Category: Data Structures
Blog Entry Thursday, June 20, 2024 (c) James Pate Williams, Jr. Some 3D Graphs (Application Edited 2024)
C# Three-Dimensional Cartesian Vector Calculator (c) September 24, 2023, by James Pate Williams, Jr. All Applicable Rights Reserved
I wrote and debugged this C# code after I found out that my 1989 vector calculator in Modula-2 for the Commadore Amiga 2000 was not working correctly.
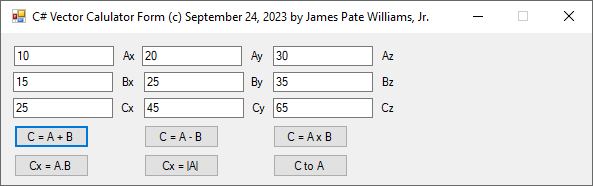
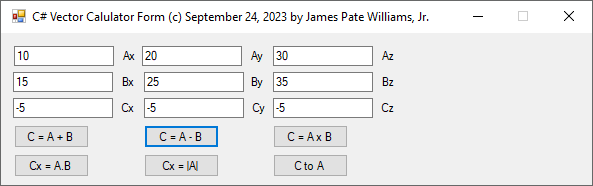
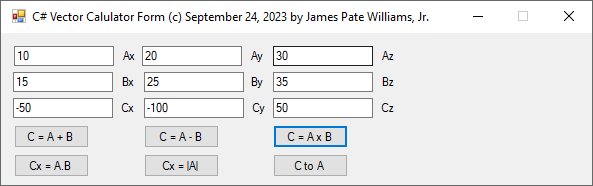
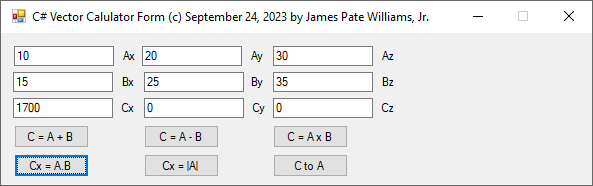
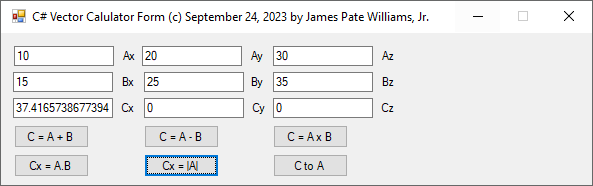
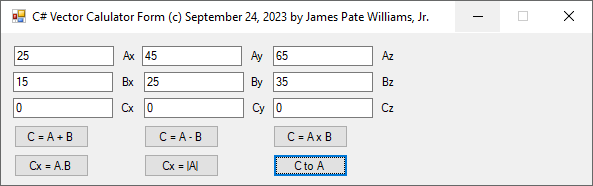
// C# Three-Dimensional Cartesian Vector Calculator
// (c) September 24, 2023 by James Pate Williams, Jr.
// All Applicable Rights Reserved
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CSVectorCalculator
{
public partial class MainForm : Form
{
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private static double[] A = new double[3];
private static double[] B = new double[3];
private static double[] C = new double[3];
private void ValidateAB(
ref bool valid)
{
try
{
A[0] = double.Parse(textBox1.Text);
A[1] = double.Parse(textBox2.Text);
A[2] = double.Parse(textBox3.Text);
B[0] = double.Parse(textBox4.Text);
B[1] = double.Parse(textBox5.Text);
B[2] = double.Parse(textBox6.Text);
valid = true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Warning",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Warning);
valid = false;
}
}
private void FillC(double[] C)
{
textBox7.Text = C[0].ToString();
textBox8.Text = C[1].ToString();
textBox9.Text = C[2].ToString();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool valid = true;
ValidateAB(ref valid);
if (valid)
{
C[0] = A[0] + B[0];
C[1] = A[1] + B[1];
C[2] = A[2] + B[2];
FillC(C);
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool valid = true;
ValidateAB(ref valid);
if (valid)
{
C[0] = A[0] - B[0];
C[1] = A[1] - B[1];
C[2] = A[2] - B[2];
FillC(C);
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool valid = true;
ValidateAB(ref valid);
if (valid)
{
C[0] = A[1] * B[2] - A[2] * B[1];
C[1] = A[0] * B[2] - A[2] * B[0];
C[2] = A[1] * B[0] - A[0] * B[1];
FillC(C);
}
}
private void button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool valid = true;
ValidateAB(ref valid);
if (valid)
{
C[0] = A[0] * B[0] + A[1] * B[1] + A[2] * B[2];
C[1] = C[2] = 0.0;
FillC(C);
}
}
private void button5_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool valid = true;
ValidateAB(ref valid);
if (valid)
{
C[0] = Math.Sqrt(A[0] * A[0] + A[1] * A[1] + A[2] * A[2]);
C[1] = C[2] = 0.0;
FillC(C);
}
}
private void button6_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
bool valid = true;
ValidateAB(ref valid);
if (valid)
{
textBox1.Text = C[0].ToString();
textBox2.Text = C[1].ToString();
textBox3.Text = C[2].ToString();
C[0] = C[1] = C[2] = 0.0;
FillC(C);
}
}
}
}
Multiple Precision Arithmetic in C++ Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
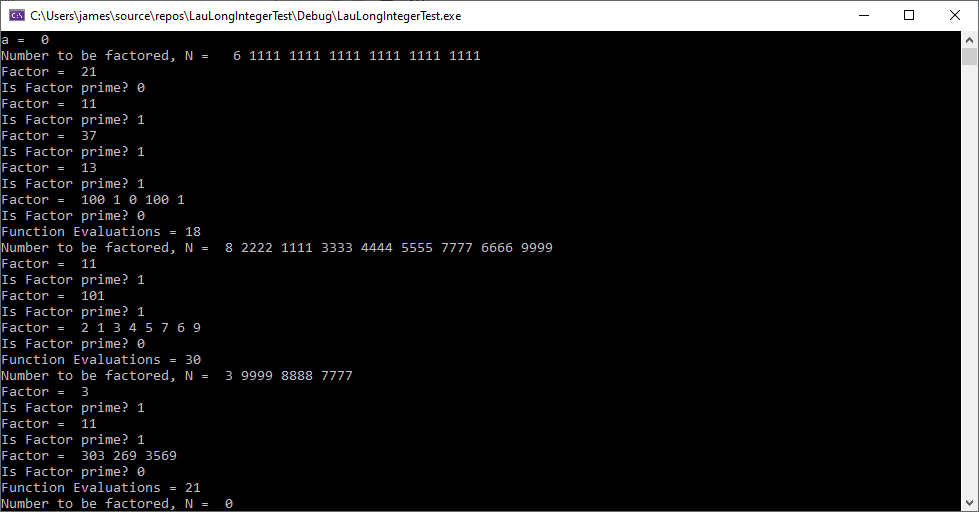
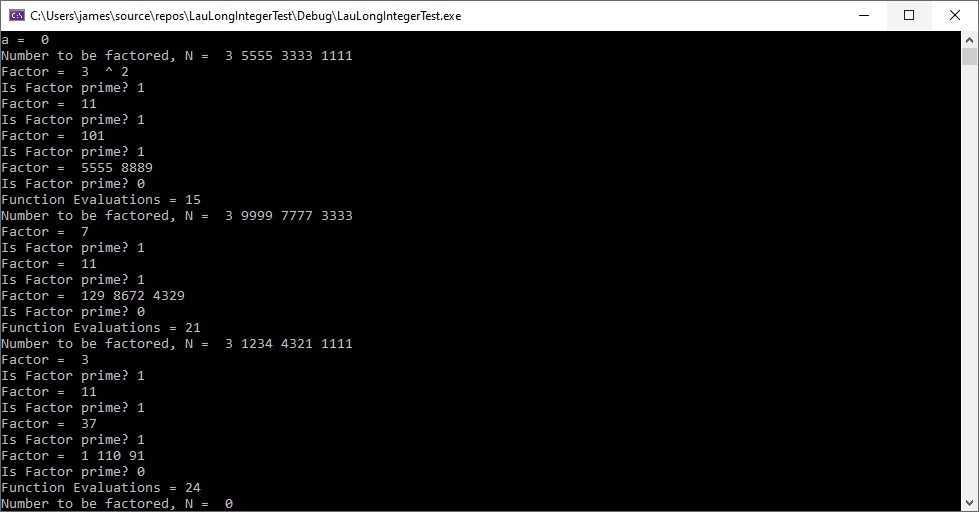
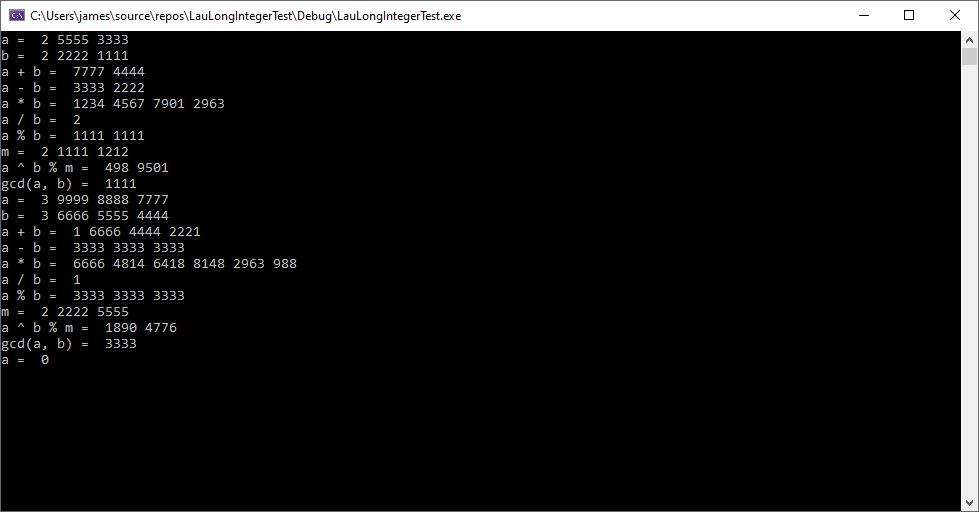
I have developed a long integer package in C++ using H. T. Lau’s “A Numerical Library in C for Scientists and Engineers”. That library is based on the NUMAL Numerical Algorithms in Algol library. I use 32-bit integers (long) as the basis of the LongInteger type. The base (radix) is 10000 which is the largest base using 32-bit integers. As a test of the library, I use Pollard’s original rho factorization method. I utilized the Alfred J. Menezes et al “Handbook of Applied Cryptography” Miller-Rabin algorithm and ANSI X9.17 pseudo random number generator with Triple-DES as the encryption algorithm. I translated Hans Riesel Pascal code for Euclid’s algorithm and the power modulus technique. I don’t use dynamic long integers a la Hans Riesel’s Pascal multiple precision library. The single precision is 32 32-bit longs and multiple precision 64 32-bit longs.
Here is a typical factorization:
Number to be factored, N = 3 1234 5678 9012
Factor = 3
Is Factor prime? 1
Factor = 4
Is Factor prime? 0
Factor = 102 8806 5751
Is Factor prime? 1
Function Evaluations = 6
Number to be factored, N = 0
The first number of N is the number of base 10000 digits. I verified that 10288065751 was prime using Miller-Rabin and the table found online below:
http://compoasso.free.fr/primelistweb/page/prime/liste_online_en.php
C++ Linear Algebra Package Extension Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
Input file:
The dimensions of the linear system of equations (m and n, m = n): 2 2 The matrix of the linear system of equations (n by n): 1 1 1 2 The right-hand side of the linear system of equations (n by 1): 7 11 The dimensions of the linear system of equations (m and n, m = 2): 2 2 The matrix of the linear system of equations (n by n): 1 1 1 3 The right-hand side of the linear system of equations (n by 1): 7 11 The dimensions of the linear system of equations (m and n, m = n): 2 2 The matrix of the linear system of equations (n by n): 6 3 4 8 The right-hand side of the linear system of equations (n by 1): 5 6 The dimensions of the linear system of equations (m and n, m = n): 2 2 The matrix of the linear system of equations (n by n): 5 3 10 4 The right-hand side of the linear system of equations (n by 1): 8 6 The dimensions of the linear system of equations (m and n, m = n): 3 3 The matrix of the linear system of equations (n by n): 2 1 -1 -3 -1 2 -2 1 2 The right-hand side of the linear system of equations (n by 1): 8 -11 -3
Output file:
The 1st solution of the linear system of equations:
3 4
The 2nd solution of the linear system of equations:
3 4
The determinant of the linear system of equations:
1
The inverse of the linear system of equations:
2 -1
-1 1
The adjoint of the linear system of equations:
2 -0
-0 2
The characteristic polynomial of the linear system of equations:
1 2
The image of the matrix:
1 -1
1 2
Rank = 2
The 1st solution of the linear system of equations:
5 2
The 2nd solution of the linear system of equations:
5 2
The determinant of the linear system of equations:
2
The inverse of the linear system of equations:
1.5 -0.5
-0.5 0.5
The adjoint of the linear system of equations:
3 -0
-0 3
The characteristic polynomial of the linear system of equations:
1 3
The image of the matrix:
1 -1
1 3
Rank = 2
The 1st solution of the linear system of equations:
0.61111 0.44444
The 2nd solution of the linear system of equations:
0.61111 0.44444
The determinant of the linear system of equations:
36
The inverse of the linear system of equations:
0.22222 -0.11111
-0.083333 0.16667
The adjoint of the linear system of equations:
48 -0
-0 48
The characteristic polynomial of the linear system of equations:
1 48
The image of the matrix:
6 -1
4 8
Rank = 2
The 1st solution of the linear system of equations:
-1.4 5
The 2nd solution of the linear system of equations:
-1.4 5
The determinant of the linear system of equations:
-10
The inverse of the linear system of equations:
-0.4 1
0.3 -0.5
The adjoint of the linear system of equations:
20 -0
-0 20
The characteristic polynomial of the linear system of equations:
1 20
The image of the matrix:
5 -1
10 4
Rank = 2
The 1st solution of the linear system of equations:
2 3 -1
The 2nd solution of the linear system of equations:
2 3 -1
The determinant of the linear system of equations:
1
The inverse of the linear system of equations:
4 5 -2
3 4 -2
-1 -1 1
The adjoint of the linear system of equations:
-4 0 0
0 -4 0
0 0 -4
The characteristic polynomial of the linear system of equations:
1 -7 4
The image of the matrix:
2 -1 2
-3 0 -1
-2 0 4
Rank = 3
// Algorithms from "A Course in Computational
// Algebraic Number Theory" by Henri Cohen
// Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
// Copyright (c) 2023 All Rights Reserved
#pragma once
#include "pch.h"
template<class T> class Matrix
{
public:
size_t m, n;
T** data;
Matrix() { m = 0; n = 0; data = NULL; };
Matrix(size_t m, size_t n)
{
this->m = m;
this->n = n;
data = new T*[m];
if (data == NULL)
exit(-300);
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
data[i] = new T[n];
if (data[i] == NULL)
exit(-301);
}
};
void OutputMatrix(
fstream& outs, char fill, int precision, int width)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
outs << setfill(fill) << setprecision(precision);
outs << setw(width) << data[i][j] << '\t';
}
outs << endl;
}
};
};
template<class T> class Vector
{
public:
size_t n;
T* data;
Vector() { n = 0; data = NULL; };
Vector(size_t n)
{
this->n = n;
data = new T[n];
};
void OutputVector(
fstream& outs, char fill, int precision, int width)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
outs << setfill(fill) << setprecision(precision);
outs << setw(width) << data[i] << '\t';
}
outs << endl;
};
};
class LinearAlgebra
{
public:
bool initialized;
size_t m, n;
Matrix<double> M;
Vector<double> B;
LinearAlgebra()
{
initialized = false;
m = 0; n = 0;
M.data = NULL;
B.data = NULL;
};
LinearAlgebra(size_t m, size_t n)
{
initialized = false;
this->m = m;
this->n = n;
this->M.m = m;
this->M.n = n;
this->B.n = n;
this->M.data = new double*[m];
this->B.data = new double[n];
if (M.data != NULL)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
this->M.data[i] = new double[n];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
this->M.data[i][j] = 0;
}
}
if (B.data != NULL)
{
this->B.data = new double[n];
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
this->B.data[i] = 0;
}
initialized = this->B.data != NULL && this->M.data != NULL;
};
LinearAlgebra(
size_t m, size_t n,
double** M,
double* B)
{
this->m = m;
this->n = n;
this->M.m = m;
this->M.n = n;
this->M.data = new double*[m];
this->B.data = new double[n];
if (M != NULL)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
this->M.data[i] = new double[n];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
this->M.data[i][j] = M[i][j];
}
}
if (B != NULL)
{
this->B.data = new double[n];
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
this->B.data[i] = B[i];
}
initialized = this->B.data != NULL && this->M.data != NULL;
}
~LinearAlgebra()
{
M.m = m;
M.n = n;
B.n = n;
if (B.data != NULL)
delete[] B.data;
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
if (M.data[i] != NULL)
delete[] M.data[i];
if (M.data != NULL)
delete[] M.data;
}
double DblDeterminant(bool failure);
Vector<double> DblGaussianElimination(
bool& failure);
// The following four methods are from the
// textbook "Elementary Numerical Analysis
// An Algorithmic Approach" by S. D. Conte
// and Carl de Boor Translated from the
// original FORTRAN by James Pate Williams, Jr.
// Copyright (c) 2023 All Rights Reserved
bool DblGaussianFactor(
Vector<int>& pivot);
bool DblGaussianSolution(
Vector<double>& x,
Vector<int>& pivot);
bool DblSubstitution(
Vector<double>& x,
Vector<int>& pivot);
bool DblInverse(
Matrix<double>& A,
Vector<int>& pivot);
// Henri Cohen Algorithm 2.2.7
void DblCharPolyAndAdjoint(
Matrix<double>& adjoint,
Vector<double>& a);
// Henri Cohen Algorithm 2.3.1
void DblMatrixKernel(
Matrix<double>& X, size_t& r);
// Henri Cohen Algorithm 2.3.1
void DblMatrixImage(
Matrix<double>& N, size_t& rank);
};
// pch.h: This is a precompiled header file.
// Files listed below are compiled only once, improving build performance for future builds.
// This also affects IntelliSense performance, including code completion and many code browsing features.
// However, files listed here are ALL re-compiled if any one of them is updated between builds.
// Do not add files here that you will be updating frequently as this negates the performance advantage.
#ifndef PCH_H
#define PCH_H
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#endif //PCH_H
#include "pch.h"
#include "LinearAlgebra.h"
double LinearAlgebra::DblDeterminant(
bool failure)
{
double deter = 1;
Vector<int> pivot(n);
if (!initialized || m != n)
{
failure = true;
return 0.0;
}
if (!DblGaussianFactor(pivot))
{
failure = true;
return 0.0;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
deter *= M.data[i][i];
return deter;
}
Vector<double> LinearAlgebra::DblGaussianElimination(
bool& failure)
{
double* C = new double[m];
Vector<double> X(n);
X.data = new double[n];
if (X.data == NULL)
exit(-200);
if (!initialized)
{
failure = true;
delete[] C;
return X;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
C[i] = -1;
failure = false;
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
bool found = false;
size_t i = j;
while (i < n && !found)
{
if (M.data[i][j] != 0)
found = true;
else
i++;
}
if (!found)
{
failure = true;
break;
}
if (i > j)
{
for (size_t l = j; l < n; l++)
{
double t = M.data[i][l];
M.data[i][l] = M.data[j][l];
M.data[j][l] = t;
t = B.data[i];
B.data[i] = B.data[j];
B.data[j] = t;
}
}
double d = 1.0 / M.data[j][j];
for (size_t k = j + 1; k < n; k++)
C[k] = d * M.data[k][j];
for (size_t k = j + 1; k < n; k++)
{
for (size_t l = j + 1; l < n; l++)
M.data[k][l] = M.data[k][l] - C[k] * M.data[j][l];
B.data[k] = B.data[k] - C[k] * B.data[j];
}
}
for (int i = (int)n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
double sum = 0;
for (size_t j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
sum += M.data[i][j] * X.data[j];
X.data[i] = (B.data[i] - sum) / M.data[i][i];
}
delete[] C;
return X;
}
bool LinearAlgebra::DblGaussianFactor(
Vector<int>& pivot)
// returns false if matrix is singular
{
Vector<double> d(n);
double awikod, col_max, ratio, row_max, temp;
int flag = 1;
size_t i_star, itemp;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
pivot.data[i] = i;
row_max = 0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
row_max = max(row_max, abs(M.data[i][j]));
if (row_max == 0)
{
flag = 0;
row_max = 1;
}
d.data[i] = row_max;
}
if (n <= 1) return flag != 0;
// factorization
for (size_t k = 0; k < n - 1; k++)
{
// determine pivot row the row i_star
col_max = abs(M.data[k][k]) / d.data[k];
i_star = k;
for (size_t i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
{
awikod = abs(M.data[i][k]) / d.data[i];
if (awikod > col_max)
{
col_max = awikod;
i_star = i;
}
}
if (col_max == 0)
flag = 0;
else
{
if (i_star > k)
{
// make k the pivot row by
// interchanging with i_star
flag *= -1;
itemp = pivot.data[i_star];
pivot.data[i_star] = pivot.data[k];
pivot.data[k] = itemp;
temp = d.data[i_star];
d.data[i_star] = d.data[k];
d.data[k] = temp;
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
temp = M.data[i_star][j];
M.data[i_star][j] = M.data[k][j];
M.data[k][j] = temp;
}
}
// eliminate x[k]
for (size_t i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
{
M.data[i][k] /= M.data[k][k];
ratio = M.data[i][k];
for (size_t j = k + 1; j < n; j++)
M.data[i][j] -= ratio * M.data[k][j];
}
}
if (M.data[n - 1][n - 1] == 0) flag = 0;
}
if (flag == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
bool LinearAlgebra::DblGaussianSolution(
Vector<double>& x,
Vector<int>& pivot)
{
if (!DblGaussianFactor(pivot))
return false;
return DblSubstitution(x, pivot);
}
bool LinearAlgebra::DblSubstitution(
Vector<double>& x,
Vector<int>& pivot)
{
double sum;
size_t j, n1 = n - 1;
if (n == 1)
{
x.data[0] = B.data[0] / M.data[0][0];
return true;
}
// forward substitution
x.data[0] = B.data[pivot.data[0]];
for (int i = 1; i < (int)n; i++)
{
for (j = 0, sum = 0; j < (size_t)i; j++)
sum += M.data[i][j] * x.data[j];
x.data[i] = B.data[pivot.data[i]] - sum;
}
// backward substitution
x.data[n1] /= M.data[n1][n1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
double sum = 0.0;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
sum += M.data[i][j] * x.data[j];
x.data[i] = (x.data[i] - sum) / M.data[i][i];
}
return true;
}
bool LinearAlgebra::DblInverse(
Matrix<double>& A,
Vector<int>& pivot)
{
Vector<double> x(n);
if (!DblGaussianFactor(pivot))
return false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
B.data[j] = 0;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
B.data[i] = 1;
if (!DblSubstitution(x, pivot))
return false;
B.data[i] = 0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
A.data[i][j] = x.data[pivot.data[j]];
}
return true;
}
void LinearAlgebra::DblCharPolyAndAdjoint(
Matrix<double>& adjoint,
Vector<double>& a)
{
Matrix<double> C(n, n);
Matrix<double> I(n, n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
C.data[i][j] = I.data[i][j] = 0;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
C.data[i][i] = I.data[i][i] = 1;
a.data[0] = 1;
for (size_t i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (size_t k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
double sum = 0.0;
for (size_t l = 0; l < n; l++)
sum += M.data[j][l] * C.data[l][k];
C.data[j][k] = sum;
}
}
double tr = 0.0;
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
tr += C.data[j][j];
a.data[i] = -tr / i;
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (size_t k = 0; k < n; k++)
C.data[j][k] += a.data[i] * I.data[j][k];
}
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
double sum = 0.0;
for (size_t k = 0; k < n; k++)
sum += M.data[i][k] * C.data[k][j];
C.data[i][j] = sum;
}
}
double trace = 0.0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
trace += C.data[i][i];
trace /= n;
a.data[n - 1] = -trace;
double factor = 1.0;
if ((n - 1) % 2 != 0)
factor = -1.0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
adjoint.data[i][j] = factor * C.data[i][j];
}
}
void LinearAlgebra::DblMatrixKernel(Matrix<double>& X, size_t& r)
{
double D = 0.0;
Vector<int> c(m);
Vector<int> d(n);
r = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
c.data[i] = -1;
size_t j, k = 1;
Step2:
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if (M.data[j][k] != 0 && c.data[j] == -1)
break;
}
if (j == m)
{
r++;
d.data[k] = 0;
goto Step4;
}
D = -1.0 / M.data[j][k];
M.data[j][k] = -1;
for (size_t s = k + 1; s < n; s++)
{
M.data[j][s] = D * M.data[j][s];
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (i != j)
{
D = M.data[i][k];
M.data[i][k] = 0;
}
}
}
for (size_t s = k + 1; s < n; s++)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
M.data[i][s] += D * M.data[j][s];
}
}
c.data[j] = k;
d.data[k] = j;
Step4:
if (k < n - 1)
{
k++;
goto Step2;
}
X.n = n;
if (r != 0)
{
for (k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
if (d.data[k] == 0)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (d.data[i] > 0)
X.data[k][i] = M.data[d.data[i]][k];
else if (i == k)
X.data[k][i] = 1;
else
X.data[k][i] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
void LinearAlgebra::DblMatrixImage(
Matrix<double>& N, size_t& rank)
{
double D = 0.0;
size_t r = 0;
Matrix<double> copyM(m, n);
Vector<int> c(m);
Vector<int> d(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
c.data[i] = -1;
size_t j, k = 1;
N = copyM = M;
Step2:
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if (copyM.data[j][k] != 0 && c.data[j] == -1)
break;
}
if (j == m)
{
r++;
d.data[k] = 0;
goto Step4;
}
D = -1.0 / copyM.data[j][k];
copyM.data[j][k] = -1;
for (size_t s = k + 1; s < n; s++)
{
copyM.data[j][s] = D * copyM.data[j][s];
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
if (i != j)
{
D = copyM.data[i][k];
copyM.data[i][k] = 0;
}
}
}
for (size_t s = k + 1; s < n; s++)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
copyM.data[i][s] += D * copyM.data[j][s];
}
}
c.data[j] = k;
d.data[k] = j;
Step4:
if (k < n - 1)
{
k++;
goto Step2;
}
rank = n - r;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if (c.data[j] != 0)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
N.data[i][c.data[j]] = M.data[i][c.data[j]];
}
}
}
}
/*
** Cohen's linear algebra test program
** Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
** Copyright (c) 2023 All Rights Reserved
*/
#include "pch.h"
#include "LinearAlgebra.h"
double GetDblNumber(fstream& inps)
{
char ch = inps.get();
string numberStr;
while (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\r' || ch == '\n')
ch = inps.get();
while (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '.' ||
ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
numberStr += ch;
ch = inps.get();
}
double x = atof(numberStr.c_str());
return x;
}
int GetIntNumber(fstream& inps)
{
char ch = inps.get();
string numberStr;
while (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\r' || ch == '\n')
ch = inps.get();
while (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
numberStr += ch;
ch = inps.get();
}
int x = atoi(numberStr.c_str());
return x;
}
int main()
{
fstream inps;
inps.open("CLATestFile.txt", fstream::in);
if (inps.fail())
{
cout << "Input file opening error!" << endl;
return -1;
}
fstream outs;
outs.open("CLAResuFile.txt", fstream::out | fstream::ate);
if (outs.fail())
{
cout << "Output file opening error!" << endl;
return -2;
}
size_t m, n;
while (!inps.eof())
{
char buffer[256] = { '\0' };
inps.getline(buffer, 256);
m = GetIntNumber(inps);
if (inps.eof())
return 0;
if (m < 1)
{
cout << "The number of rows must be >= 1" << endl;
return -100;
}
n = GetIntNumber(inps);
if (n < 1)
{
cout << "The number of colums must be >= 1" << endl;
return -101;
}
LinearAlgebra la(m, n);
Matrix<double> copyM(m, n);
Vector<double> copyB(n);
inps.getline(buffer, 256);
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
double x = GetDblNumber(inps);
la.M.data[i][j] = x;
copyM.data[i][j] = x;
}
}
inps.getline(buffer, 256);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
la.B.data[i] = GetDblNumber(inps);
copyB.data[i] = la.B.data[i];
}
bool failure = false;
Vector<double> X = la.DblGaussianElimination(failure);
if (!failure)
{
outs << "The 1st solution of the linear system of equations:" << endl;
X.OutputVector(outs, ' ', 5, 8);
}
else
{
cout << "Cohen Gaussian elimination failure!" << endl;
exit(-102);
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
la.B.data[i] = copyB.data[i];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
la.M.data[i][j] = copyM.data[i][j];
}
}
Matrix<double> A(n, n);
Vector<int> pivot(n);
if (!la.DblGaussianSolution(X, pivot))
exit(-103);
outs << "The 2nd solution of the linear system of equations:" << endl;
X.OutputVector(outs, ' ', 5, 8);
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
la.B.data[i] = copyB.data[i];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
la.M.data[i][j] = copyM.data[i][j];
}
}
double deter = la.DblDeterminant(failure);
outs << "The determinant of the linear system of equations:" << endl;
outs << deter << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
la.B.data[i] = copyB.data[i];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
la.M.data[i][j] = copyM.data[i][j];
}
}
outs << "The inverse of the linear system of equations:" << endl;
if (!la.DblInverse(A, pivot))
{
cout << "Conte Gaussian inverse matrix failure!" << endl;
exit(-104);
}
else
A.OutputMatrix(outs, ' ', 5, 8);
Matrix<double> adjoint(n, n);
Vector<double> a(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
la.B.data[i] = copyB.data[i];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
la.M.data[i][j] = copyM.data[i][j];
}
}
la.DblCharPolyAndAdjoint(adjoint, a);
outs << "The adjoint of the linear system of equations:" << endl;
adjoint.OutputMatrix(outs, ' ', 5, 8);
outs << "The characteristic polynomial of the linear system of equations:" << endl;
a.OutputVector(outs, ' ', 5, 8);
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
la.B.data[i] = copyB.data[i];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
la.M.data[i][j] = copyM.data[i][j];
}
}
Matrix<double> kernel(m, n);
size_t r = 0;
la.DblMatrixKernel(kernel, r);
if (r > 0)
{
outs << "The kernel of the matrix: " << endl;
kernel.OutputMatrix(outs, ' ', 5, 8);
outs << "Dimension of the kernel: " << r << endl;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
la.B.data[i] = copyB.data[i];
for (size_t j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
la.M.data[i][j] = copyM.data[i][j];
}
}
Matrix<double> N(m, n);
size_t rank;
la.DblMatrixImage(N, rank);
if (rank > 0)
{
outs << "The image of the matrix: " << endl;
N.OutputMatrix(outs, ' ', 5, 8);
outs << "Rank = " << rank << endl;
}
}
inps.close();
outs.close();
}
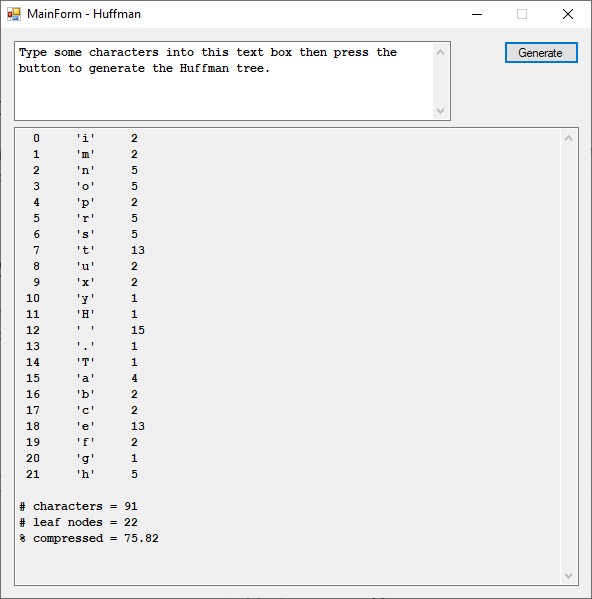
Huffman Compression in C# Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
Algorithms are found in the textbook “Introduction to Algorithms” by Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest p. 340.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace Huffman
{
public partial class MainForm : Form
{
private int leafNodes;
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void InorderTraversal(BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> node)
{
if (node != null)
{
InorderTraversal(node.Left);
CharFreq cf = node.Value;
int ord = (int)cf.ch;
if (node.Left == null && node.Right == null)
{
textBox2.Text += leafNodes.ToString("F0").PadLeft(3) + '\t';
textBox2.Text += "'" + new string(cf.ch, 1) + "' " + '\t';
textBox2.Text += node.Value.freq.ToString() + "\r\n";
leafNodes++;
}
InorderTraversal(node.Right);
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string s = textBox1.Text;
int n = s.Length;
List<CharFreq> list = new List<CharFreq>();
textBox2.Text = string.Empty;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
bool found = false;
char c = s[i];
CharFreq cf = new CharFreq();
for (int j = 0; !found && j < list.Count; j++)
{
if (c == list[j].ch)
{
found = true;
cf.ch = c;
cf.freq = 1 + list[j].freq;
list.RemoveAt(j);
list.Add(cf);
}
}
if (!found)
{
cf.ch = c;
cf.freq = 1;
list.Add(cf);
}
}
HuffmanTree ht = new HuffmanTree();
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> root = ht.Build(list, list.Count);
InorderTraversal(root);
textBox2.Text += "\r\n# characters = " + n.ToString() + "\r\n";
textBox2.Text += "# leaf nodes = " + leafNodes.ToString() + "\r\n";
textBox2.Text += "% compressed = " +
(100.0 - 100.0 * ((double)leafNodes) / n).ToString("F2") + "\r\n";
}
}
}
namespace Huffman
{
public class BinaryTreeNode<T> : Node<T>
{
public BinaryTreeNode() : base() { }
public BinaryTreeNode(T data) : base(data, null) { }
public BinaryTreeNode(T data, BinaryTreeNode<T> left, BinaryTreeNode<T> right)
{
base.Value = data;
NodeList<T> children = new NodeList<T>(2)
{
[0] = left,
[1] = right
};
base.Neighbors = children;
}
public BinaryTreeNode<T> Left
{
get
{
if (base.Neighbors == null)
return null;
else
return (BinaryTreeNode<T>)base.Neighbors[0];
}
set
{
if (base.Neighbors == null)
base.Neighbors = new NodeList<T>(2);
base.Neighbors[0] = value;
}
}
public BinaryTreeNode<T> Right
{
get
{
if (base.Neighbors == null)
return null;
else
return (BinaryTreeNode<T>)base.Neighbors[1];
}
set
{
if (base.Neighbors == null)
base.Neighbors = new NodeList<T>(2);
base.Neighbors[1] = value;
}
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Huffman
{
public class HuffmanTree
{
public BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> Build(List<CharFreq> charFreq, int n)
{
PriorityQueue Q = new PriorityQueue();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> z = new BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>(charFreq[i]);
Q.insert(z);
}
Q.buildHeap();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> x = Q.extractMin();
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> y = Q.extractMin();
CharFreq chFreq = new CharFreq();
chFreq.ch = (char)((int)x.Value.ch + (int)y.Value.ch);
chFreq.freq = x.Value.freq + y.Value.freq;
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> z = new BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>(chFreq);
z.Left = x;
z.Right = y;
Q.insert(z);
}
return Q.extractMin();
}
}
}
namespace Huffman
{
public class Node<T>
{
// Private member-variables
private T data;
private NodeList<T> neighbors = null;
public Node() { }
public Node(T data) : this(data, null) { }
public Node(T data, NodeList<T> neighbors)
{
this.data = data;
this.neighbors = neighbors;
}
public T Value
{
get
{
return data;
}
set
{
data = value;
}
}
protected NodeList<T> Neighbors
{
get
{
return neighbors;
}
set
{
neighbors = value;
}
}
}
}
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
namespace Huffman
{
public class NodeList<T> : Collection<Node<T>>
{
public NodeList() : base() { }
public NodeList(int initialSize)
{
// Add the specified number of items
for (int i = 0; i < initialSize; i++)
base.Items.Add(default(Node<T>));
}
public Node<T> FindByValue(T value)
{
// search the list for the value
foreach (Node<T> node in Items)
if (node.Value.Equals(value))
return node;
// if we reached here, we didn't find a matching node
return null;
}
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Huffman
{
public struct CharFreq
{
public char ch;
public int freq;
}
public class PriorityQueue
{
int heapSize;
List<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>> nodeList;
public List<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>> NodeList
{
get
{
return nodeList;
}
}
public PriorityQueue()
{
nodeList = new List<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>>();
}
public PriorityQueue(List<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>> nl)
{
heapSize = nl.Count;
nodeList = new List<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>>();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.Count; i++)
nodeList.Add(nl[i]);
}
public void exchange(int i, int j)
{
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> temp = nodeList[i];
nodeList[i] = nodeList[j];
nodeList[j] = temp;
}
public void heapify(int i)
{
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
int largest = -1;
if (l < heapSize && nodeList[l].Value.ch > nodeList[i].Value.ch)
largest = l;
else
largest = i;
if (r < heapSize && nodeList[r].Value.ch > nodeList[largest].Value.ch)
largest = r;
if (largest != i)
{
exchange(i, largest);
heapify(largest);
}
}
public void buildHeap()
{
for (int i = heapSize / 2; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(i);
}
public int size()
{
return heapSize;
}
public BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> elementAt(int i)
{
return nodeList[i];
}
public void heapSort()
{
int temp = heapSize;
buildHeap();
for (int i = heapSize - 1; i >= 1; i--)
{
exchange(0, i);
heapSize--;
heapify(0);
}
heapSize = temp;
}
public BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> extractMin()
{
if (heapSize < 1)
return null;
heapSort();
exchange(0, heapSize - 1);
heapSize--;
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> node = nodeList[heapSize];
nodeList.RemoveAt(heapSize);
heapSize = nodeList.Count;
return node;
}
public void insert(BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> node)
{
nodeList.Add(node);
heapSize = nodeList.Count;
buildHeap();
}
}
}
Huffman Compression in C++ Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
The original string is: abbbccddeefffghhhhijkllmm # characters = 25 The compressed codes and frequencies are: 0 e 2 1 l 2 2 f 3 3 b 3 4 i 1 5 c 2 6 g 1 7 a 1 8 d 2 9 m 2 10 k 1 11 j 1 12 h 4 # leaf nodes = 13 % compressed = 48 C:\Users\james\source\repos\HuffmanCodes\Debug\HuffmanCodes.exe (process 36772) exited with code 0. Press any key to close this window . . .
// Algorithm is found in the textbook
// "Introduction to Algorithms"
// by Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E.
// Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest p. 340
#include "pch.h"
int leafNodes = 0;
void InorderTraversal(BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>* node)
{
if (node != NULL)
{
InorderTraversal(node->lt);
if (node->lt == NULL && node->rt == NULL)
{
CharFreq cf = node->data;
std::cout << setw(3) << leafNodes << '\t';
std::cout << cf.ch << '\t';
std::cout << setw(3) << cf.freq << '\n';
leafNodes++;
}
InorderTraversal(node->rt);
}
}
int main()
{
int f[128] = { 0 };
string str = "abbbccddeefffghhhhijkllmm";
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> charFreqTree;
vector<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>> v;
std::cout << "The original string is: " << endl;
std::cout << str << endl << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < strlen(str.c_str()); i++)
{
bool found = false;
char ch = str.c_str()[i];
for (auto iter = v.begin(); !found &&
iter != v.end(); iter++)
{
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> node = *iter;
if (node.data.ch == ch)
{
node.data.freq++;
*iter = node;
found = true;
}
}
if (!found)
{
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> node;
node.data.ch = ch;
node.data.freq = 1;
node.lt = node.rt = NULL;
v.push_back(node);
}
}
priority_queue<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>, vector<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>>,
greater<BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>>> Q(v.begin(), v.end());
size_t n = Q.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>* x = new
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>();
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>* y = new
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>();
*x = Q.top();
Q.pop();
*y = Q.top();
Q.pop();
CharFreq charFreq;
charFreq.ch = (char)(x->data.ch + y->data.ch);
charFreq.freq = x->data.freq + y->data.freq;
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>* z = new
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq>(charFreq, x, y);
Q.push(*z);
}
BinaryTreeNode<CharFreq> root = Q.top();
std::cout << "# characters = " << strlen(str.c_str()) << endl;
std::cout << "The compressed codes and frequencies are:" << endl;
InorderTraversal(&root);
std::cout << "# leaf nodes = " << leafNodes << endl;
std::cout << "% compressed = " <<
(100.0 - 100.0 * ((double)leafNodes) / strlen(str.c_str())) << endl;
return 0;
}
#pragma once
#include "pch.h"
using namespace std;
template <class T>
class BinaryTreeNode
{
public:
T data;
BinaryTreeNode* lt;
BinaryTreeNode* rt;
BinaryTreeNode() {
lt = rt = nullptr;
};
BinaryTreeNode(T data)
{
this->data = data;
lt = rt = nullptr;
};
BinaryTreeNode(T data, BinaryTreeNode* lt, BinaryTreeNode* rt)
{
this->data = data;
this->lt = lt;
this->rt = rt;
};
friend bool operator > (BinaryTreeNode lhs, BinaryTreeNode rhs)
{
return lhs.data > rhs.data;
};
friend bool operator < (BinaryTreeNode lhs, BinaryTreeNode rhs)
{
return lhs.data < rhs.data;
};
friend bool operator == (BinaryTreeNode lhs, BinaryTreeNode rhs)
{
return lhs.data == rhs.data;
};
};
#pragma once
class CharFreq
{
public:
char ch;
int freq;
CharFreq()
{
ch = '\0';
freq = 0;
};
CharFreq(char c)
{
ch = c;
freq = 0;
};
CharFreq(char c, int f)
{
ch = c;
freq = f;
};
friend int operator - (CharFreq lhs, CharFreq rhs)
{
return lhs.freq - rhs.freq;
}
friend bool operator > (CharFreq lhs, CharFreq rhs)
{
return lhs.freq > rhs.freq;
};
friend bool operator < (CharFreq lhs, CharFreq rhs)
{
return lhs.freq < rhs.freq;
};
friend bool operator == (CharFreq lhs, CharFreq rhs)
{
return lhs.freq == rhs.freq && lhs.ch == rhs.ch;
};
};
// pch.h: This is a precompiled header file.
// Files listed below are compiled only once, improving build performance for future builds.
// This also affects IntelliSense performance, including code completion and many code browsing features.
// However, files listed here are ALL re-compiled if any one of them is updated between builds.
// Do not add files here that you will be updating frequently as this negates the performance advantage.
#ifndef PCH_H
#define PCH_H
// add headers that you want to pre-compile here
#include "BinaryTreeNode.h"
#include "CharFreq.h"
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#endif //PCH_H
Infix Notation to Postfix Notation and Postfix Evaluator Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
I translated a Pascal program that is found in “Applied Data Structures Using Pascal” by Guy J. Hale and Richard J. Easton. The original Pascal program only used single digits and four arithmetic operators: ‘*’, ‘/’, ‘+’, and ‘-‘. I extended the code to multiple digit positive integers and added an exponentiation operator ‘^’. The priority of the operators is ‘^’, ‘*’, and ‘/’ highest value and ‘+’ and ‘-‘ lowest priority. I could easily add a modulus operator ‘%’ and Boolean bit operators. Extension to negative integers should be a facile operation. Below is the output from my C++ application.
3 + 7 * 8 - 5 3 7 8 * + 5 - Positive integer value = 54 3 * 7 - 4 / 2 3 7 * 4 2 / - Positive integer value = 19 (3 + 7) * 8 - 5 3 7 + 8 * 5 - Positive integer value = 75 (3 + 4) * 8 - (7 * 3 - 4) 3 4 + 8 * 7 3 * 4 - - Positive integer value = 39 (100 + 50) * 20 - 100 / 2 100 50 + 20 * 100 2 / - Positive integer value = 2950 2 ^ 16 - 5 * 100 2 16 ^ 5 100 * - Positive integer value = 65036
#pragma once
#include <list>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const char Exp = '^';
const char Mul = '*';
const char Div = '/';
const char Add = '+';
const char Sub = '-';
const char LtParen = '(';
const char RtParen = ')';
class InfixToPostFix
{
public:
stack<char> numberStack;
int Convert(
string infixStr, string& postfixStr);
int EvaluatePostFix(string postfixStr);
int Priority(char opcode);
};
#include "pch.h"
#include "InfixToPostFix.h"
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int InfixToPostFix::Convert(
string infixStr, string& postfixStr)
{
char ch = 0;
int number = 0, opcode = 0, opcode1 = 0, parenLevel = 0;
string numberStr;
for (size_t i = 0; i < infixStr.size();)
{
//while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] == ' ')
//i++;
while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] >= '0' &&
infixStr[i] <= '9')
numberStr.push_back(infixStr[i++]);
if (numberStr.size() != 0)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < numberStr.size(); j++)
postfixStr.push_back(numberStr[j]);
postfixStr.push_back(' ');
numberStr.clear();
}
//while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] == ' ')
//i++;
if (infixStr[i] == '(')
{
numberStack.push(infixStr[i]);
parenLevel++;
}
//while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] == ' ')
//i++;
if (infixStr[i] == ')')
{
ch = numberStack.top();
numberStack.pop();
parenLevel--;
//while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] == ' ')
//i++;
while (ch != '(')
{
postfixStr.push_back(ch);
postfixStr.push_back(' ');
parenLevel++;
ch = numberStack.top();
numberStack.pop();
}
}
//while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] == ' ')
//i++;
if (infixStr[i] == '^' || infixStr[i] == '*' ||
infixStr[i] == '/' || infixStr[i] == '+' ||
infixStr[i] == '-')
{
if (numberStack.empty())
numberStack.push(infixStr[i]);
else
{
ch = numberStack.top();
numberStack.pop();
//while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] == ' ')
//i++;
while (Priority(ch) >= Priority(infixStr[i]) &&
!numberStack.empty() && ch != '(')
{
postfixStr.push_back(ch);
postfixStr.push_back(' ');
ch = numberStack.top();
numberStack.pop();
}
//while (i < infixStr.size() && infixStr[i] == ' ')
//i++;
if (ch != '(')
{
if (Priority(infixStr[i]) <= Priority(ch))
{
postfixStr.push_back(ch);
postfixStr.push_back(' ');
numberStack.push(infixStr[i]);
}
else
{
numberStack.push(ch);
numberStack.push(infixStr[i]);
}
}
else
{
numberStack.push(ch);
numberStack.push(infixStr[i]);
}
}
}
i++;
}
while (!numberStack.empty())
{
ch = numberStack.top();
numberStack.pop();
postfixStr.push_back(ch);
postfixStr.push_back(' ');
}
return 0;
}
int InfixToPostFix::EvaluatePostFix(string postfixStr)
{
char opcode = 0;
int charValue = 0, result = 0, value1 = 0, value2 = 0;
stack<int> intStack;
for (size_t i = 0; i < postfixStr.size();)
{
string numberStr;
if (postfixStr[i] != ' ')
{
while (postfixStr[i] >= '0' && postfixStr[i] <= '9')
numberStr.push_back(postfixStr[i++]);
if (!numberStr.empty())
intStack.push(atoi(numberStr.c_str()));
else
{
value2 = intStack.top();
intStack.pop();
value1 = intStack.top();
intStack.pop();
opcode = postfixStr[i++];
if (opcode == '^')
result = (int)pow(value1, value2);
else if (opcode == '*')
result = value1 * value2;
else if (opcode == '/')
result = value1 / value2;
else if (opcode == '+')
result = value1 + value2;
else if (opcode == '-')
result = value1 - value2;
intStack.push(result);
}
}
else
i++;
}
result = intStack.top();
intStack.pop();
return result;
}
int InfixToPostFix::Priority(char opcode)
{
int result = 0;
switch (opcode)
{
case Exp:
result = 2;
break;
case Mul:
result = 2;
break;
case Div:
result = 2;
break;
case Add:
result = 1;
break;
case Sub:
result = 1;
break;
case LtParen:
result = 0;
}
return result;
}
#include "pch.h"
#include "InfixToPostFix.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
fstream inps, outs;
char line[256];
inps.open("TestFile.txt", fstream::in);
outs.open("ResuFile.txt", fstream::out | fstream::ate);
while (!inps.eof())
{
string postfixStr;
inps.getline(line, 256);
if (strlen(line) == 0)
break;
string infixStr(line, strlen(line));
InfixToPostFix translate;
int con = translate.Convert(
infixStr, postfixStr);
if (con != 0)
{
cout << "Conversion error!" << endl;
cout << "Error code = " << con << endl;
}
else
{
char newline[] = { '\n' };
outs.write(infixStr.c_str(), infixStr.size());
outs.write(newline, 1);
outs.write(postfixStr.c_str(), postfixStr.size());
outs.write(newline, 1);
int val = translate.EvaluatePostFix(postfixStr);
if (val < 0)
{
cout << "Evaluation error!" << endl;
cout << "Error code = " << val << endl;
}
else
{
char buffer[256] = { '\0' };
string str = "Positive integer value = ";
_itoa_s(val, buffer, 10);
outs.write(str.c_str(), strlen(str.c_str()));
outs.write(buffer, strlen(buffer));
outs.write(newline, 1);
}
}
}
inps.close();
outs.close();
return 0;
}
Create an Index Using C++ and the Map Data Structure Designed and Implemented by James Pate Williams, Jr.
I recall that way back in the early to mid-1980s I had the pleasure of perusing a copy of the source code for a Pascal compiler. It was probably created directly under the inventor Nicklaus Wirth in Switzerland. I partially implemented a Pascal emulator for a Data General Eclipse minicomputer.
Here are some of the phases required for the creation of a Pascal computer program:
- Parse the source code.
- Create a symbol table.
- Interpret the symbols.
- Create P-Code for the interpreter.
Running the interpreter code involves translation of the P-Code to a computer readable bit string. Every computer scientist should at some time in her/his formal education should implement an assembler and a compiler.
Yesterday, April 11, 2023, I created a word index C++ application that takes a text file, parses the words, and creates an index also known as an English language symbol table. The app utilizes a C++ map that consists of integer keys and a node containing information about the words and their order in the text file. Below are the indexable text file and the symbol table (index).
This is a test of my index generator. The text file has
two lines. The second line is dummy definitions.
This is a test of my index generator. The text file has two lines. The second line is dummy definitions.
The first number is the line number and the second the position within a line. The 1 39 The 2 12 This 1 1 a 1 9 definitions 2 37 dummy 2 31 file 1 48 generator 1 28 has 1 53 index 1 22 is 2 28 is 1 6 line 2 23 lines 2 5 my 1 19 of 1 16 second 2 16 test 1 11 text 1 43 two 2 1