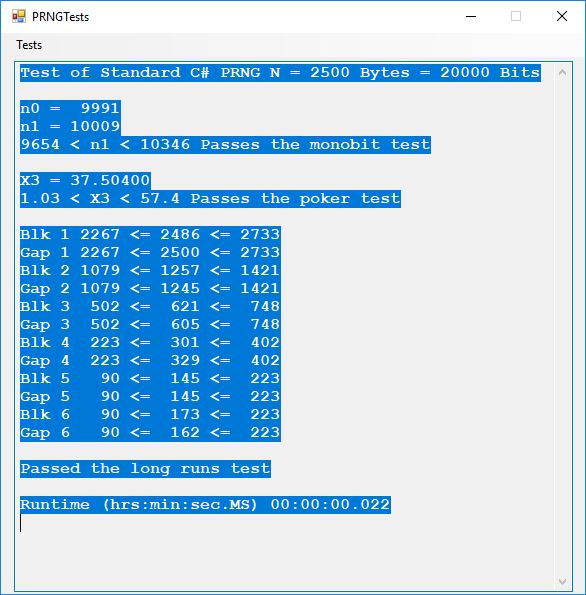
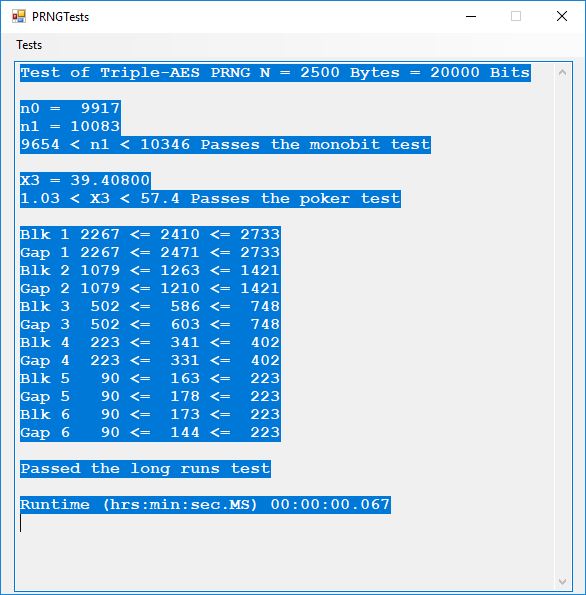
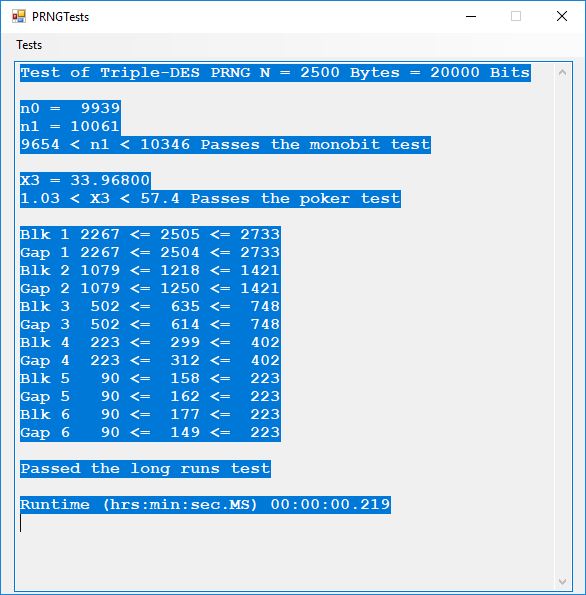
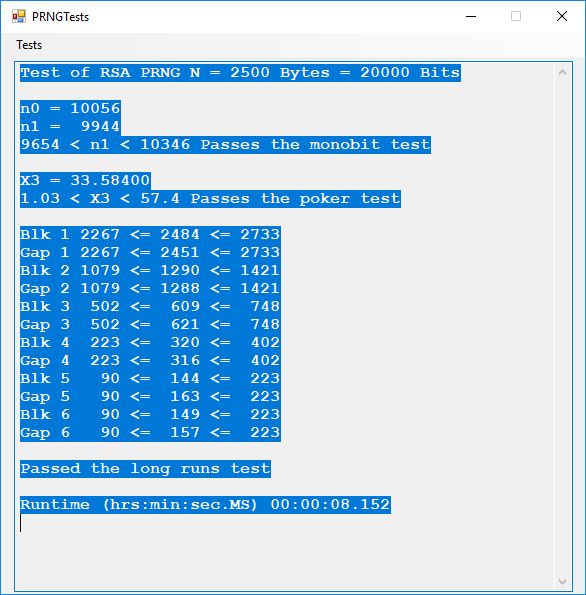
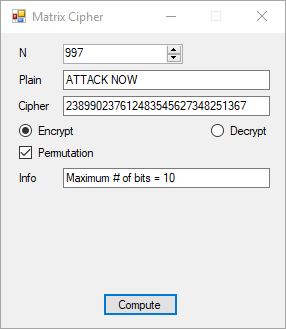
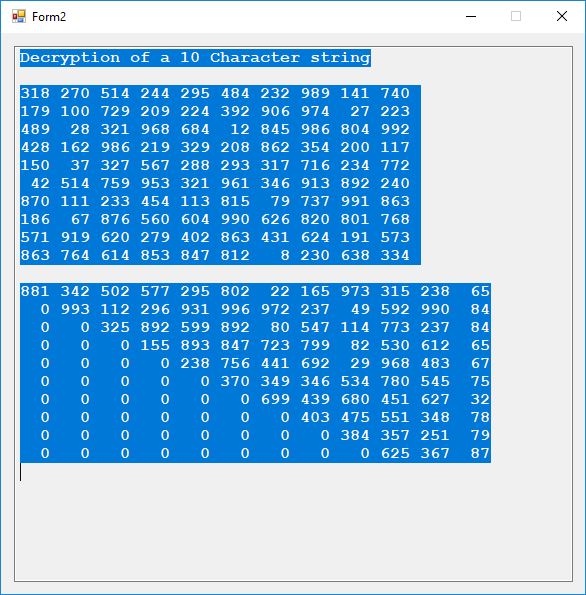
The five pseudorandom number generators are:
- Triple-AES based ANSI X9.17 PRNG
- Triple-DES based ANSI x9.17 PRNG
- RSA based PRNG
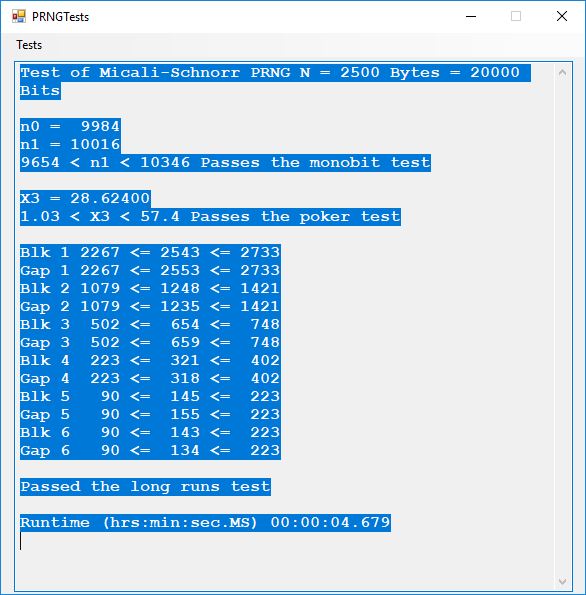
- Micali-Schnorr PRNG
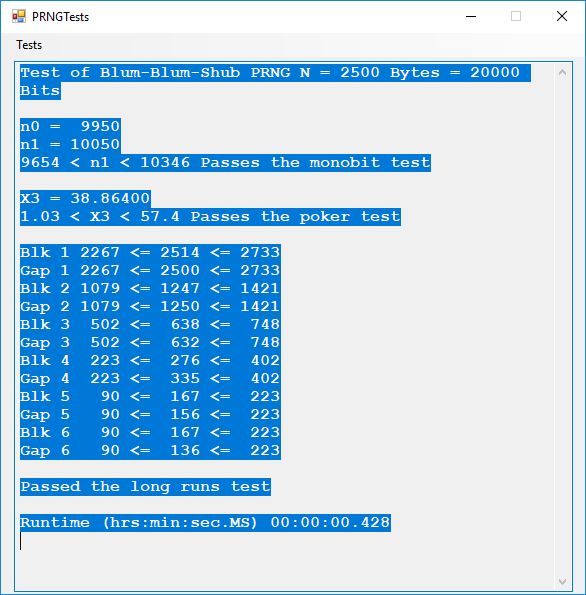
- Blum-Blum-Shub PRNG
Five stream ciphers were created using 1 to 5. Screenshots of the C# application follow:

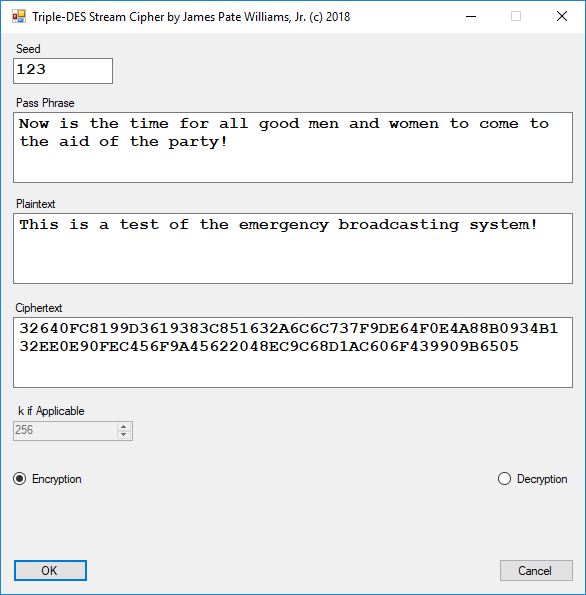
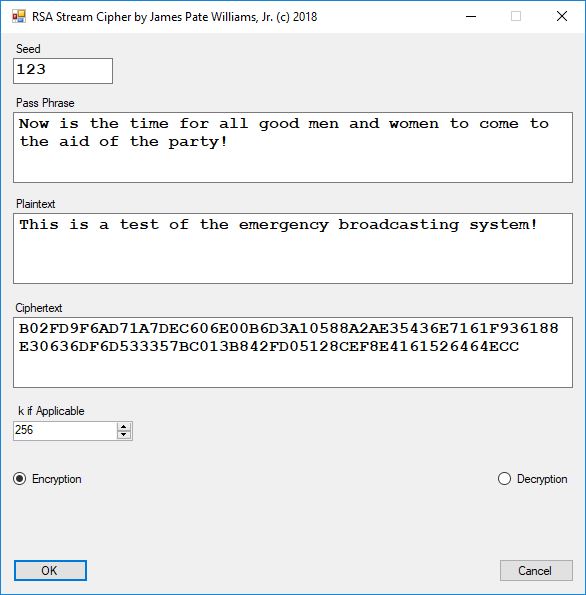

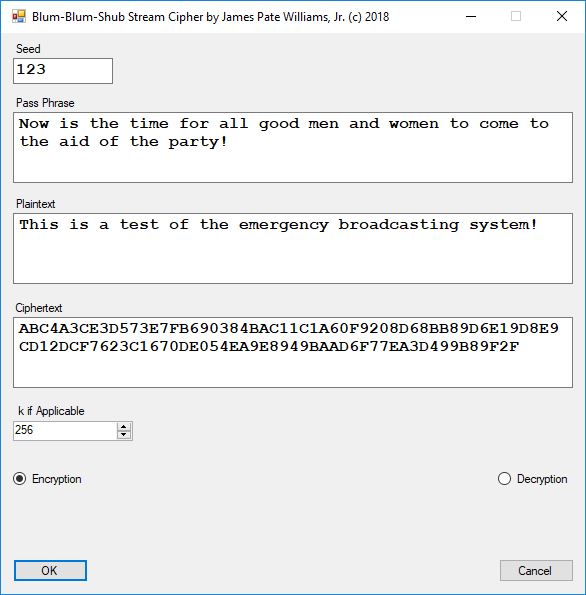
The pass phrase optimally should consist of 147 ASCII characters. If the number of pass phrase ASCII characters is less than 147 then more random ASCII characters are added using the standard C# pseudorandom number generator seeded with the parameter named Seed. The user defined parameter k is used by RSA, Micali-Schnorr, and Blum-Blum-Shub pseudorandom number generators. It is the approximate bit length of the large composite number composed of two large probable prime numbers. The real key lengths of all the stream ciphers is about 1024-bits for 1, 3, 4, and 5 and 296-bits for 2. I’d strongly suggest using 1 and/or 5.