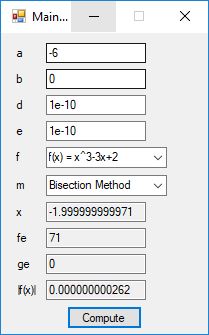
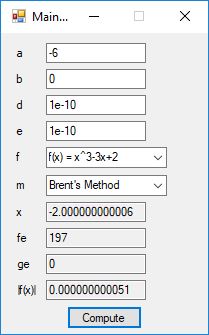
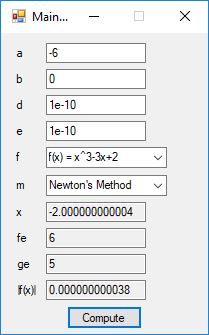
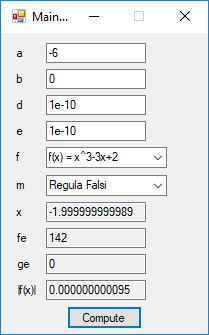
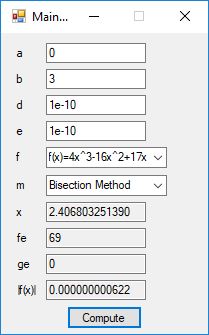
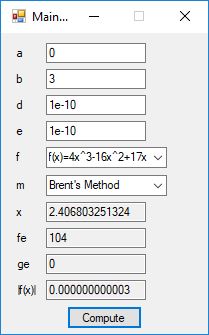
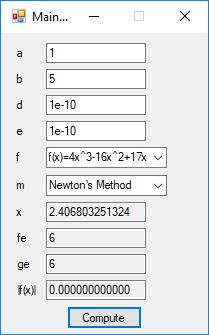
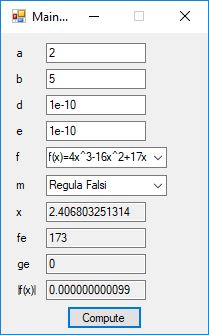
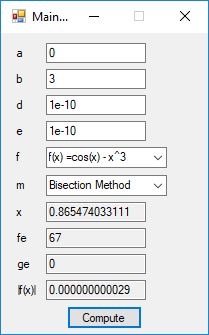
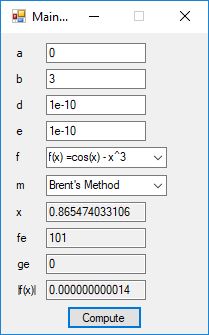
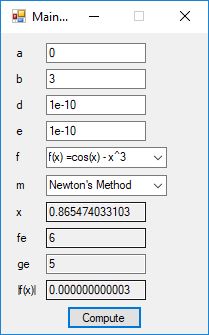
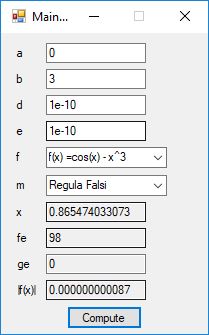
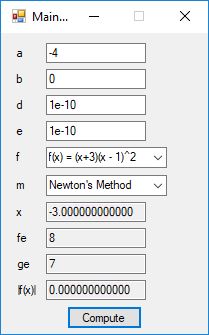
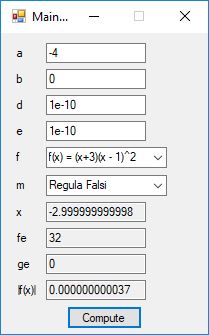
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
typedef double real;
static real f(real x)
{
double pi2 = 2.0 * atan(1.0);
return(exp(-x) - sin(pi2 * x));
}
static real g(real x)
{
double pi2 = 2.0 * atan(1.0);
return(-exp(-x) - pi2 * cos(pi2 * x));
}
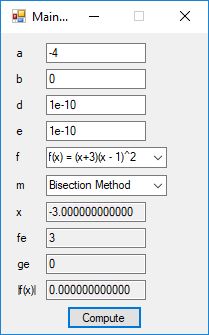
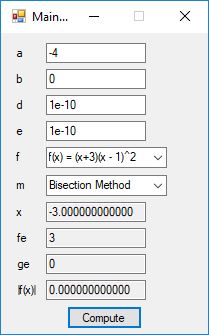
static int bisection(
real(*f)(real), real* a, real* b, real xtol, int* flag)
{
real error, fa, fm, xm;
int n = 0;
fa = (*f)(*a);
if (fa * (*f)(*b) > 0.0)
{
*flag = -1;
return(n);
}
error = fabsl(*b - *a);
while (error > xtol)
{
n++;
error *= 0.5;
if (error <= xtol)
{
*flag = 0;
return(n);
}
xm = 0.5 * (*a + *b);
if (xm + error == xm)
{
*flag = 1;
return(n);
}
fm = (*f)(xm);
if (fa * fm > 0.0)
{
*a = xm;
fa = fm;
}
else
*b = xm;
}
*flag = 2;
return(n);
}
static int regula(
real (*f)(real), real a, real b, real xtol,
real ftol, int ntol, real* w, int* flag)
{
int n = 0;
real fa, fb, fw, signfa, prvsfw;
fa = f(a);
if (fa >= 0.0) signfa = +1.0; else signfa = -1.0;
fb = f(b);
if (signfa * fb >= 0.0)
{
*flag = -1;
return n;
}
*w = a;
fw = fa;
for (n = 0; n <= ntol; n++)
{
if (fabs(a - b) <= xtol)
{
*flag = 0;
return n;
}
if (fabs(fw) <= ftol)
{
*flag = 1;
return n;
}
*w = (fa * b - fb * a) / (fa - fb);
if (fw >= 0.0) prvsfw = +1.0; else prvsfw = -1.0;
fw = f(*w);
if (signfa * fw > 0.0)
{
a = *w;
fa = fw;
if (fw * prvsfw > 0.0) fb = 0.5 * fb;
}
else
{
b = *w;
fb = fw;
if (fw * prvsfw > 0.0) fa = 0.5 * fa;
}
}
*flag = 2;
return n;
}
static int secantMethod(
real(*f)(real), real xtol, real ftol,
int ntol, real xm1, real x0, real* w)
{
real fm1 = f(xm1), f0 = f(x0);
real df = fabs(fm1 - f0), f1 = 0.0;
real dx = fabs(xm1 - x0), x1 = 0.0;
int n = 0;
while (n < ntol && df > ftol && dx > xtol)
{
x1 = (f0 * xm1 - fm1 * x0) / (f0 - fm1);
f1 = f(x1);
df = fabs(f(x1) - f0);
dx = fabs(x1 - x0);
fm1 = f0;
f0 = f1;
xm1 = x0;
x0 = x1;
n++;
}
*w = x1;
return n;
}
static int NewtonsMethod(
real(*f)(real), real(*g)(real),
real xtol, real ftol, int ntol,
real* w)
{
// f is the function
// g is the function's derivative
// xtol is root's tolerance
// ftol is the function's tolerance
// ntol is the maximum # of iterations
real f1 = 0.0, g1 = 0.0, x0 = *w, x1 = 0.0;
real f0 = f(x0), g0 = g(x0);
real deltaX = DBL_MAX, deltaF = DBL_MAX;
int n = 0;
while (n < ntol && deltaX > xtol && deltaF > ftol)
{
x1 = x0 - f0 / g0;
f1 = f(x1);
g1 = g(x1);
deltaX = fabs(x1 - x0);
deltaF = fabs(f1 - f0);
f0 = f1;
g0 = g1;
x0 = x1;
n++;
}
*w = x1;
return n;
}
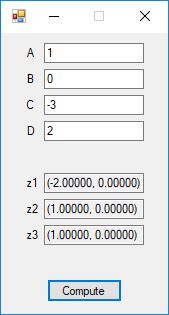
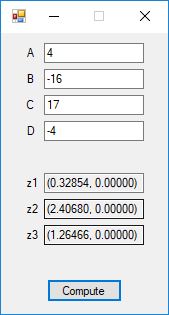
int main(void)
{
int flag = 0, ntol = 0;
real a0 = 0, b0 = 0, ftol = 0, w1 = 0, w2 = 1.0;
real a1 = 0, b1 = 0, w3 = 0, xtol = 0;
a0 = 0.0;
b0 = 1.0;
ntol = 128;
ftol = 1.0e-15;
xtol = 1.0e-15;
int its1 = bisection(f, &a0, &b0, xtol, &flag);
a1 = 0.0;
b1 = 1.0;
int its2 = regula(f, a1, b1, xtol, ftol, ntol, &w1, &flag);
int its3 = secantMethod(f, ftol, xtol, ntol, 0.0, 1.0, &w2);
int its4 = NewtonsMethod(f, g, xtol, ftol, ntol, &w3);
printf("function exp(-x) - sin(0.5 * pi * x)\n");
printf("The interval found by bisection is:\n");
printf("a = %+13.10lf b = %+13.10lf\n", a0, b0);
printf("bisection # iterations = %ld\n", its1);
printf("The root by regula falsi:\n");
printf("x = %+13.10lf f(x) = %+13.10lf\n", w1, f(w1));
printf("regula falsi # iterations = %ld\n", its2);
printf("The root by the secant method:\n");
printf("x = %+13.10lf f(x) = %+13.10lf\n", w2, f(w2));
printf("secant method # iterations = %ld\n", its3);
printf("The root by Newton's Method:\n");
printf("x = %+13.10lf f(x) = %+13.10lf\n", w2, f(w3));
printf("Newton's Method # iterations = %ld\n", its4);
return(0);
}