I originally implemented this algorithm in FORTRAN IV in the Summer Quarter of 1982 at the Georgia Institute of Technology. I was taking a course named “Scientific Computing I” taught by Professor Gunter Meyer. I made a B in the class. Later in 2015 I re-implemented the recipe in C# using Visual Studio 2008 Professional. VS 2015 did not have support for complex numbers nor large integers. In December of 2015 I upgraded to Visual Studio 2015 Professional which has support for big integers and complex numbers. I used Visual Studio 2019 Community version for this project. Root below should be function.
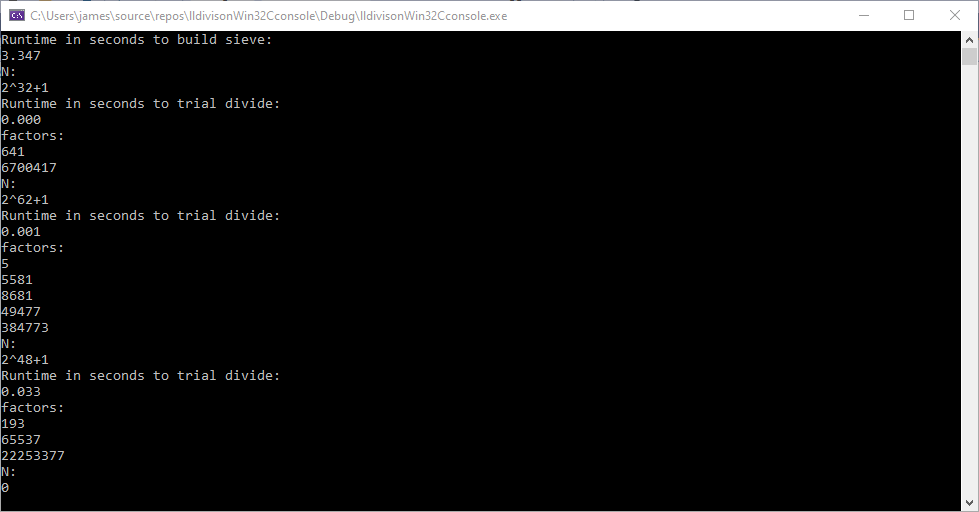
Degree (0 to quit) = 2
coefficient[2].real = 1
coefficient[2].imag = 0
coefficient[1].real = 1
coefficient[1].imag = 0
coefficient[0].real = 1
coefficient[0].imag = 0
zero[0].real = -5.0000000000e-01 zero[0].imag = 8.6602540378e-01
zero[1].real = -5.0000000000e-01 zero[1].imag = -8.6602540378e-01
root[0].real = 0.0000000000e+00 root[0].imag = -2.2204460493e-16
root[1].real = 3.3306690739e-16 root[1].imag = -7.7715611724e-16
Degree (0 to quit) = 3
coefficient[3].real = 1
coefficient[3].imag = 0
coefficient[2].real = 0
coefficient[2].imag = 0
coefficient[1].real = -18.1
coefficient[1].imag = 0
coefficient[0].real = -34.8
coefficient[0].imag = 0
zero[0].real = -2.5026325486e+00 zero[0].imag = -8.3036679880e-01
zero[1].real = -2.5026325486e+00 zero[1].imag = 8.3036679880e-01
zero[2].real = 5.0052650973e+00 zero[2].imag = 2.7417672687e-15
root[0].real = 0.0000000000e+00 root[0].imag = 1.7763568394e-15
root[1].real = 3.5527136788e-14 root[1].imag = -1.7763568394e-14
root[2].real = 2.8421709430e-14 root[2].imag = 1.5643985575e-13
Degree (0 to quit) = 5
coefficient[5].real = 1
coefficient[5].imag = 0
coefficient[4].real = 2
coefficient[4].imag = 0
coefficient[3].real = 3
coefficient[3].imag = 0
coefficient[2].real = 4
coefficient[2].imag = 0
coefficient[1].real = 5
coefficient[1].imag = 0
coefficient[0].real = 6
coefficient[0].imag = 0
zero[0].real = -8.0578646939e-01 zero[0].imag = 1.2229047134e+00
zero[1].real = -8.0578646939e-01 zero[1].imag = -1.2229047134e+00
zero[2].real = 5.5168546346e-01 zero[2].imag = 1.2533488603e+00
zero[3].real = 5.5168546346e-01 zero[3].imag = -1.2533488603e+00
zero[4].real = -1.4917979881e+00 zero[4].imag = 1.8329656063e-15
root[0].real = 8.8817841970e-16 root[0].imag = 4.4408920985e-16
root[1].real = -2.6645352591e-15 root[1].imag = -4.4408920985e-16
root[2].real = 8.8817841970e-16 root[2].imag = 1.7763568394e-15
root[3].real = 3.4638958368e-14 root[3].imag = -1.4210854715e-14
root[4].real = 8.8817841970e-16 root[4].imag = 2.0710031449e-14