Category: Astrophysics
Persides Solution of a Well-Known Space-Time Metric and the Legendre Functions (Polynomials) of the First and Second Kind
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0022247X73902771
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laplace%27s_equation
https://math.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Differential_Equations/A_First_Course_in_Differential_Equations_for_Scientists_and_Engineers_(Herman)/04%3A_Series_Solutions/4.05%3A_Legendre_Polynomials#:~:text=Solutions%20to%20this%20equation%2C%20Pm%20n%28x%29%20and%20Qm,Legendre%20functions%20of%20the%20first%20and%20second%20kind
Planetary Precession by James Pate Williams, Jr.
There are three classic theoretical tests of Albert Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity: the perihelion precession of Mercury, the other Solar System planets, and the planetoid Pluto, the bending of light by massive bodies, and the gravitational red shift. I recently wrote a C# program for displaying the exaggerated Rosette motion of theoretical planets (Schwarzschild’s solution to Einstein’s general relativity field equation that admit the existence of black holes). I also wrote a C++ program to calculate planetary precession values that agree with experimental results.
Precession.cpp (c) James Pate Williams, Jr. August 2022
This program calculates the planetary precessions of the planets in our solar system. Some of the equations and data are from “General Relativity” by Hans Stephani 1982 page 103 and the following websites. Also, two calculations of the mass of the Sun are exhibited, along with my weight on different planets:
https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/factsheet/
https://farside.ph.utexas.edu/teaching/celestial/Celestialhtml/node44.html
https://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/features/yba/CygX1_mass/gravity/sun_mass.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surface_gravity
https://www.schoolsobservatory.org/discover/quick/weight/https://physicscalc.com/physics/escape-velocity-calculator/#:~:text=Steps%20to%20Find%20Escape%20Velocity%201%20Obtain%20the,the%20double%20the%20result%20is%20the%20escape%20velocity

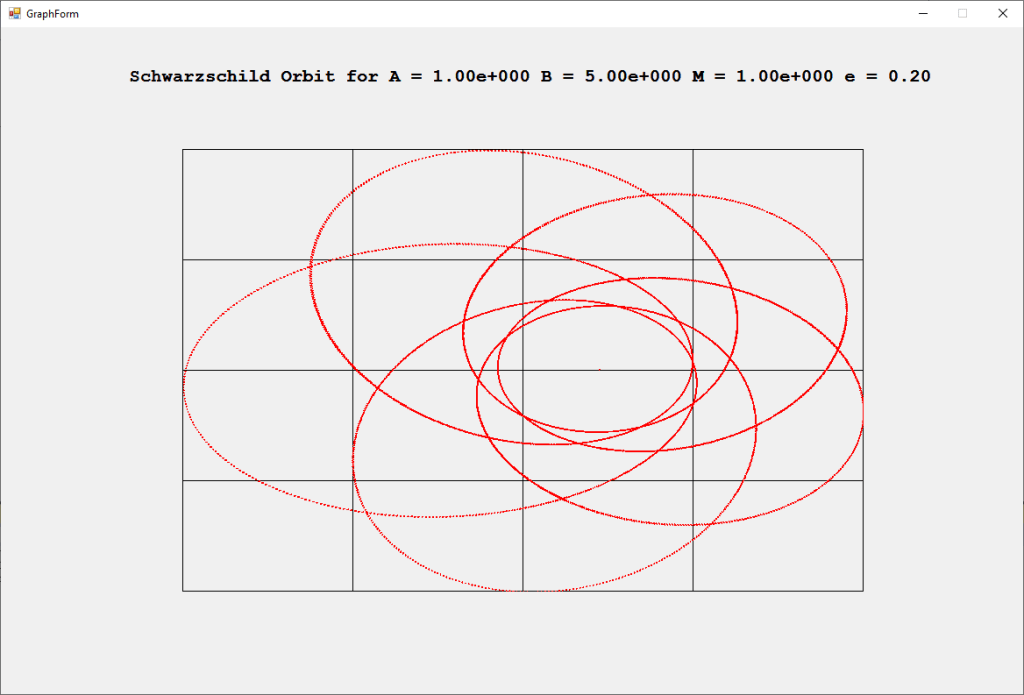
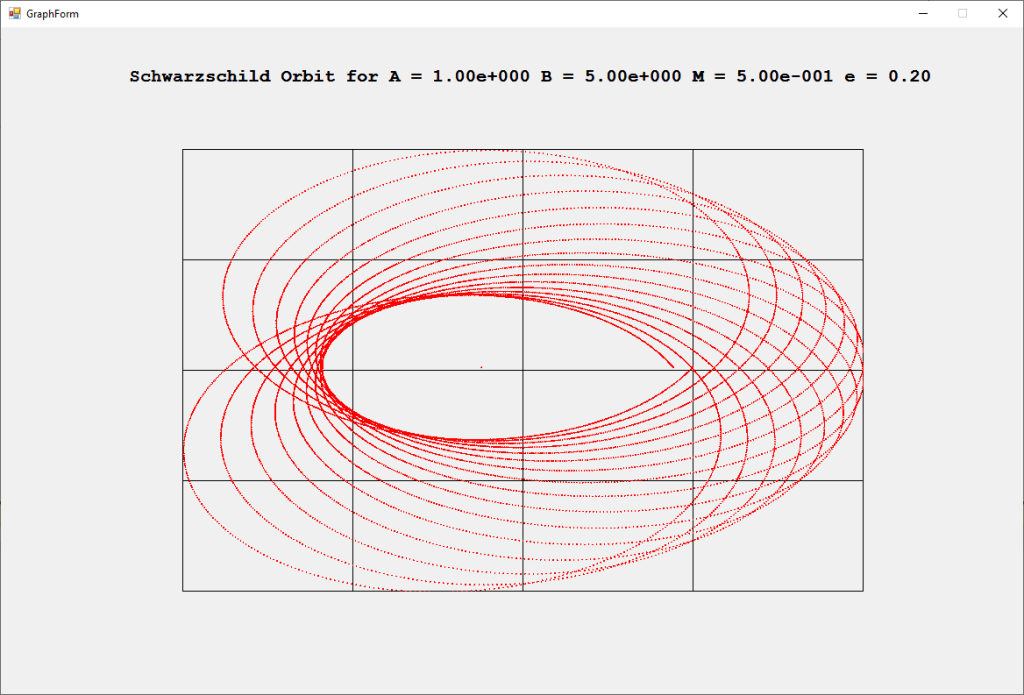





Schwarzschild Orbit by James Pate Williams, Jr.
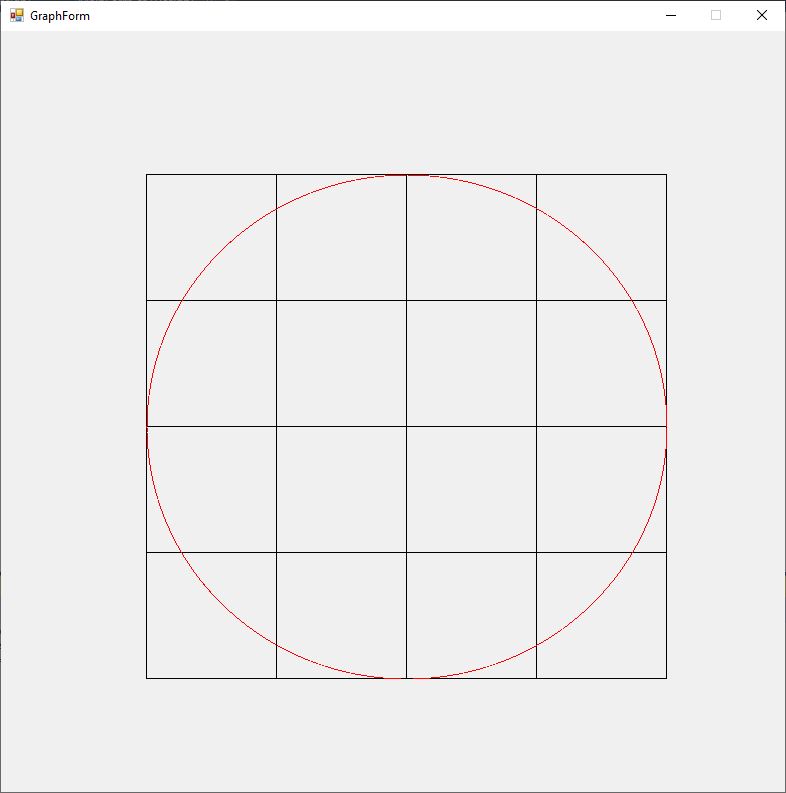
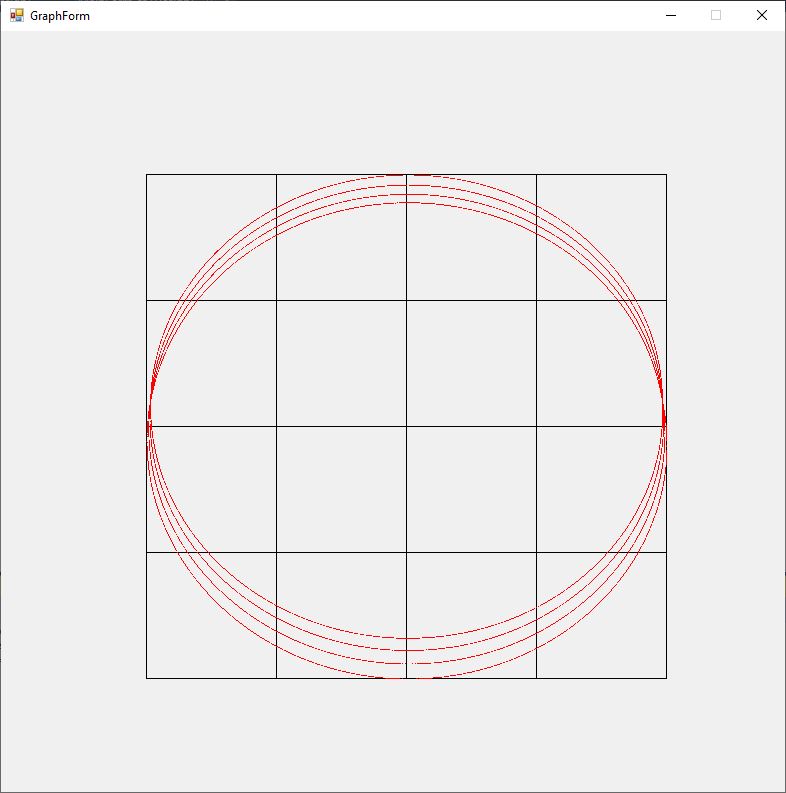
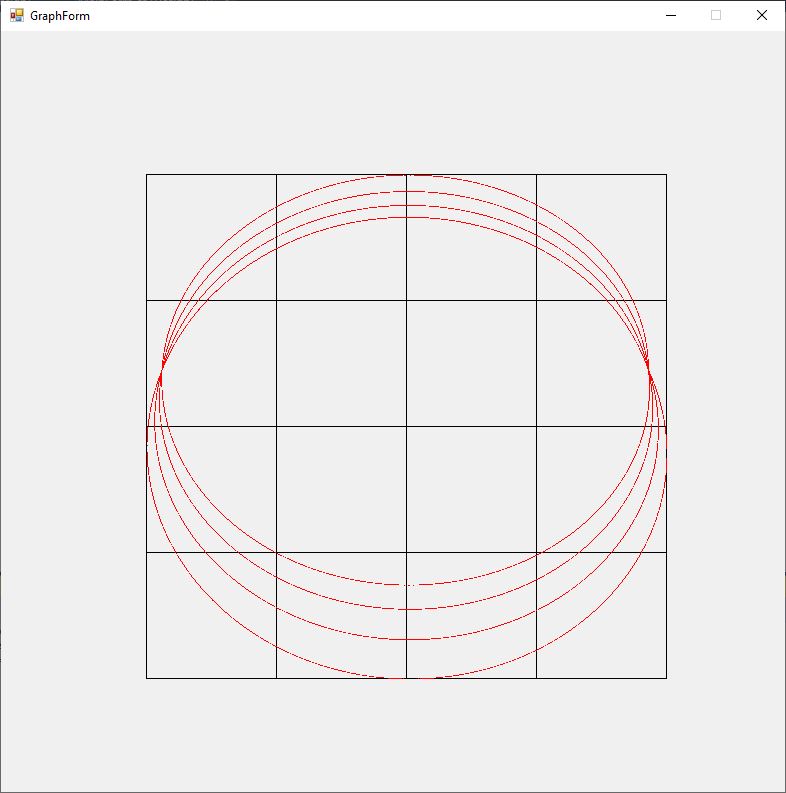
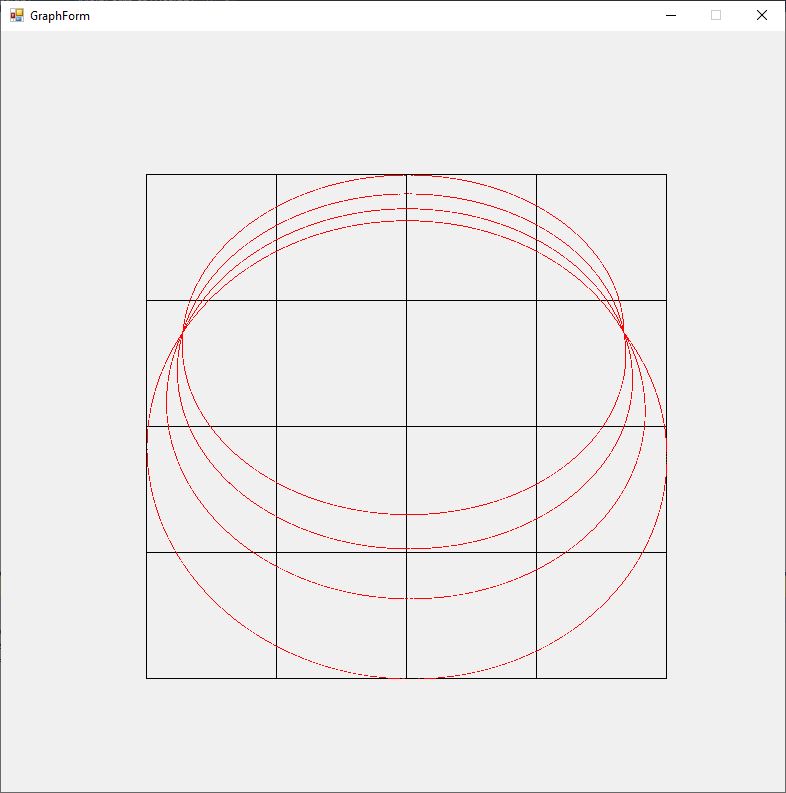
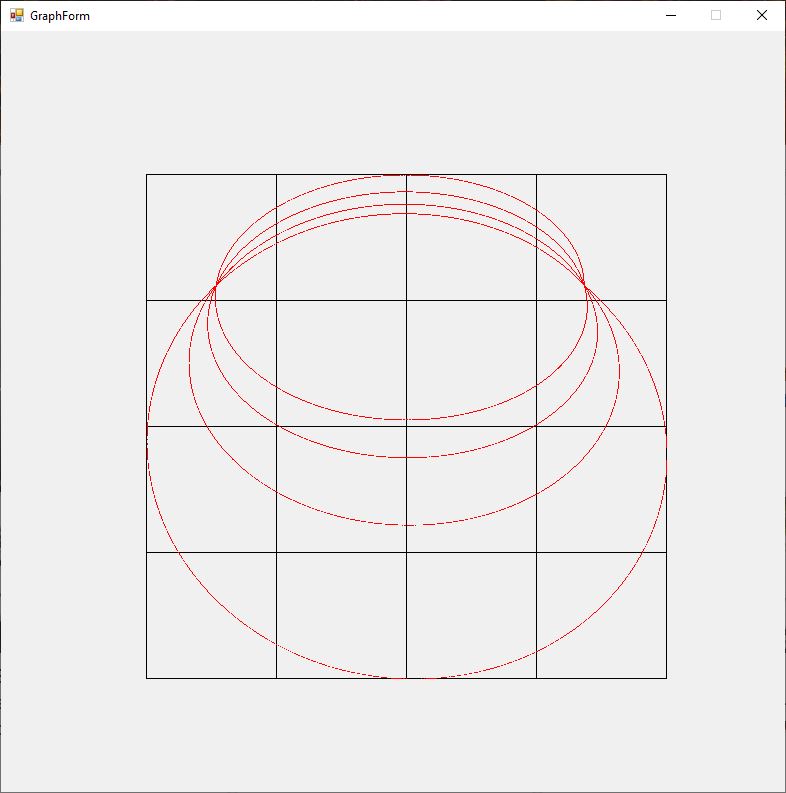
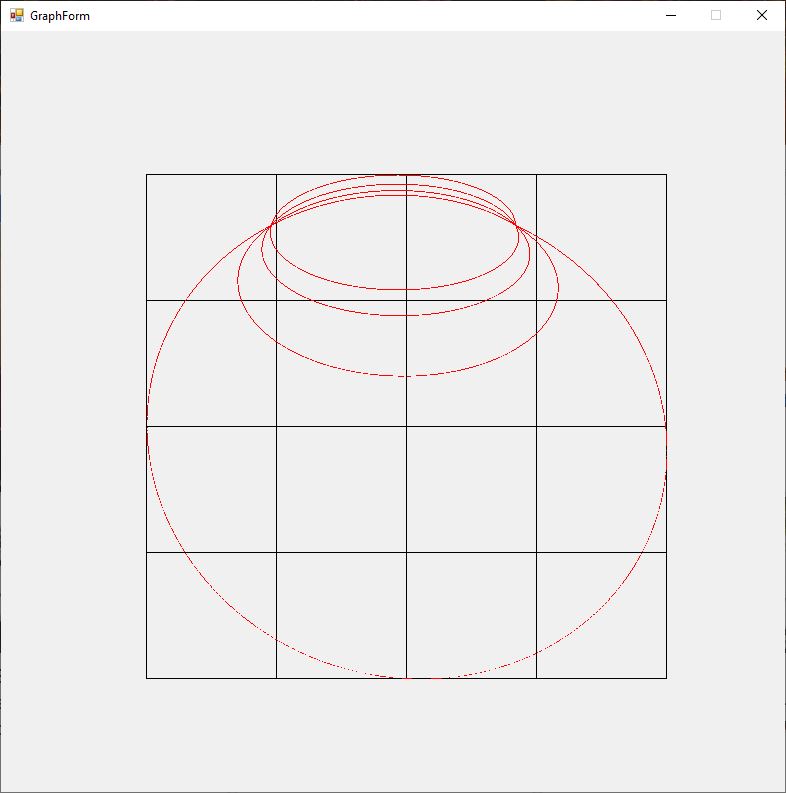
The Rosette motion of the perihelion precession of a massive object orbiting a black hole (Schwarzschild solution Einstein’s general relativity field equations is illustrated by the graphs below for varying values of eccentricity of the ellipsoidal orbit 0.00, 0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04, and 0.05. The angular momentum constant is B = 1, and the mass is M = 10.
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace SchwarzschildOrbit
{
public partial class GraphForm : Form
{
private double B, B2, B4, M, M2, M3, epsilon;
public GraphForm(double B, double M, double epsilon)
{
InitializeComponent();
this.B = B;
this.M = M;
this.epsilon = epsilon;
B2 = B * B;
B4 = B2 * B2;
M2 = M * M;
M3 = M * M2;
panel1.Paint += Panel1_Paint;
}
private double u0(double phi)
{
return M * (1.0 + epsilon * Math.Cos(phi)) / B2;
}
private double u1(double phi)
{
return u0(phi) + 3.0 * M3 * (1.0 + epsilon * phi * Math.Sin(phi)
+ epsilon * epsilon * (0.5 - Math.Cos(2.0 * phi) / 6.0)) / B4;
}
private double X(double r, double phi)
{
return r * Math.Cos(phi);
}
private double Y(double r, double phi)
{
return r * Math.Sin(phi);
}
private void Maximums(out double maxR, out double maxPhi,
out double XMax, out double XMin, out double YMax, out double YMin)
{
double phi = 0.0, r = 0.0, XC = 0.0, YC = 0.0;
maxPhi = 0.0;
maxR = double.MinValue;
XMax = double.MinValue;
YMax = double.MinValue;
XMin = double.MaxValue;
YMin = double.MaxValue;
while (phi <= 8.0 * Math.PI)
{
r = 1.0 / u1(phi);
if (r > maxR)
{
maxR = r;
maxPhi = phi;
}
XC = X(r, phi);
if (XC > XMax)
XMax = XC;
YC = Y(r, phi);
if (YC > YMax)
YMax = YC;
if (XC < XMin)
XMin = XC;
if (YC < YMin)
YMin = YC;
phi += 0.001;
}
}
private void Minimums(out double minR, out double minPhi,
out double XMax, out double XMin, out double YMax, out double YMin)
{
double phi = 0.0, r = 0.0, XC = 0.0, YC = 0.0;
minPhi = 0.0;
minR = double.MaxValue;
XMax = double.MinValue;
YMax = double.MinValue;
XMin = double.MaxValue;
YMin = double.MaxValue;
while (phi <= 8.0 * Math.PI)
{
r = 1.0 / u1(phi);
if (r < minR)
{
minR = r;
minPhi = phi;
}
XC = X(r, phi);
if (XC > XMax)
XMax = XC;
YC = Y(r, phi);
if (YC > YMax)
YMax = YC;
if (XC < XMin)
XMin = XC;
if (YC < YMin)
YMin = YC;
phi += 0.001;
}
}
private void Panel1_Paint(object sender, PaintEventArgs e)
{
panel1.Size = ClientSize;
int width = ClientSize.Width;
int height = ClientSize.Height;
int deltaX = width / 6;
int deltaY = height / 6;
int minX = deltaX;
int maxX = 5 * deltaX;
int minY = deltaY;
int maxY = 5 * deltaY;
double maxPhi, minPhi, maxR, minR;
double XMax, XMin, YMax, YMin;
double UMax, UMin, VMax, VMin;
Maximums(out maxR, out maxPhi, out XMax, out XMin, out YMax, out YMin);
Minimums(out minR, out minPhi, out UMax, out UMin, out VMax, out VMin);
double slopeX = (maxX - minX) / (XMax - XMin);
double slopeY = (minY - maxY) / (YMax - YMin);
double interX = minX - slopeX * XMin;
double interY = maxY - slopeY * YMin;
double chi = 0.0, eta = 0.0, phi = 0.0, r = 0.0, x, y;
Graphics g = e.Graphics;
Pen bp = new Pen(Color.Black);
SolidBrush rb = new SolidBrush(Color.Red);
g.Clip = new Region(new Rectangle(minX, minY, maxX - minX + 1, maxY - minY + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
g.DrawLine(bp, (i + 1) * deltaX, minY, (i + 1) * deltaX, maxY);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
g.DrawLine(bp, minX, (i + 1) * deltaY, maxX, (i + 1) * deltaY);
while (phi <= 8.0 * Math.PI)
{
r = 1.0 / u1(phi);
x = X(r, phi);
y = Y(r, phi);
chi = slopeX * x + interX;
eta = slopeY * y + interY;
g.FillEllipse(rb, (float)chi, (float)eta, 1, 1);
phi += 0.001;
}
}
}
}