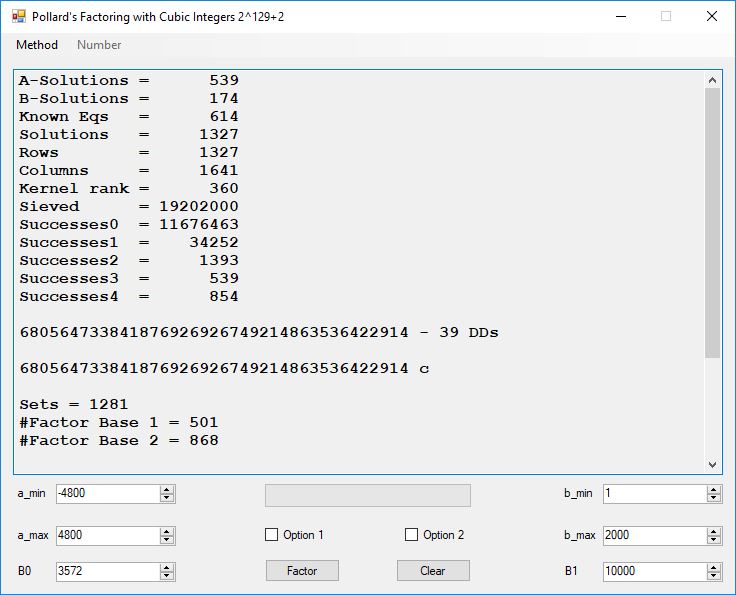
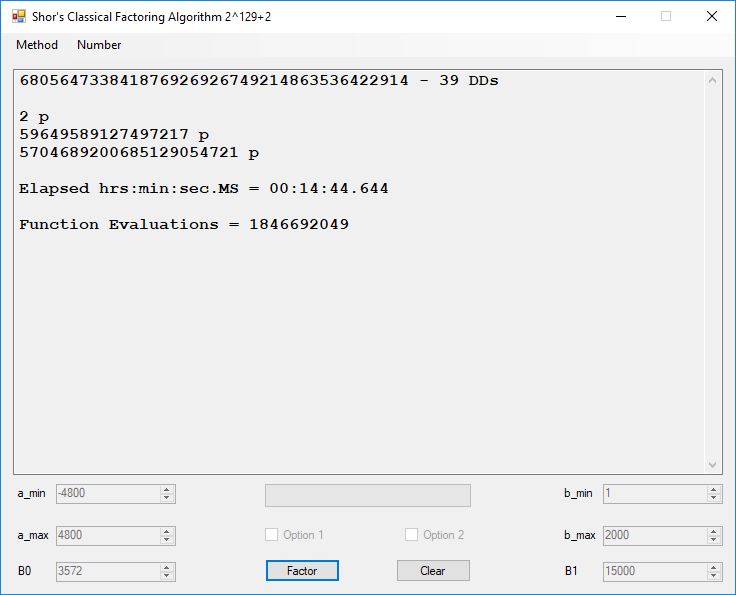
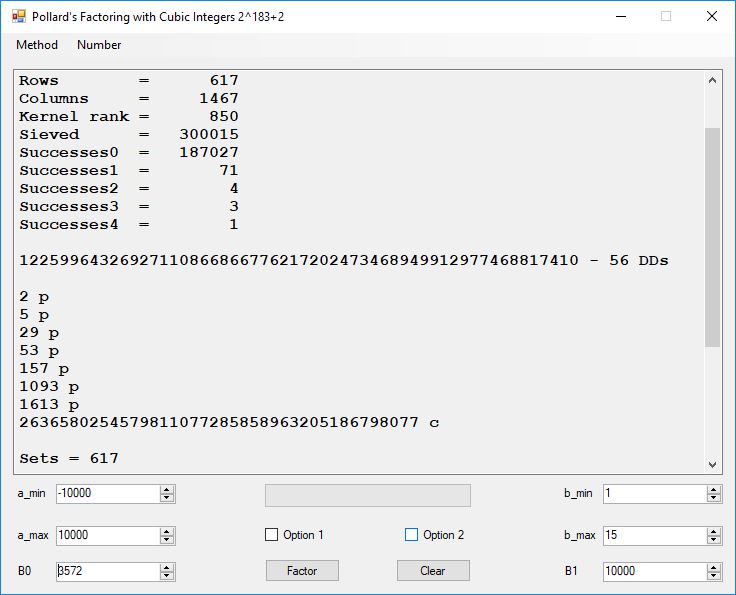
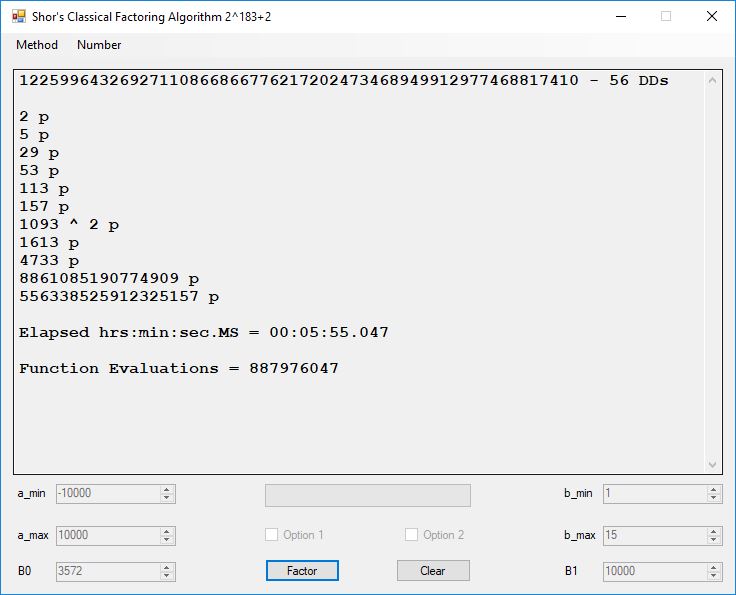
Typical full output from factoring with cubic integers:
A-Solutions = 973 B-Solutions = 234 Known Eqs = 614 Solutions = 1821 Rows = 1821 Columns = 1701 Kernel rank = 423 Sieved = 326434 Successes0 = 200863 Successes1 = 47073 Successes2 = 2708 Successes3 = 973 Successes4 = 1735 2417851639229258349412354 - 25 DDs 2 p 65537 p 414721 p 44479210368001 p Sets = 189 #Factor Base 1 = 501 #Factor Base 2 = 868 FactB1 time = 00:00:00.000 FactB2 time = 00:00:05.296 Sieve time = 00:00:17.261 Kernel time = 00:00:06.799 Factor time = 00:00:02.327 Total time = 00:00:31.742
A-solutions have no large prime. B-solutions have a large prime between B0 and B1 exclusively which is this case is between 3272 and 50000 exclusively. The known equations are between the rational primes and the cubic primes and their associates of the form p = 6k + 1 that have -2 as a cubic residue. There are 81 rational primes of the form and 243 cubic primes but we keep many other associates of the cubic primes so more a and b pairs are successfully algebraically factored. In out case the algebraic factor base has 868 members. The rational prime factor base also includes the negative unit -1. The kernel rank is the number of independent columns in the matrix. The number of dependent sets is equal to columns – rank which is this case 1701 – 423 = 1278. The number of (a, b) pairs sieved is 326434. Successes0 is the pairs that have gcd(a, b) = 1. Successes1 is the number of (a, b) pairs such that a+b*r is B0-smooth or can be factored by the first 500 primes and the negative unit. r is equal to 2^27. Successes2 is the number of (a, b) pairs whose N[a, b] = a^2-2*b^3 can be factored using the norms of the algebraic primes. Successes3 is the number of A-solutions that are algebraically and rationally smooth. Successes4 is the number of B-solutions without combining to make the count modulo 2 = 0. Successes3 + Successes4 should equal Successes2 provided all proper algebraic primes and their associates are utilized.
Note factoring with cubic integers is very fickle with respect to parameter choice.