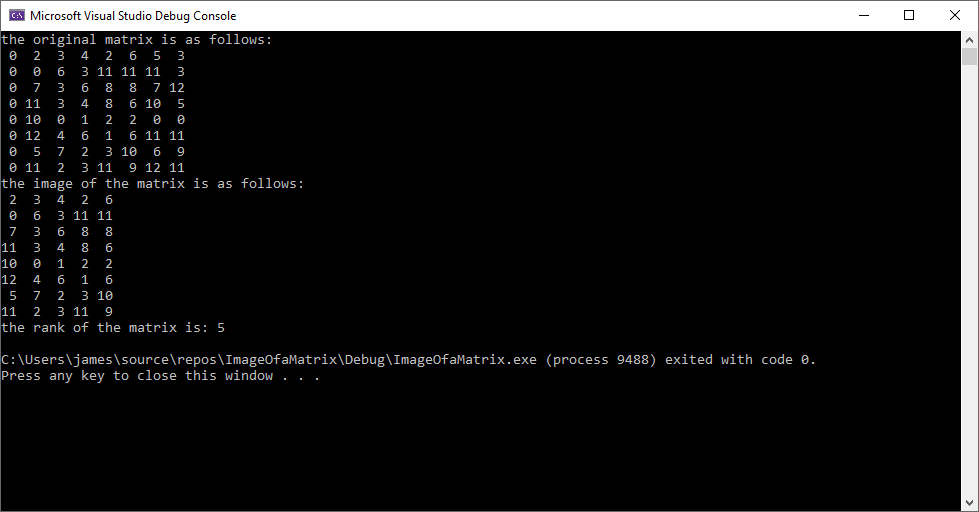
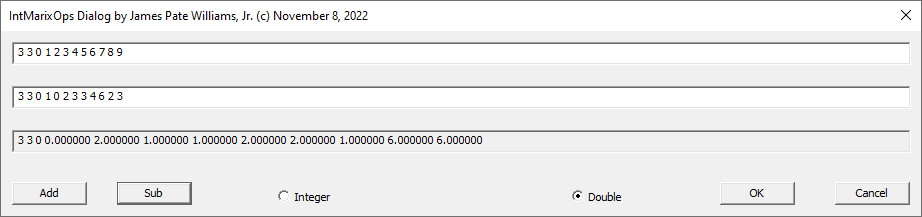
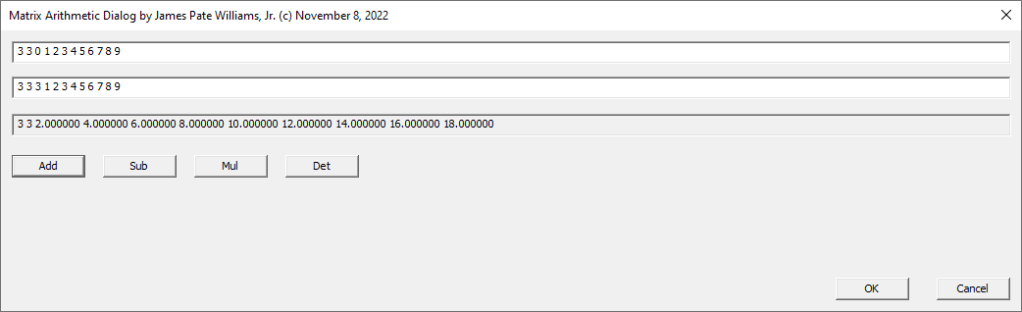
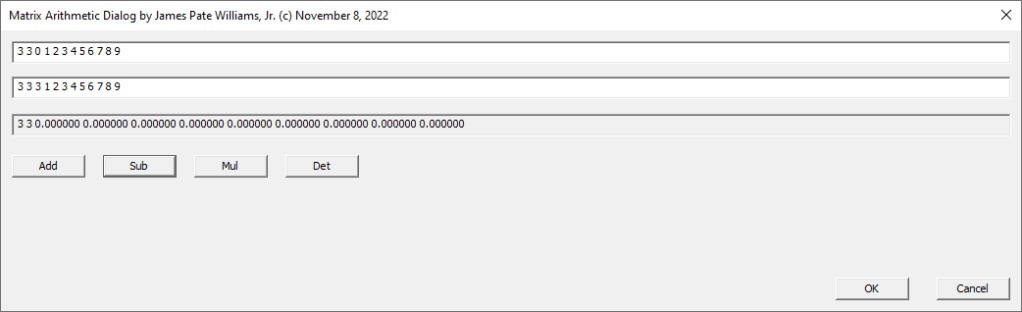
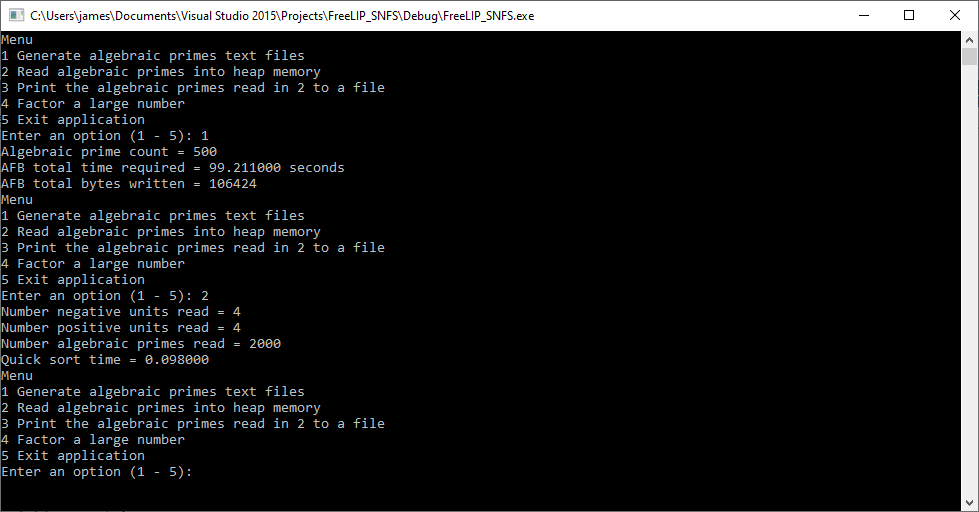
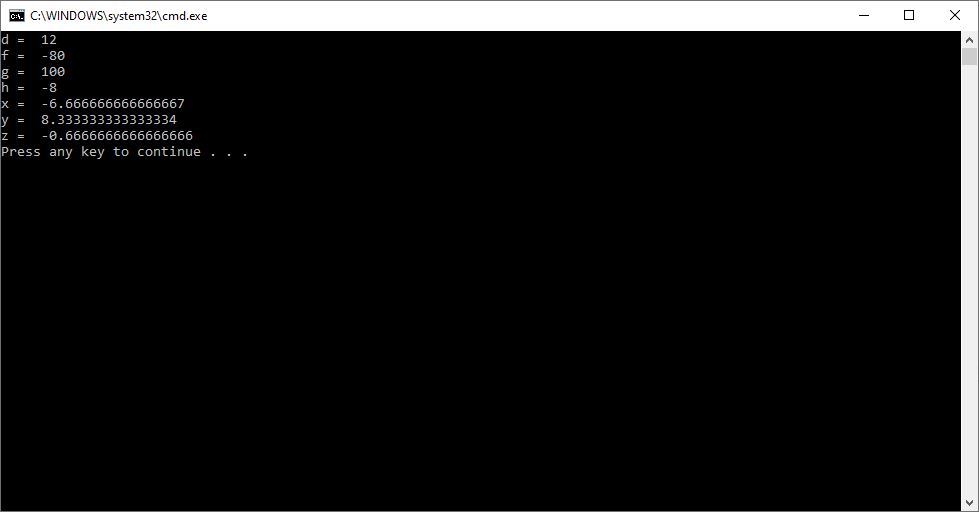
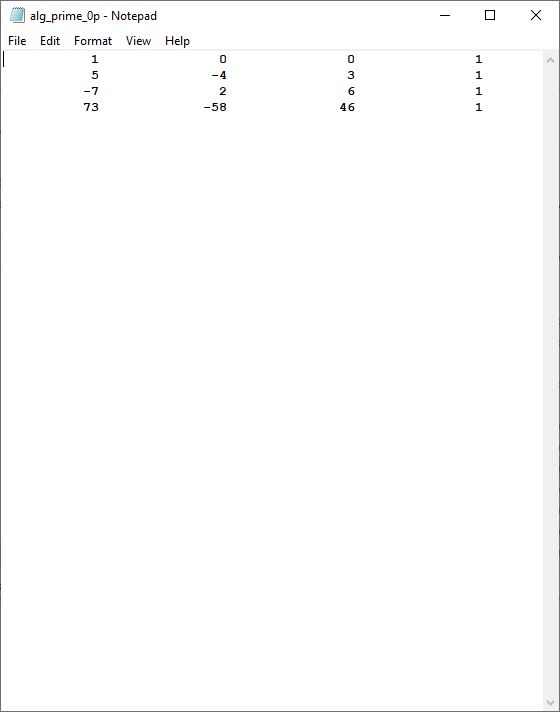Below are three screenshots of two methods of calculating the determinant of a matrix, namely the Bareiss Algorithm and Gaussian Elimination:




using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MatrixInverseComparison
{
public partial class MainForm : Form
{
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
static private string FormatNumber(double x)
{
string result = string.Empty;
if (x > 0)
result += x.ToString("F5").PadLeft(10);
else
result += x.ToString("F5").PadLeft(10);
return result;
}
private void MultiplyPrintMatricies(
double[,] A, double[,] B, int n)
{
double[,] I = new double[n, n];
textBox1.Text += "Matrix Product:\r\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
double sum = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
sum += A[i, k] * B[k, j];
I[i, j] = sum;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
textBox1.Text += FormatNumber(I[i, j]) + " ";
}
textBox1.Text += "\r\n";
}
}
private void PrintMatrix(string title, double[,] A, int n)
{
textBox1.Text += title + "\r\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
textBox1.Text += FormatNumber(A[i, j]) + " ";
}
textBox1.Text += "\r\n";
}
}
private void Compute(double[,] MI, int n)
{
double determinantGE = 1;
double[] b = new double[n];
double[] x = new double[n];
double[,] MB1 = new double[n, n];
double[,] MB2 = new double[n, n];
double[,] MG = new double[n, n];
double[,] MS = new double[n, n];
double[,] IG = new double[n, n];
double[,] IS = new double[n, n];
int[] pivot = new int[n];
Stopwatch sw = new();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
MB1[i, j] = MB2[i, j] = MG[i, j] = MS[i, j] = MI[i, j];
}
PrintMatrix("Initial Matrix: ", MI, n);
sw.Start();
int flag = DirectMethods.Factor(MG, n, pivot);
if (flag != 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
determinantGE *= MG[i, i];
determinantGE *= flag;
}
sw.Stop();
PrintMatrix("Gaussian Elimination Final:", MG, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
b[i] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
b[j] = 1.0;
DirectMethods.Substitute(MG, b, x, n, pivot);
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
IG[k, j] = x[k];
b[j] = 0.0;
}
}
PrintMatrix("Gaussian Elimination Inverse:", IG, n);
textBox1.Text += "Determinant: " +
FormatNumber(determinantGE) + "\r\n";
MultiplyPrintMatricies(IG, MI, n);
textBox1.Text += "Runtime (MS) = " +
sw.ElapsedMilliseconds + "\r\n";
sw.Start();
double determinant1 = BareissAlgorithm.Determinant1(MB1, n);
sw.Stop();
PrintMatrix("Bareiss Algorithm Final 1:", MB1, n);
textBox1.Text += "Determinant: " +
FormatNumber(determinant1) + "\r\n";
textBox1.Text += "Runtime (MS) = " +
sw.ElapsedMilliseconds + "\r\n";
sw.Start();
double determinant2 = BareissAlgorithm.Determinant2(MB2, n);
sw.Stop();
PrintMatrix("Bareiss Algorithm Final 2:", MB2, n);
textBox1.Text += "Determinant: " +
FormatNumber(determinant2) + "\r\n";
textBox1.Text += "Runtime (MS) = " +
sw.ElapsedMilliseconds + "\r\n";
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int n = (int)numericUpDown1.Value;
int seed = (int)numericUpDown2.Value;
double[,] A = new double[n, n];
Random random = new Random(seed);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
double q = n * random.NextDouble();
while (q == 0.0)
q = n * random.NextDouble();
A[i, j] = q;
}
}
Compute(A, n);
}
private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = string.Empty;
}
}
}
using System;
namespace MatrixInverseComparison
{
public class DirectMethods
{
// Substitute and Factor translated from FORTRAN 77
// source code found in "Elementary Numerical Analysis:
// An Algorithmic Approach" by S. D. Conte and Carl de
// Boor. Translator: James Pate Williams, Jr. (c)
// August 14 - 17, 2023
static public void Substitute(
double[,] w,
double[] b,
double[] x,
int n,
int[] pivot)
{
double sum;
int i, j, n1 = n - 1;
if (n == 1)
{
x[0] = b[0] / w[0, 0];
return;
}
// forward substitution
x[0] = b[pivot[0]];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0, sum = 0.0; j < i; j++)
sum += w[i, j] * x[j];
x[i] = b[pivot[i]] - sum;
}
// backward substitution
x[n1] /= w[n1, n1];
for (i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
for (j = i + 1, sum = 0.0; j < n; j++)
sum += w[i, j] * x[j];
x[i] = (x[i] - sum) / w[i, i];
}
}
// Factor returns +1 if an even number of exchanges
// Factor returns -1 if an odd number of exchanges
// Factor retrurn 0 if matrix is singular
static public int Factor(
double[,] w, int n, int[] pivot)
// returns 0 if matrix is singular
{
double awikod, col_max, ratio, row_max, temp;
double[] d = new double[n];
int flag = 1, i, i_star, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
pivot[i] = i;
row_max = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
row_max = Math.Max(row_max, Math.Abs(w[i, j]));
if (row_max == 0)
{
flag = 0;
row_max = 1;
}
d[i] = row_max;
}
if (n <= 1)
return flag;
// factorization
for (k = 0; k < n - 1; k++)
{
// determine pivot row the row i_star
col_max = Math.Abs(w[k, k]) / d[k];
i_star = k;
for (i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
{
awikod = Math.Abs(w[i, k]) / d[i];
if (awikod > col_max)
{
col_max = awikod;
i_star = i;
}
}
if (col_max == 0)
flag = 0;
else
{
if (i_star > k)
{
// make k the pivot row by
// interchanging with i_star
flag *= -1;
i = pivot[i_star];
pivot[i_star] = pivot[k];
pivot[k] = i;
temp = d[i_star];
d[i_star] = d[k];
d[k] = temp;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
temp = w[i_star, j];
w[i_star, j] = w[k, j];
w[k, j] = temp;
}
}
// eliminate x[k]
for (i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
{
w[i, k] /= w[k, k];
ratio = w[i, k];
for (j = k + 1; j < n; j++)
w[i, j] -= ratio * w[k, j];
}
}
}
if (w[n - 1, n - 1] == 0)
flag = 0;
return flag;
}
}
}
namespace MatrixInverseComparison
{
// One implementation is based on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bareiss_algorithm
// Another perhaps better implementation is found on the following webpage
// https://cs.stackexchange.com/questions/124759/determinant-calculation-bareiss-vs-gauss-algorithm
class BareissAlgorithm
{
static public double Determinant1(double[,] M, int n)
{
double M00;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
{
if (k - 1 == -1)
M00 = 1;
else
M00 = M[k - 1, k - 1];
for (int i = k + 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = k + 1; j < n; j++)
{
M[i, j] = (
M[i, j] * M[k, k] -
M[i, k] * M[k, j]) / M00;
}
}
}
return M[n - 1, n - 1];
}
static public double Determinant2(double[,] A, int dim)
{
if (dim <= 0)
{
return 0;
}
double sign = 1;
for (int k = 0; k < dim - 1; k++)
{
//Pivot - row swap needed
if (A[k, k] == 0)
{
int m;
for (m = k + 1; m < dim; m++)
{
if (A[m, k] != 0)
{
double[] tempRow = new double[dim];
for (int i = 0; i < dim; i++)
tempRow[i] = A[m, i];
for (int i = 0; i < dim; i++)
A[m, i] = A[k, i];
for (int i = 0; i < dim; i++)
A[k, i] = tempRow[i];
sign = -sign;
break;
}
}
//No entries != 0 found in column k -> det = 0
if (m == dim)
{
return 0;
}
}
//Apply formula
for (int i = k + 1; i < dim; i++)
{
for (int j = k + 1; j < dim; j++)
{
A[i, j] = A[k, k] * A[i, j] - A[i, k] * A[k, j];
if (k >= 1)
{
A[i, j] /= A[k - 1, k - 1];
}
}
}
}
return sign * A[dim - 1, dim - 1];
}
}
}