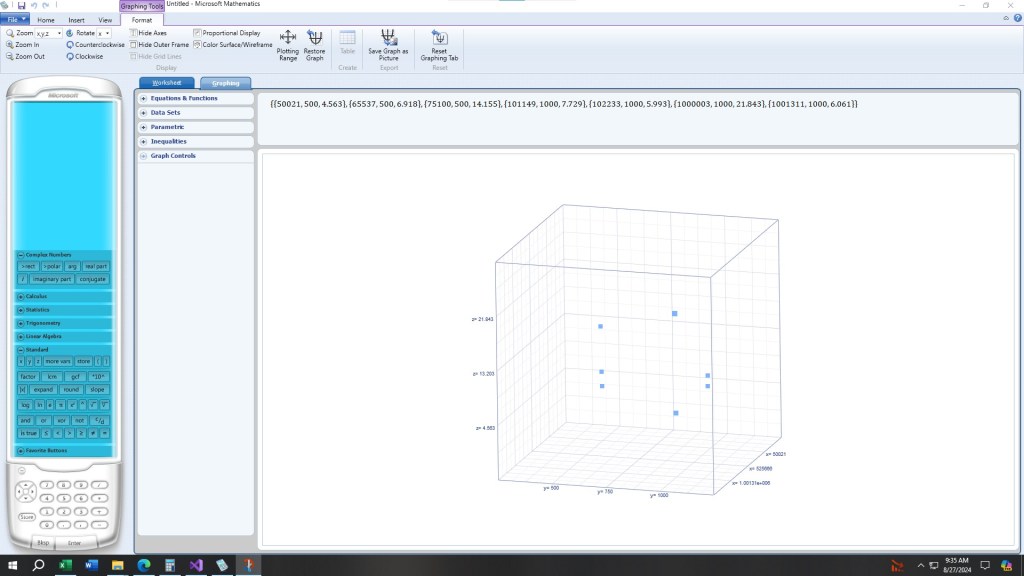
#pragma once
// Insertion sort, heap sort, and quick sort algorithms
// From "Algortihms" by Thomas H. Cormen, et. al.
// Selection sort, Singleton's sort, and Tree Sort 3, etc.
// From "Sorting and Sort Systems" by Harold Lorin
class Sorting {
public:
// Translated from Lorin's PL/I procedure
static void BasicExchange(long long tosort[], int number);
// Translated from Lorin's PL/I procedure
static void StandardExchange(long long tosort[], int number);
static void InsertionSort(long long a[], int n);
static void SelectionSort(long long a[], int n);
// CACM Algorithm 175
static void SimpleShifting(long long tosort[], int number);
// CACM Algorithm 201 1963
static void ShellSort(long long tosort[], int number);
static void HeapSort(long long a[], int n);
static void QuickSort(long long a[], int n);
// CACM Algorithm 347 Ricahrd C. Singleton 1968
// Translated from Lorin's PL/I procedure
static void SingletonsSort(long long a[], int n);
// CACM Algorithm 245 Robert W. Floyd 1964
// Translated from Lorin's PL/I procedure
static void TreeSort3(long long a[], int n);
// see "Algortihms" by Thomas H. Cormen, et. al.
// A is the array to be sorted, B is the sorted
// array and k is maximum number in A
static void CountingSort(
long long A[],
long long B[],
long long C[],
int n, long long k);
private:
// five helper methods for Heap Sort
static int Parent(int i);
static int Left(int i);
static int Right(int i);
static void BuildHeap(long long a[], int n, int& heapSize);
static void Heapify(long long a[], int i, int n, int& heapSize);
/* helper functions for SETHEAP
static void SWOPHEAP(long long A[], int n, long long& in, long long& out);
static void INHEAP(long long A[], int& n, long long& in);
static void OUTHEAP(long long A[], int& n, long long& out);
static void SETHEAP(long long A[], int n);*/
// helper methods for Quick Sort
static int Partition(long long a[], int n, int lo, int hi);
static void DoQuickSort(long long a[], int n, int p, int r);
// helper function for Singleton's sort
static void DoSingletonsSort(long long a[], int ii, int jj);
// helper function for TreeSort3
static void SiftUp(long long a[], int i, int n);
};
#include "Sorting.h"
#include <math.h>
void Sorting::BasicExchange(long long tosort[], int number)
{
int adjust = 2 * (number / 2);
int elimit, olimit;
if (adjust < number)
{
elimit = adjust;
olimit = adjust - 1;
}
else
{
elimit = number - 2;
olimit = number - 1;
}
odd:
int passw = 1;
int limit = olimit;
int oddeve = 1;
pass:
int excount = 0;
for (int i = oddeve; i <= limit; i += 2)
{
if (tosort[i] > tosort[i + 1])
{
long long temp = tosort[i];
tosort[i] = tosort[i + 1];
tosort[i + 1] = temp;
excount = 1;
}
}
if (excount == 0)
return;
if (passw == 1)
{
passw = 0;
oddeve = 0;
limit = elimit;
goto pass;
}
goto odd;
}
void Sorting::StandardExchange(long long tosort[], int number)
{
pass:
int excount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < number - 1; i++)
{
if (tosort[i] > tosort[i + 1])
{
long long temp = tosort[i];
tosort[i] = tosort[i + 1];
tosort[i + 1] = temp;
excount = 1;
}
}
if (excount == 0)
return;
goto pass;
}
void Sorting::InsertionSort(long long a[], int n)
{
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
long long key = a[j];
int i = j - 1;
while (i >= 0 && a[i] > key)
{
a[i + 1] = a[i];
i--;
}
a[i + 1] = key;
}
}
void Sorting::SelectionSort(long long a[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (a[i] > a[j])
{
long long t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
}
}
}
void Sorting::SimpleShifting(long long tosort[], int number)
{
for (int i = 0; i < number - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (tosort[j] > tosort[j + 1])
{
long long temp = tosort[j];
tosort[j] = tosort[j + 1];
tosort[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void Sorting::ShellSort(long long tosort[], int number)
{
int lognumber = log2(number);
int distance = (int)pow(2, lognumber) - 1;
while (distance > 0)
{
int limit = number - distance;
for (int j = 0; j < limit; j++)
{
for (int i = j; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (tosort[i + distance] < tosort[i])
{
long long temp = tosort[i];
tosort[i] = tosort[i + distance];
tosort[i + distance] = temp;
}
}
}
distance /= 2;
}
}
int Sorting::Parent(int i)
{
return i / 2;
}
int Sorting::Left(int i)
{
return 2 * i;
}
int Sorting::Right(int i)
{
return 2 * i + 1;
}
void Sorting::Heapify(long long a[], int i, int n, int& heapSize)
{
int l = Left(i);
int r = Right(i);
int largest = -1;
if (l < heapSize && a[l] > a[i])
largest = l;
else
largest = i;
if (r < heapSize && a[r] > a[largest])
largest = r;
if (largest != i)
{
long long t = a[i];
a[i] = a[largest];
a[largest] = t;
Heapify(a, largest, n, heapSize);
}
}
void Sorting::BuildHeap(long long a[], int n, int& heapSize)
{
for (int i = n / 2; i >= 0; i--)
Heapify(a, i, n, heapSize);
}
void Sorting::HeapSort(long long a[], int n)
{
int heapSize = n;
BuildHeap(a, n, heapSize);
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
long long t = a[0];
a[0] = a[i];
a[i] = t;
heapSize--;
Heapify(a, 0, n, heapSize);
}
}
void SWOPHEAP(long long A[], int n,
long long& in, long long& out)
{
if (in <= A[0])
out = in;
else
{
int i = 0;
A[n] = in;
out = A[0];
scan:
int j = i + i;
if (j <= n - 1)
{
long long temp = A[j];
long long temp1 = A[j + 1];
if (temp1 < temp)
{
temp = temp1;
j++;
}
if (temp < in)
{
A[i] = temp;
i = j;
goto scan;
}
}
A[i] = in;
}
}
void INHEAP(long long A[], int& n, long long& in)
{
int i = n;
n++;
scan:
if (i > 0)
{
int j = i / 2;
if (in < A[j])
{
A[i] = A[j];
i = j;
goto scan;
}
}
A[i] = in;
}
void OUTHEAP(long long A[], int& n, long long& out)
{
SWOPHEAP(A, n - 1, A[n - 1], out);
n = n - 2;
}
void SETHEAP(long long A[], int n)
{
int j = 0;
L:
INHEAP(A, j, A[j + 1]);
if (j < n - 2)
goto L;
}
void HEAP(long long A[], int n)
{
SETHEAP(A, n);
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
OUTHEAP(A, i, A[i]);
}
int Sorting::Partition(long long a[], int n, int lo, int hi)
{
int pivotIndex = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
long long x = a[pivotIndex];
long long t = x;
a[pivotIndex] = a[hi];
a[hi] = t;
int storeIndex = lo;
for (int i = lo; i < hi; i++)
{
if (a[i] < x)
{
t = a[i];
a[i] = a[storeIndex];
a[storeIndex++] = t;
}
}
t = a[storeIndex];
a[storeIndex] = a[hi];
a[hi] = t;
return storeIndex;
}
void Sorting::DoQuickSort(long long a[], int n, int p, int r)
{
if (p < r)
{
int q = Partition(a, n, p, r);
DoQuickSort(a, n, p, q - 1);
DoQuickSort(a, n, q + 1, r);
}
}
void Sorting::QuickSort(long long a[], int n)
{
DoQuickSort(a, n, 0, n - 1);
}
void QuickerSort(long long tosort[], int number)
{
const int limit = 20;
int highlim = 0, lowlim, origin, partind, pivot;
long long exch, temp = 0;
int partablow[limit] = { 0 }, parttabhigh[limit] = { 0 };
origin = partind = 0;
testsize:
if (number - 1 - origin > 0)
{
pivot = (number - 1 + origin) / 2;
temp = tosort[pivot];
tosort[pivot] = tosort[origin];
highlim = number - 1;
for (lowlim = origin + 1; lowlim <= highlim; lowlim++)
{
if (tosort[lowlim] > temp)
{
for (highlim = highlim; highlim >= lowlim; highlim--)
{
if (tosort[highlim] < temp)
{
exch = tosort[lowlim];
tosort[lowlim] = tosort[highlim];
tosort[highlim] = exch;
highlim = lowlim - 1;
goto limsmet;
}
}
highlim = lowlim - 1;
goto limsmet;
}
}
}
limsmet:
tosort[origin] = tosort[highlim];
tosort[highlim] = temp;
if (2 * highlim > origin + number - 1)
{
partablow[partind] = origin;
parttabhigh[partind] = highlim - 1;
origin = highlim + 1;
}
else
{
partablow[partind] = highlim + 1;
parttabhigh[partind] = number - 1;
number = highlim - 1;
}
partind++;
goto testsize;
if (origin == number - 1)
goto setpart;
if (tosort[origin] > tosort[number - 1])
{
exch = tosort[origin];
tosort[origin] = tosort[number - 1];
tosort[number - 1] = exch;
}
setpart:
partind--;
if (partind > -1)
{
origin = partablow[partind];
number = parttabhigh[partind];
goto testsize;
}
}
void Sorting::DoSingletonsSort(long long a[], int ii, int jj)
{
int m = 0;
int i = ii;
int j = jj;
int iu[50] = { 0 };
int il[50] = { 0 };
int ij = 0, l = 1, k = 0;
long long t = 0, tt = 0;
Label1:
if (i >= j)
goto Label8;
goto Label2;
Label2:
k = i;
ij = (j + i) / 2;
t = a[ij];
if (a[i] <= t)
goto Label3;
a[ij] = a[i];
a[i] = t;
t = a[ij];
goto Label3;
Label3:
l = j;
if (a[j] >= t)
goto Label5;
a[ij] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
t = a[ij];
if (a[i] <= t)
goto Label5;
a[ij] = a[i];
a[i] = t;
t = a[ij];
goto Label5;
Label4:
a[l] = a[k];
a[k] = tt;
goto Label5;
Label5:
l--;
if (a[l] > t)
goto Label5;
tt = a[l];
goto Label6;
Label6:
k++;
if (a[k] < t)
goto Label6;
if (k <= l)
goto Label4;
if (l - i <= j - k)
goto Label7;
il[m] = i;
iu[m] = l;
i = k;
m++;
goto Label9;
Label7:
il[m] = k;
iu[m] = j;
j = l;
m++;
goto Label9;
Label8:
m--;
if (m == -1)
return;
i = il[m];
j = iu[m];
goto Label9;
Label9:
if (j - i > 10)
goto Label2;
if (i == ii)
goto Label1;
i--;
goto Label10;
Label10:
i++;
if (i == j)
goto Label8;
t = a[i + 1];
if (a[i] <= t)
goto Label10;
k = i;
goto Label11;
Label11:
a[k + 1] = a[k];
k--;
if (t < a[k])
goto Label11;
a[k + 1] = t;
goto Label10;
}
void Sorting::SingletonsSort(long long a[], int n)
{
DoSingletonsSort(a, 0, n - 1);
}
void Sorting::SiftUp(long long a[], int i, int n)
{
long long copy = a[i];
int j;
while (true)
{
j = i + i;
if (j <= n)
{
if (j < n)
{
if (a[j + 1] > a[j])
j++;
}
if (a[j] > copy)
{
a[i] = a[j];
i = j;
continue;
}
}
break;
}
a[i] = copy;
}
void Sorting::TreeSort3(long long a[], int n)
{
for (int i = n / 2; i >= 1; i--)
SiftUp(a, i, n - 1);
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
{
SiftUp(a, 0, i);
long long t = a[0];
a[0] = a[i];
a[i] = t;
}
}
void Sorting::CountingSort(
long long A[],
long long B[],
long long C[],
int n, long long k)
{
for (long long i = 0; i <= k; i++)
C[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
B[j] = 0;
C[A[j]]++;
}
for (long long i = 1; i <= k; i++)
C[i] += C[i - 1];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
long long j = A[i];
C[j]--;
B[C[j]] = A[i];
}
}
#pragma once
#include <limits.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class SampleStatistics {
public:
inline static long long Mean(vector<long long> x) {
long long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)x.size(); i++)
sum += (long long)x[i];
return sum / (int)x.size();
};
inline static long long Max(vector<long long> x)
{
long long max = LLONG_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)x.size(); i++)
if (x[i] > max)
max = x[i];
return max;
};
inline static long long Min(vector<long long> x)
{
long long min = LLONG_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)x.size(); i++)
if (x[i] < min)
min = x[i];
return min;
};
inline static long long Median(vector<long long> x)
{
unsigned int n0 = (unsigned int)x.size();
unsigned int n1 = n0 / 2 - 1;
unsigned int n2 = n0 / 2;
long long median = 0, lt = x[n1], rt = x[n2];
if ((n0 & 1) == 1)
median = x[n0 / 2];
else
median = (lt + rt) / 2;
return median;
};
inline static long long Variance(vector<long long> x)
{
long long mean = Mean(x), sumSq = 0;
int n = (int)x.size();
int n1 = n - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
long long delta = x[i] - mean;
sumSq += delta * delta;
}
return sumSq / n1;
};
};
#include "SampleStatistics.h"
#include "Sorting.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <chrono>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std::chrono;
using namespace std;
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/measure-execution-time-function-cpp/
int GetSubOption(char title[])
{
char line[128];
cout << title << endl;
cout << "1 Basic Exchange" << endl;
cout << "2 Standard Exchange" << endl;
cout << "3 Insertion Sort" << endl;
cout << "4 Selection Sort" << endl;
cout << "5 Simple Sifting (Shuttle Sort)" << endl;
cout << "6 Shell Sort" << endl;
cout << "7 Heap Sort" << endl;
cout << "8 Quick Sort" << endl;
cout << "9 Singleton's Sort" << endl;
cout << "10 Tree Sort 3" << endl;
cout << "11 Counting Sort" << endl;
cout << "12 Exit Submenu" << endl;
cout << "13 Exit Program" << endl;
cout << "Suboption Number: ";
cin.getline(line, 128);
int so = 0;
if (strlen(line) > 1)
{
so = 10 * (line[0] - '0');
so += line[1] - '0';
}
else
so = line[0] - '0';
return so;
}
int DoSort(char option) {
char line[128];
char title[128] = { 0 };
char name[11][64] = { { 0 } };
int subOption;
strcpy_s(name[0], 64, "Basic Exchange");
strcpy_s(name[1], 64, "Standard Exchange");
strcpy_s(name[2], 64, "Insertion Sort");
strcat_s(name[3], 64, "Selection Sort");
strcpy_s(name[4], 64, "Simple Shifting");
strcpy_s(name[5], 64, "Shell Sort");
strcat_s(name[6], 64, "Heap Sort");
strcat_s(name[7], 64, "Quick Sort");
strcat_s(name[8], 64, "Singleton's Sort");
strcat_s(name[9], 64, "Tree Sort 3");
strcpy_s(name[10], 64, "Counting Sort");
vector<long long> runtime;
if (option == '1')
{
strcpy_s(title, 128, "Single Sorting Tests Submenu");
}
else {
strcpy_s(title, 128, "Statistical Sorting Tests Submenu");
}
subOption = GetSubOption(title);
if (subOption < 1 || subOption > 13)
{
cout << "Illegal Suboption Exiting Application!" << endl;
exit(-1);
}
if (subOption == 12)
return subOption;
if (subOption == 13)
exit(1);
int index = subOption - 1, maximum = 0, n = 0, seed = 1;
cout << name[index] << endl;
do {
cout << "PRNG Seed = ";
cin.getline(line, 128);
seed = atoi(line);
} while (seed < 1);
do {
cout << "Number of Samples = ";
cin.getline(line, 128);
n = atoi(line);
} while (n < 2);
do {
cout << "Maximum Sample Value = ";
cin.getline(line, 128);
maximum = atoi(line);
} while (maximum < 10);
srand(seed);
int number = 0;
if (option == '2')
{
do {
cout << "Number of Experiments = ";
cin.getline(line, 128);
number = atoi(line);
} while (number < 1);
}
else
{
number = 1;
}
long long k = 0;
long long* B = new long long[n];
long long* sample = new long long[n];
long long* shadow = new long long[n];
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
long long* C = NULL;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
sample[j] = rand() % maximum;
if (option == '1') {
shadow[j] = sample[j];
}
}
if (subOption == 11)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (sample[j] > k)
k = sample[j];
C = new long long[(unsigned int)(k + 1)];
}
auto start = high_resolution_clock::now();
switch (subOption) {
case 1:
Sorting::BasicExchange(sample, n);
break;
case 2:
Sorting::StandardExchange(sample, n);
break;
case 3:
Sorting::InsertionSort(sample, n);
break;
case 4:
Sorting::SelectionSort(sample, n);
break;
case 5:
Sorting::SimpleShifting(sample, n);
break;
case 6:
Sorting::ShellSort(sample, n);
break;
case 7:
Sorting::HeapSort(sample, n);
break;
case 8:
Sorting::QuickSort(sample, n);
break;
case 9:
Sorting::SingletonsSort(sample, n);
break;
case 10:
Sorting::TreeSort3(sample, n);
break;
case 11:
Sorting::CountingSort(sample, B, C, n, k);
break;
default:
cout << "Unknown Suboption" << endl;
break;
}
auto stop = high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = duration_cast<microseconds>(stop - start);
long long rt = (long long)duration.count();
runtime.push_back(rt);
if (subOption == 11)
{
if (C != NULL)
delete[] C;
}
}
if (option == '1')
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << setw(2) << shadow[i] << ' ';
if (subOption != 11)
cout << setw(2) << sample[i] << endl;
else
cout << setw(2) << B[i] << endl;
}
}
else if (option == '2') {
sort(runtime.begin(), runtime.end());
cout << "Runtimes in Microseconds" << endl;
if (runtime.size() <= 15)
{
for (int i = 0; i < (int)runtime.size(); i++)
cout << setw(4) << runtime[i] << endl;
}
cout << "Minimum Runtime = "
<< setw(4) << fixed << setprecision(0)
<< SampleStatistics::Min(runtime) << endl;
cout << "Maximum Runtime = "
<< setw(4) << fixed << setprecision(0)
<< SampleStatistics::Max(runtime) << endl;
cout << "Mean Runtime = "
<< setw(4) << fixed << setprecision(0)
<< SampleStatistics::Mean(runtime) << endl;
cout << "Median Runtime = "
<< setw(4) << fixed << setprecision(0) <<
SampleStatistics::Median(runtime) << endl;
}
delete[] B;
delete[] sample;
delete[] shadow;
return subOption;
}
int main() {
while (true) {
char line[128];
cout << "Menu" << endl;
cout << "1 Single Sorting Tests" << endl;
cout << "2 Statistical Tests" << endl;
cout << "3 Exit" << endl;;
cout << "Option number: ";
cin.getline(line, 128);
if (line[0] == '3')
break;
if (line[0] == '1' || line[0] == '2') {
while (true)
{
int doSort = DoSort(line[0]);
if (doSort == 12)
break;
else if (doSort == 13)
exit(1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}