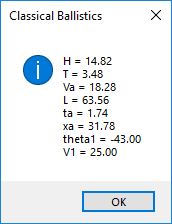
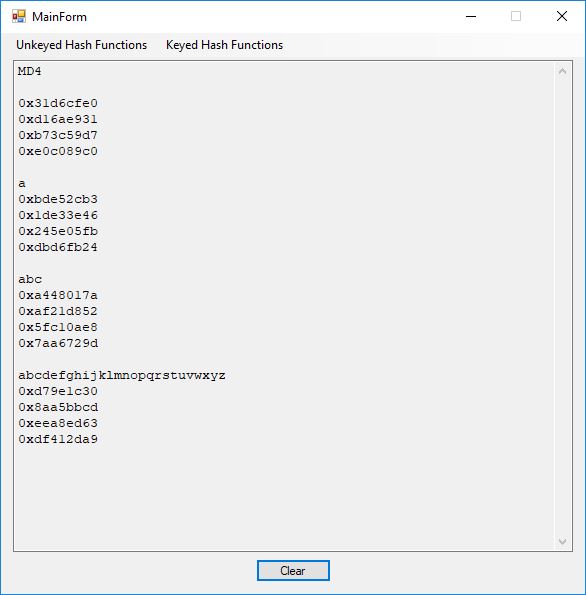
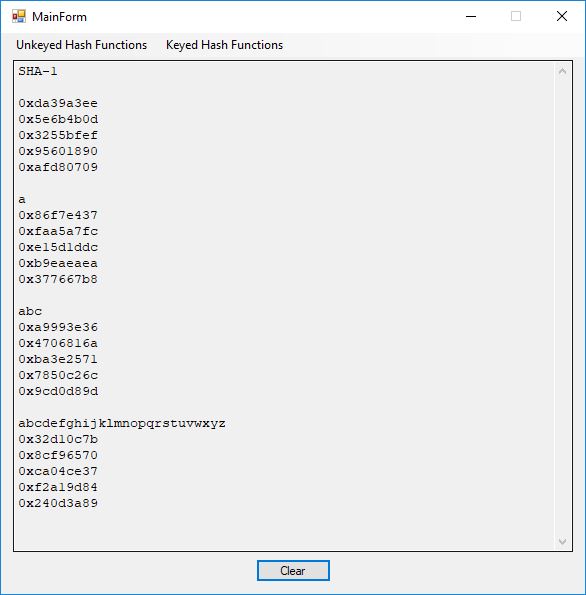
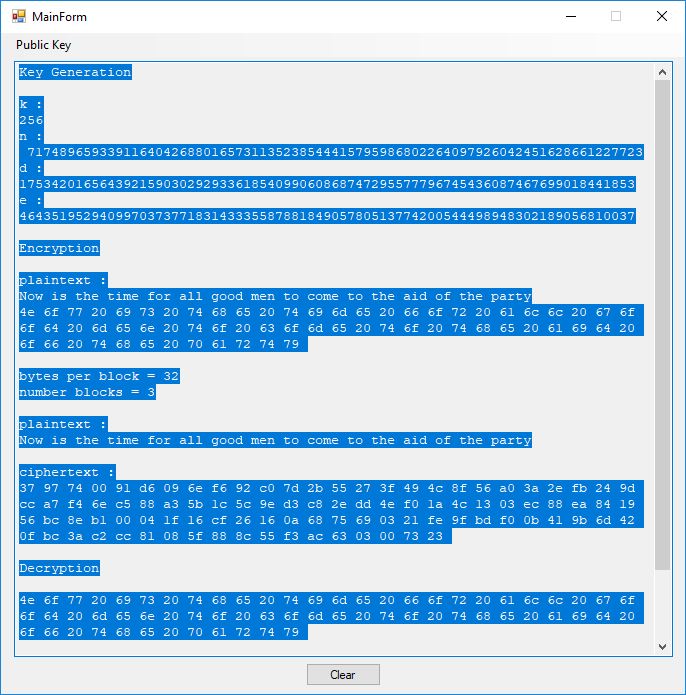
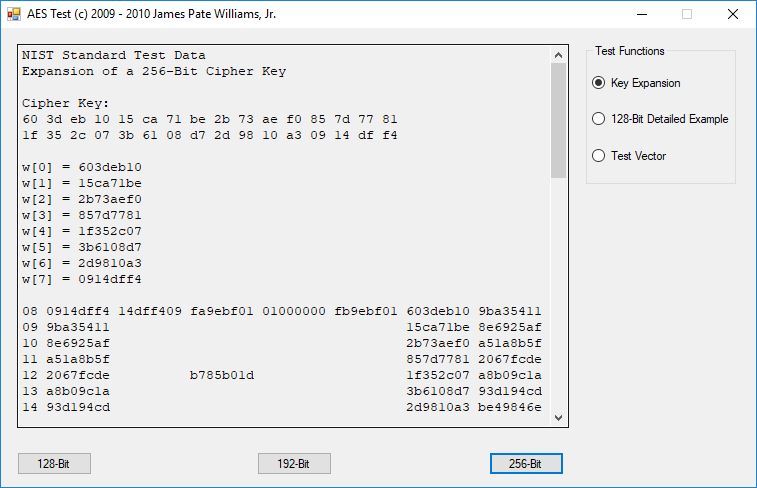
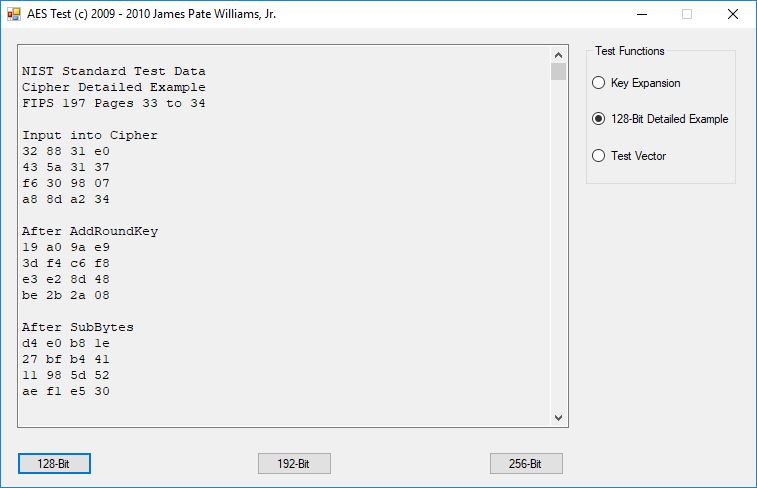
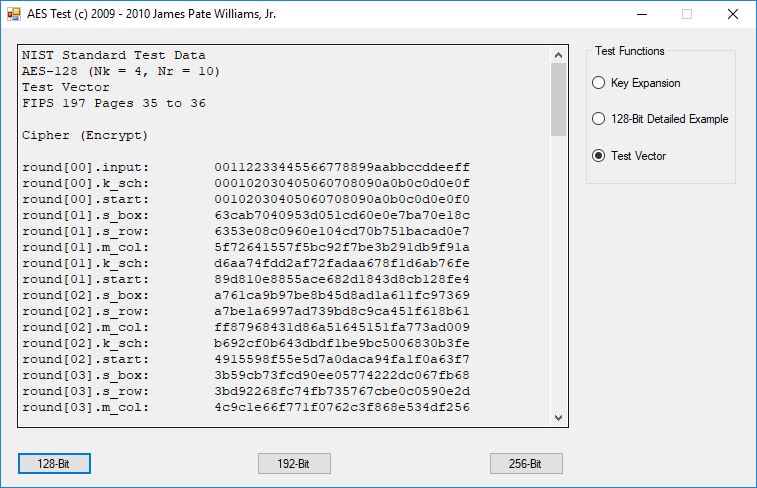
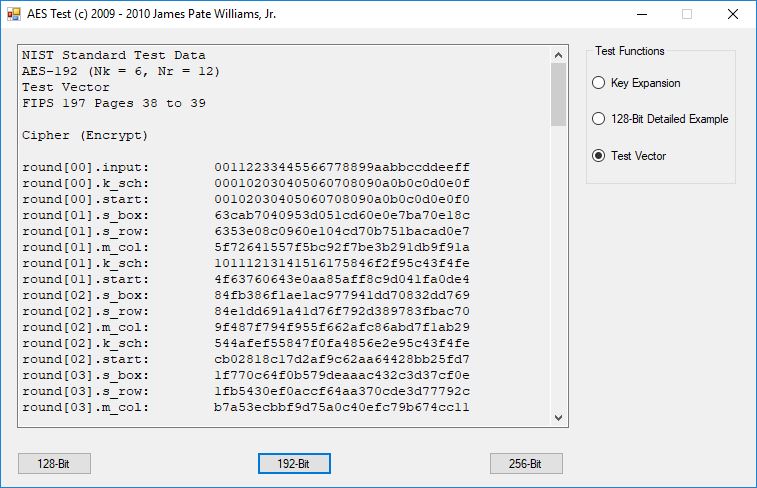
I believe in late spring quarter of 1978, Mr. P.M. Hicks, a chemistry and physics professor at LaGrange College, introduced me to a large desktop Texas Instruments (TI) programmable calculator. I immediately became immersed in the manual and I learned the rudiments of calculator programming on this machine.
I advanced onto LaGrange College’s new Data General Eclipse minicomputer in the summer of 1978. I taught myself Dayton BASIC (Beginner’s All Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) using the book “BASIC Programming” by Paul W. Murrill and Cecil L. Smith of which I still own a copy and it is copyrighted 1971. I seem to recall I special ordered the textbook from the LaGrange College library. This self-study put me many steps in front of my peers in the Fall Quarter of 1978 when I took a course under Professor Kenneth Cooper on BASIC programming. I taught Professor Cooper how to perform matrix and vector calculations using the Data General BASIC interpreter.
I also was taking my first course in physical chemistry in the fall of 1978. During the week of Monday, November 6, 1978 my physical chemistry partner Chuck H. Pitts (now Dr. Chuck H. Pitts, a prominent dentist in LaGrange, GA) did an experiment whose lab report title was “Determination of Molecular Size and Avogadro’s Number”. I seem to recall the division of labor was that I perform the calculations with the aid of a BASIC computer and Chuck and I would write up the experiment and I believe someone in the Callaway Foundation office or Chuck did the actual typing of the document at the Callaway Foundation office on Broome Street in LaGrange, GA. Well it took a lot of persuasion by Chuck to get me to do my part, since back in that era I was prone to destructive perfectionism. (Incidentally, I did not give up on being a perfectionist until Professor Felton at Georgia Tech in 1981 stated categorically “There is no room for perfectionism in science.”)
In the Winter Quarter of 1979 I took a FORTRAN (Formula Translator) IV course under Professor Kenneth Cooper. That quarter I also had Professor Cooper for Physical Chemistry II and Biochemistry. I did well in the computer programming course and I can remember helping several fellow students to pass the course. Professor Brooks Shelhorse then of the Math Department was one of my fellow classmates that I tutored. Biochemistry was an 8:00 AM course. I spent a lot of late nights in the computer lab, so I would sometimes fall asleep during the biochemistry lectures. I distinctly remember Dr. Cooper hurling an eraser near me to wake me up one morning. I made B’s in the two chemistry courses.
Spring Quarter of 1979 was my final quarter as a chemistry student at LaGrange College. I took Quantitative Analysis II, an Independent Study in Chemistry, General Physics III, and Angling. I made all A’s that quarter. The independent study was an introductory course to architecture and programming of the Intel 8085 microprocessor. Dr. Cooper in his time as a computer engineering student at Auburn University had built two very nice and unique computers, a rather large analog computer and a digital computer that consisted of an Intel 8085 microprocessor in a wooden box with hexadecimal keypad, two seven segment red light emitting diode displays, EEPROM, and RAM memory. I used the digital computer in my independent study. Professor Cooper taught me about the instruction set for the microprocessor and I would hand assemble my assembly language programs into two hexadecimal digit strings of machine code and manually enter the machine code via the keypad. One of my first assignments was to count down from 0xFF = 255 decimal to 0x00 = 0 decimal. I had a delay of about a ¼ second built into the program, so it took me one minute and four seconds to count down to zero. I was the only student in my independent study, therefore, it sometimes felt funny to have Professor Cooper give a whole one-hour lecture to an audience of one.
I bought the IBM book “Sorting and Sort Systems” by Harold Lorin in the summer of 1979. I proceeded to implement most of the sorting and merge algorithms in the book. I first translated the IBM PL/I (Programming Language I) code to BASIC and later for FORTRAN IV. Professor Cooper had developed a large BASIC program for the LaGrange College Registrar, Jimmy Herring. This program used a slow sorting algorithm which was either Shell sort of Bubble sort. I implemented a very fast sorting algorithm named Singleton’s sort in BASIC and was able to dramatically cut the time required to sort all the students by their Social Security Administration numbers which many colleges and universities then used as their primary flat-file or database key. I also began teaching myself the Data General Advanced Operating System (AOS) macro-assembly language. Like many computer programmers before I became infatuated with all the control over an operating system that assembly language afforded a knowledgeable programmer.
I convinced my parents to pay for me to audit Calculus and Analytic Geometry IV under Professor Shelhorse during the Fall Quarter of 1979, so I would have an excuse to be on campus to use my favorite computer, the LaGrange College Data General Eclipse minicomputer. That quarter I re-implemented my fast sorting algorithm in assembly language and set a new sorting time record with a program that sorting about 1000 student data records. Since the code was in AOS macro-assembly language it could not be readily integrated with the existing registrar’s system.
In 1980 I bummed around the college using the computer system until I was accepted to chemistry graduate school at the Georgia Institute of Technology for the Fall Quarter of 1980. I taught myself Data General Pascal and furthered my work with macro-assembly language, BASIC, and FORTRAN IV in the Winter, Spring, and Summer Quarters of 1980 at LaGrange College. I was unpaid computer programming teaching assistant for those three quarters which allowed me to earn my keep so to speak.
http://www.lagrange.edu/index.html
https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Profile/james%20pate%20williams%20jr
https://www.facebook.com/pg/JamesPateWilliamsJrConsultant/posts/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/james-williams-1a5b1370/