Suppose you have a n vector of ASCII encoded characters, arbitrarily choose 1 <= n <= 1000. Choose a modulus N such that 128 <= N <= 1000. Also choose a pseudo-random number seed 1 <= s <= 2147483647. Next find a random n x n matrix that is invertible by Gaussian elimination over the integer field consisting of N elements. Suppose this matrix is M and its tridiagonal form is M’. Now suppose the plaintext is the n vector P and the ciphertext is the n vector C then we have for encryption:
C = M’P
Further assume the inverse of M’ is N’. For decryption we use the equation:
P = N’C
Where
M’N’ = N’M’ = I
Such that I is the n x n identity matrix.
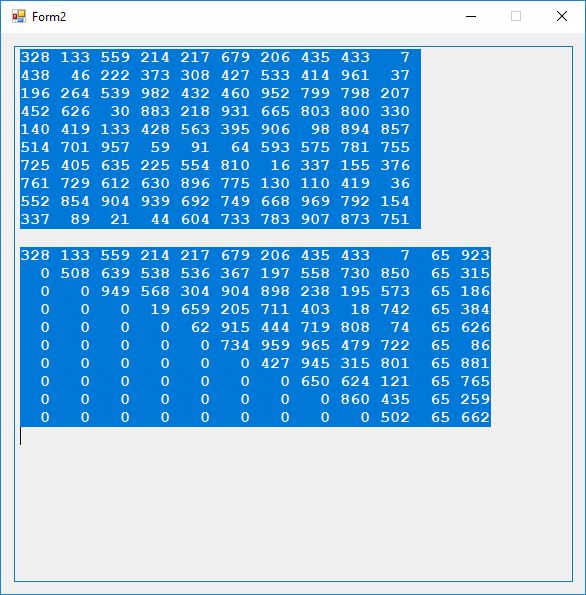
This cipher is related to the classic Hill Cipher. This cipher is polyalphabetic. We show the results of one encryption and decryption using 10 ASCII ‘A’ characters, N = 999, and s = 1. As you can see each occurrence of the letter ‘A’ which is encoded as the decimal number 65 leads to different integer in the range 0 to 998 which has a maximum of 10 bits. The key consists of the 100 integers in the original 10 x 10 matrix. The application was implemented in C# using a Gaussian elimination over a number field algorithm from Henri Cohen’s A Course in Computational Algebraic Number Theory.