Chapter 8 of the Handbook is devoted to the public key encryption systems available in the late 1990s. The most interesting algorithms in my humble opinion are:
- RSA (Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman) Public Key Algorithm
- Rabin Public Key Encryption Public Key Algorithm
- Generalized ElGamal Public Key Encryption Algorithm
My original C implementations that were created in the period 1996 to 1998 utilized the Free LIP (Free Large Integer Package) which was designed and implemented by Arjen K. Lenstra. Later, this particular Professor Lenstra helped in the development of the General and Special Number Field Sieve. He is also of factoring large integers fame. I used the C# language again in my testing implementations.
First we display the RSA results using an artificially small bit size of 256 bits.
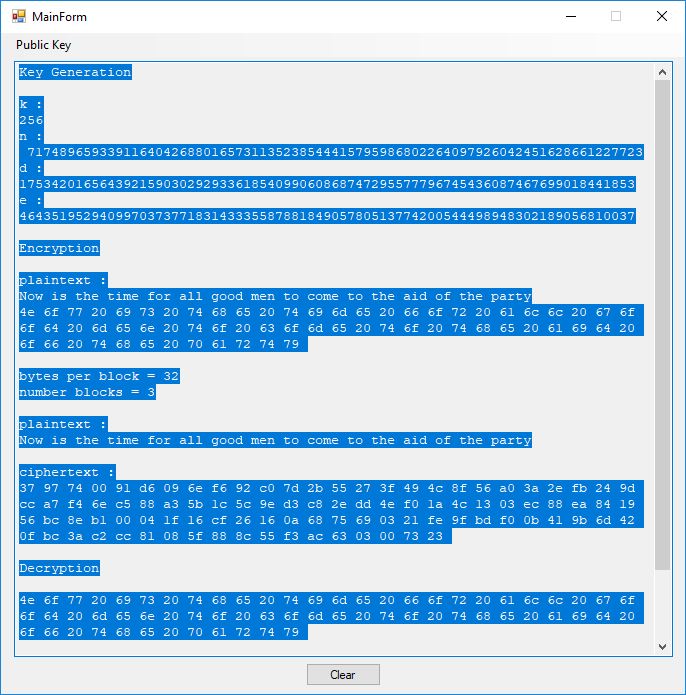
Key Generation k : 256 n : 71748965933911640426880165731135238544415795986802264097926042451628661227723 d : 17534201656439215903029293361854099060868747295577796745436087467699018441853 e : 46435195294099703737718314333558788184905780513774200544498948302189056810037 Encryption plaintext : Now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of the party 4e 6f 77 20 69 73 20 74 68 65 20 74 69 6d 65 20 66 6f 72 20 61 6c 6c 20 67 6f 6f 64 20 6d 65 6e 20 74 6f 20 63 6f 6d 65 20 74 6f 20 74 68 65 20 61 69 64 20 6f 66 20 74 68 65 20 70 61 72 74 79 bytes per block = 32 number blocks = 3 plaintext : Now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of the party ciphertext : 37 97 74 00 91 d6 09 6e f6 92 c0 7d 2b 55 27 3f 49 4c 8f 56 a0 3a 2e fb 24 9d cc a7 f4 6e c5 88 a3 5b 1c 5c 9e d3 c8 2e dd 4e f0 1a 4c 13 03 ec 88 ea 84 19 56 bc 8e b1 00 04 1f 16 cf 26 16 0a 68 75 69 03 21 fe 9f bd f0 0b 41 9b 6d 42 0f bc 3a c2 cc 81 08 5f 88 8c 55 f3 ac 63 03 00 73 23 Decryption 4e 6f 77 20 69 73 20 74 68 65 20 74 69 6d 65 20 66 6f 72 20 61 6c 6c 20 67 6f 6f 64 20 6d 65 6e 20 74 6f 20 63 6f 6d 65 20 74 6f 20 74 68 65 20 61 69 64 20 6f 66 20 74 68 65 20 70 61 72 74 79 plaintext : Now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of the party
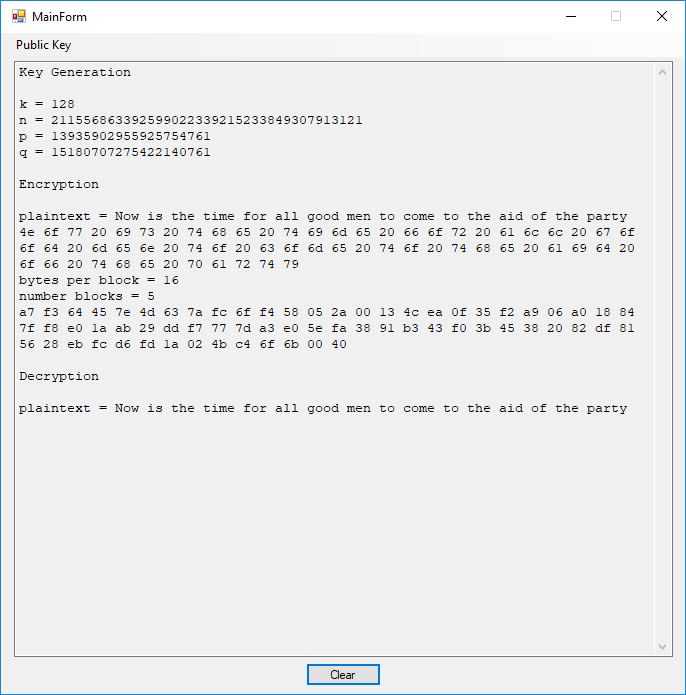
Next we illustrate the Rabin public key cryptosystem using a 12-bit key.
Key Generation k = 128 n = 211556863392599022339215233849307913121 p = 13935902955925754761 q = 15180707275422140761 Encryption plaintext = Now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of the party 4e 6f 77 20 69 73 20 74 68 65 20 74 69 6d 65 20 66 6f 72 20 61 6c 6c 20 67 6f 6f 64 20 6d 65 6e 20 74 6f 20 63 6f 6d 65 20 74 6f 20 74 68 65 20 61 69 64 20 6f 66 20 74 68 65 20 70 61 72 74 79 bytes per block = 16 number blocks = 5 a7 f3 64 45 7e 4d 63 7a fc 6f f4 58 05 2a 00 13 4c ea 0f 35 f2 a9 06 a0 18 84 7f f8 e0 1a ab 29 dd f7 77 7d a3 e0 5e fa 38 91 b3 43 f0 3b 45 38 20 82 df 81 56 28 eb fc d6 fd 1a 02 4b c4 6f 6b 00 40 Decryption plaintext = Now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of the party
Now we move onto the generalized ElGamal public key cryptosystem.
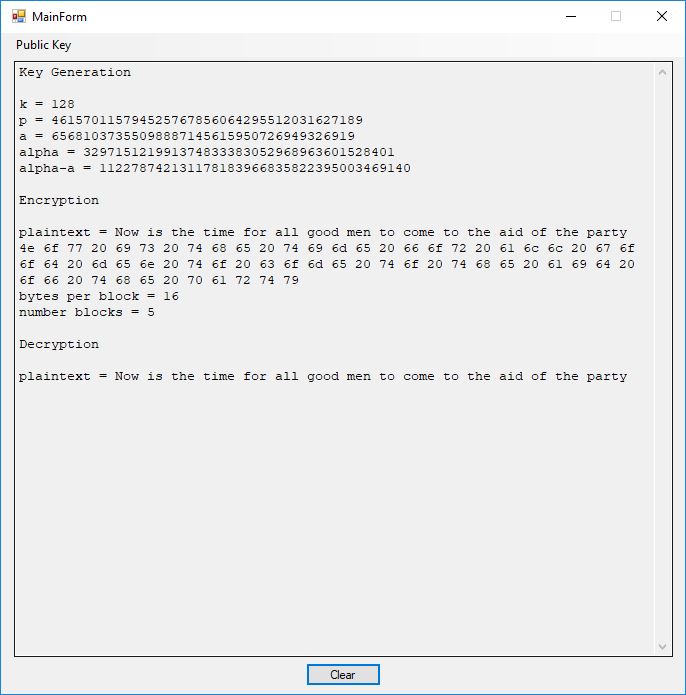
Key Generation k = 128 p = 461570115794525767856064295512031627189 a = 65681037355098887145615950726949326919 alpha = 329715121991374833383052968963601528401 alpha-a = 112278742131178183966835822395003469140 Encryption plaintext = Now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of the party 4e 6f 77 20 69 73 20 74 68 65 20 74 69 6d 65 20 66 6f 72 20 61 6c 6c 20 67 6f 6f 64 20 6d 65 6e 20 74 6f 20 63 6f 6d 65 20 74 6f 20 74 68 65 20 61 69 64 20 6f 66 20 74 68 65 20 70 61 72 74 79 bytes per block = 16 number blocks = 5 Decryption plaintext = Now is the time for all good men to come to the aid of the party